1.最原始的linear regression
标准回归函数和文本数据导入函数
from numpy import *
def loadDataSet(fileName): #general function to parse tab -delimited floats
numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split('\t')) - 1 #get number of fields '\t'是tab,每一行的特征个数
dataMat = []; labelMat = [] #数据矩阵,标签矩阵
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines(): #fr.readlines()表示读取每一行
lineArr =[] #该行的列表,注意这里保存的可是数字了
curLine = line.strip().split('\t') #strip()去掉前后的空格,split()把一个字符串分割成字符串数组
for i in range(numFeat): #数字序列,内置函数range() range(10) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
lineArr.append(float(curLine[i])) #
dataMat.append(lineArr)
labelMat.append(float(curLine[-1])) #-1表示倒数第一个
return dataMat,labelMat #返回数据矩阵和标签矩阵(目标值矩阵)
def standRegres(xArr,yArr): #用来计算最佳拟合直线
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat = mat(yArr).T #搞成矩阵形式 matrix.T transpose:返回矩阵的转置矩阵
xTx = xMat.T*xMat
if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0: # numpy.linalg模块包含线性代数的函数,计算行列式值是否为0
print "This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse" #奇异矩阵
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T*yMat) #matrix.I inverse:返回矩阵的逆矩阵,就这一步就求出来了,该算法叫做普通最小二乘法(ordinary least squares)
return ws测试
import regression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import *
xArr, yArr = regression.loadDataSet('ex0.txt')
# print xArr[0:2] #取不到2
# print yArr
#接下来来看拟合的效果
ws = regression.standRegres(xArr, yArr)
# print ws #变量ws存放的就是回归系数
xMat = mat(xArr)
yMat = mat(yArr)
yHat = xMat*ws #计算预测值
#接下来绘制数据集散点图和最佳拟合直线图
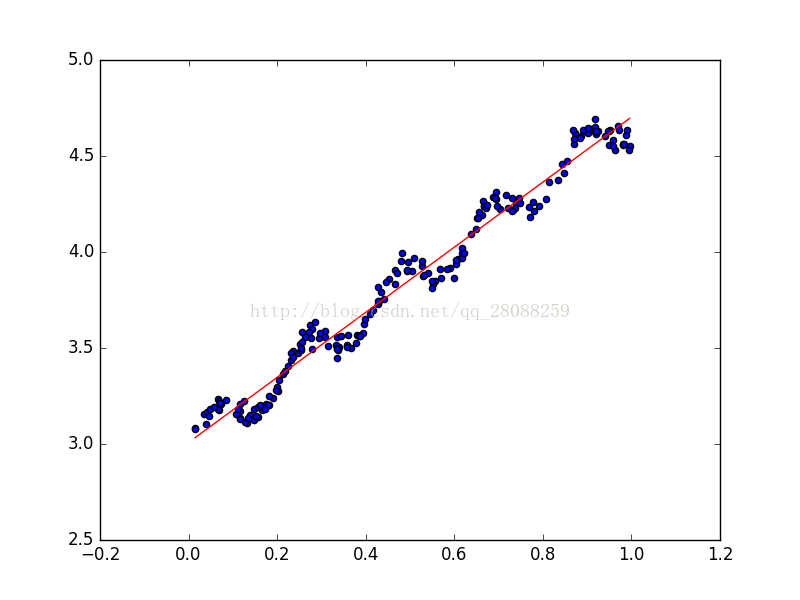
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0],yMat.T[:,0].flatten().A[0])
# flatten()方法能将matrix的元素变成一维的,
# .A能使matrix变成array
xCopy = xMat.copy()
# print xCopy
xCopy.sort(0) #按照升序排序,主要是根据第二个元素
# print xCopy
yHat = xCopy *ws
ax.plot(xCopy[:,1],yHat,'red')
plt.show()结果:
2. locally weighted linear regression
必要函数
#以下函数,对于x空间中的任意一个testPoint,输出其对应的预测值yHat
def lwlr(testPoint,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): # 参数k控制衰减速度 1.0为默认值; testPoint为输入,函数返回根据局部加权线性回归得出的预测值
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat = mat(yArr).T
m = shape(xMat)[0] #[0]指示的是行数,也就是样本点个数
weights = mat(eye((m))) #eye(m)主对角元素为1----对应于(m,m),其余为0
for j in range(m): #next 2 lines create weights matrix
diffMat = testPoint - xMat[j,:]
weights[j,j] = exp(diffMat*diffMat.T/(-2.0*k**2))
xTx = xMat.T * (weights * xMat)
if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0:
print "This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse"
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T * (weights * yMat))
return testPoint * ws
def lwlrTest(testArr,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): #loops over all the data points and applies lwlr to each one, k的默认值为1
m = shape(testArr)[0]
yHat = zeros(m) #元素全为0的向量
for i in range(m):
yHat[i] = lwlr(testArr[i],xArr,yArr,k)
return yHat
def lwlrTestPlot(xArr,yArr,k=1.0): #same thing as lwlrTest except it sorts X first
yHat = zeros(shape(yArr)) #easier for plotting
xCopy = mat(xArr)
xCopy.sort(0)
for i in range(shape(xArr)[0]):
yHat[i] = lwlr(xCopy[i],xArr,yArr,k)
return yHat,xCopy测试
import regression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import *
xArr, yArr = regression.loadDataSet('ex0.txt')
# print yArr[0]
# print regression.lwlr(xArr[0],xArr,yArr,0.001)
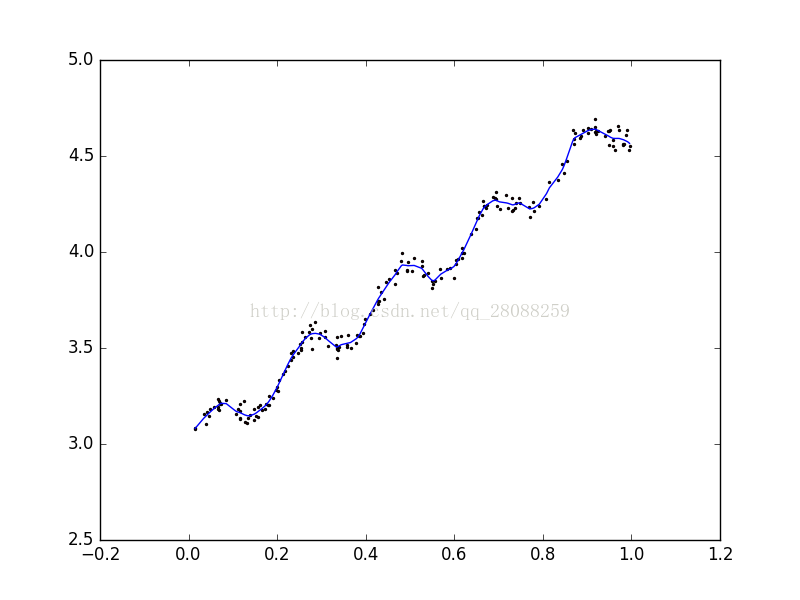
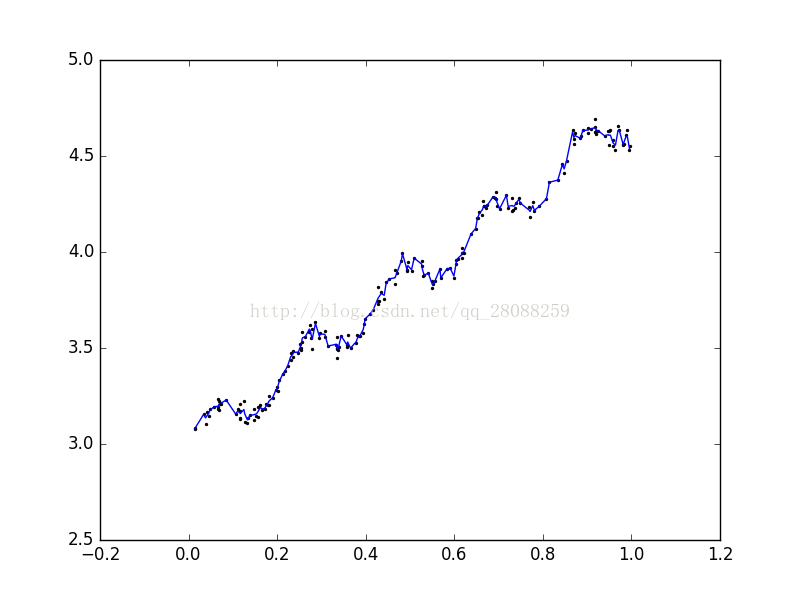
yHat, xSort = regression.lwlrTestPlot(xArr,yArr,1) #此处的这个k值得选取会直接影响到拟合的效果
# print xSort
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(xSort[:,1],yHat)
xMat = mat(xArr)
yMat = mat(yArr)
ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0],yMat.T[:,0].flatten().A[0], s=2, c='red')
plt.show()
k=1 欠拟合
k=0.01
k=0.003 过拟合
3. 预测鲍鱼的年龄
#预测鲍鱼年龄
import regression
from numpy import *
abX, abY = regression.loadDataSet('abalone.txt')
yHat01=regression.lwlrTest(abX[0:99],abX[0:99],abY[0:99],0.1) #过拟合
yHat1=regression.lwlrTest(abX[0:99],abX[0:99],abY[0:99],1)
yHat10=regression.lwlrTest(abX[0:99],abX[0:99],abY[0:99],10)
print regression.rssError(abY[0:99], yHat01.T)
print regression.rssError(abY[0:99], yHat1.T)
print regression.rssError(abY[0:99], yHat10.T)
yHat01New=regression.lwlrTest(abX[100:199],abX[0:99],abY[0:99],0.1) #过拟合
yHat1New=regression.lwlrTest(abX[100:199],abX[0:99],abY[0:99],1)
yHat10New=regression.lwlrTest(abX[100:199],abX[0:99],abY[0:99],10)
print regression.rssError(abY[100:199], yHat01New.T)
print regression.rssError(abY[100:199], yHat1New.T)
print regression.rssError(abY[100:199], yHat10New.T)
#接下里看看普通的线性回归
ws = regression.standRegres(abX[0:99], abY[0:99])
yHat =mat(abX[100:199])*ws
print regression.rssError(abY[100:199],yHat.T.A)结果:
56.8843765879
429.89056187
549.118170883
58720.7256135
573.526144189
517.571190538
518.636315325
4. 缩减系数来“理解”数据
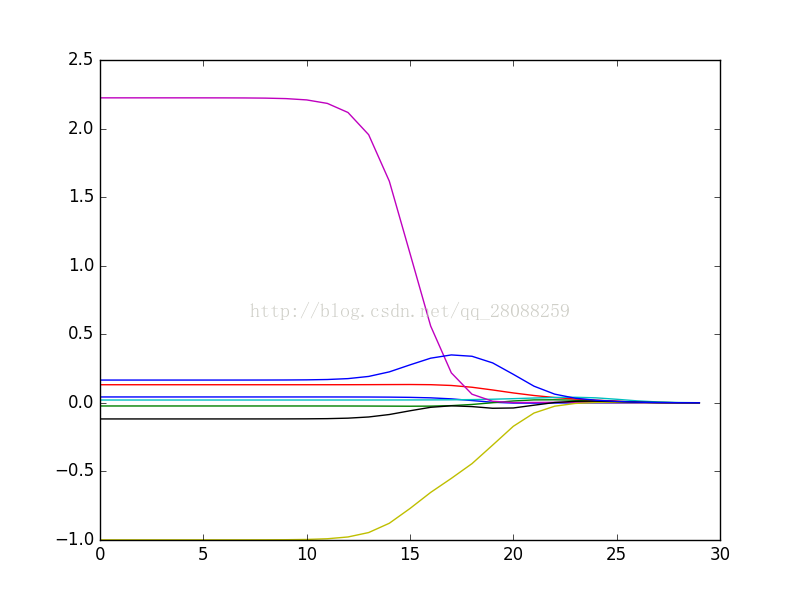
4.1 岭回归
#岭回归---在鲍鱼数据集上的效果
import regression
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
abX, abY = regression.loadDataSet('abalone.txt')
ridgeWeights = regression.ridgeTest(abX, abY)
print ridgeWeights
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(ridgeWeights)
plt.show()
4.2 前向逐步回归
def regularize(xMat):#regularize by columns
inMat = xMat.copy()
inMeans = mean(inMat,0) #calc mean then subtract it off
inVar = var(inMat,0) #calc variance of Xi then divide by it
inMat = (inMat - inMeans)/inVar
return inMat
def stageWise(xArr,yArr,eps=0.01,numIt=100): #前向逐步线性回归
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat=mat(yArr).T
yMean = mean(yMat,0)
yMat = yMat - yMean #can also regularize ys but will get smaller coef
xMat = regularize(xMat)
m,n=shape(xMat)
returnMat = zeros((numIt,n)) #testing code remove
ws = zeros((n,1)); wsTest = ws.copy(); wsMax = ws.copy()
for i in range(numIt): #numIt表示迭代次数
print ws.T
lowestError = inf; #inf表示无穷
for j in range(n):
for sign in [-1,1]: #分别显示增加和减少该特征系数对结果的影响
wsTest = ws.copy()
wsTest[j] += eps*sign
yTest = xMat*wsTest
rssE = rssError(yMat.A,yTest.A)
if rssE < lowestError:
lowestError = rssE
wsMax = wsTest
ws = wsMax.copy()
returnMat[i,:]=ws.T
return returnMat
测试
#测试前向逐步线性回归的效果
import regression
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
xArr, yArr = regression.loadDataSet('abalone.txt')
print regression.stageWise(xArr,yArr,0.001,5000)
#将其结果与最小二乘法进行比较
xMat = mat(xArr)
yMat = mat(yArr).T
xMat = regression.regularize(xMat)
yM = mean(yMat,0)
yMat = yMat - yM
weights=regression.standRegres(xMat, yMat.T)
print weights.T