文章目录
理论基础
线性插值:两点确定一条直线,线上的未知点的值可由直线方程确定。
在二维空间中,需要将线性差值拓展到双线性插值。
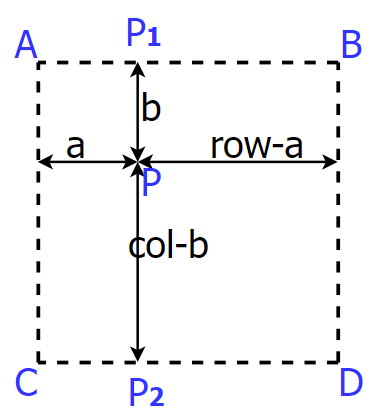
设A、B、C、D的像素值分别为A、B、C、D。
P1的像素值为 P 1 = 1 / r o w × ( ( r o w − a ) A + a B ) P1 = 1/row \times ((row-a)A + aB) P1=1/row×((row−a)A+aB)
P2的像素值为 P 2 = 1 / r o w × ( ( r o w − a ) C + a D ) P2 = 1/row \times ((row-a)C + aD) P2=1/row×((row−a)C+aD)
P的像素值为 P = 1 / c o l × ( ( c o l − b ) P 1 + b P 2 ) P = 1/col \times ((col-b)P1 + bP2) P=1/col×((col−b)P1+bP2)
将P1、P2代入得
P = 1 c o l × r o w × [ ( r o w − a ) ( c l o − b ) A + a ( c o l − b ) B ) + a ( r o w − a ) C + a b D ] P = \frac{1}{col \times row} \times \left[ (row-a)(clo-b)A + a(col-b)B) + a(row-a)C + abD\right] P=col×row1×[(row−a)(clo−b)A+a(col−b)B)+a(row−a)C+abD]
注:如果将P点投影到原图像进行插值,则row和col值为1、1。
编码实现(Python)
# coding=utf-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
def Bilinear(img, up_height, up_width, channels):
bilinear_img = np.zeros(shape=(up_height, up_width, channels), dtype=np.uint8)
img_height, img_width, img_channels = img.shape
for i in range(up_height):
for j in range(up_width):
row_up = int(i * img_height/up_height) # 原图像左像素点
col_left = int(j * img_width/up_width) # 原图像上像素点
row_bottom = row_up + 1
col_right = col_left + 1
if row_bottom == img_height:
row_bottom -= 1
if col_right == img_width:
col_right -= 1
a = j * img_width / up_width - col_left
b = i * img_height / up_height - row_up
# 这里定义bilinear_img已经强制了数据类型\
bilinear_img[i][j] = ( \
(1 - a) * (1 - b) * img[row_up][col_left] + \
a * (1 - b) * img[row_up][col_right] + \
(1 - a) * b * img[row_bottom][col_left] + \
a * b * img[row_bottom][col_right] \
)
return bilinear_img
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 无法处理透明度通道(压根就没读进来)
img_source = cv2.imread(r"Image_restoration\source\1.png")
img_height, img_width, img_channels = img_source.shape
print("height {}, width {}, channels {}".format( img_height, img_width, img_channels))
times = 3 # 放大3倍
up_height = int(img_height * times)
up_width = int(img_width * times)
print("up_height {}, up_width {}".format(up_height, up_width))
bilinear_img = Bilinear(img_source, up_height, up_width, img_channels)
cv2.imshow("img_source", img_source)
cv2.imshow("bilinear_img", bilinear_img)
cv2.imwrite(r"Image_restoration\result\1_bilinear.png", bilinear_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
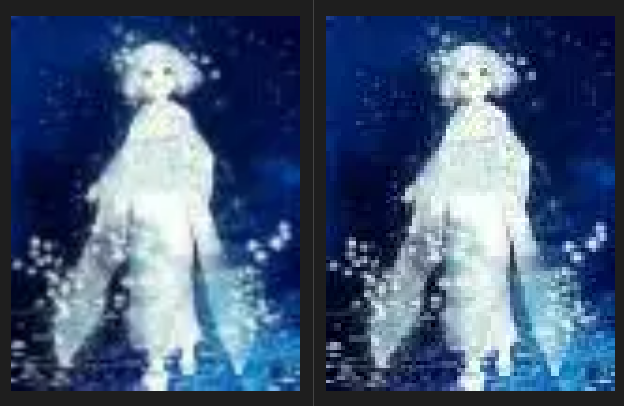
效果展示
- 利用双线性插值将图像放大后,色块减少,但清晰效果依然十分有限。

其他权重
双线性插值公式为P点附近四个点设计了一个权重。
我们也可以采用其他形式的权重。如:
- 高斯分布
设距离为r,则利用高斯公式计算其权重为:
ω ( r ) = e − ( ε r ) 2 \bf \omega(r) = e^{-(\varepsilon r)^2} ω(r)=e−(εr)2
注:因为要对权重进行归一化,所以这里直接舍去了将会被约去的系数。
在如下二维空间中。
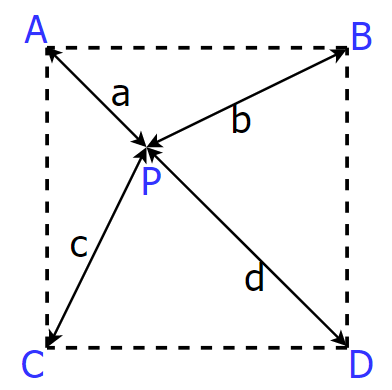
P点像素值为
P = 1 ω ( a ) + ω ( b ) + ω ( c ) + ω ( d ) [ ω ( a ) × A + ω ( b ) × B + ω ( c ) × C + ω ( d ) × D ] P = \frac{1}{\omega(a)+\omega(b)+\omega(c)+\omega(d)}[\omega(a)\times A+\omega(b)\times B+\omega(c)\times C+\omega(d)\times D] P=ω(a)+ω(b)+ω(c)+ω(d)1[ω(a)×A+ω(b)×B+ω(c)×C+ω(d)×D]
博主做出来的效果一般般。
