在网上没有lab3相应的答案,作者也卡蛮久
作者可能就自己的卡住过的问题做一些总结,不能面面俱到,请见谅
(就此补充一下答案)(完整答案在最后)
Q2: WWPD: Journey to the Center of the Earth
Use Ok to test your knowledge with the following "What Would Python Display?" questions:
python3 ok -q sr-wwpd -uFor all WWPD questions, type
Functionif you believe the answer is<function...>,Errorif it errors, andNothingif nothing is displayed.
>>> def crust():
... print("70km")
... def mantle():
... print("2900km")
... def core():
... print("5300km")
... return mantle()
... return core
... return mantle
>>> drill = crust
>>> drill = drill()
>>70km
>>> drill = drill()
>>2900km
>>> drill = drill()
>>5300km
>>2900km
>>> drill()
>>5300km
>>2900km
>>Function1.之前的drill=drill()只是调用,
但不返回其值或类型(因为是赋值行为)
2.最后一个drill()
可以理解为,
函数调用过程中打印了两个值,并返回drill()的类型-->function
Q6: Ping-pong
The ping-pong sequence counts up starting from 1 and is always either counting up or counting down. At element k, the direction switches if k is a multiple of 8 or contains the digit 8. The first 30 elements of the ping-pong sequence are listed below, with direction swaps marked using brackets at the 8th, 16th, 18th, 24th, and 28th elements:
| Index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | [8] | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | [16] | 17 | [18] | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PingPong Value | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | [8] | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | [0] | 1 | [2] | 1 | 0 | -1 | -2 | -3 |
| Index (cont.) | [24] | 25 | 26 | 27 | [28] | 29 | 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PingPong Value | [-4] | -3 | -2 | -1 | [0] | -1 | -2 |
Implement a function pingpong that returns the nth element of the ping-pong sequence without using any assignment statements.
You may use the function num_eights, which you defined in the previous question.
Use recursion - the tests will fail if you use any assignment statements.
Hint: If you're stuck, first try implementing
pingpongusing assignment statements and awhilestatement. Then, to convert this into a recursive solution, write a helper function that has a parameter for each variable that changes values in the body of the while loop.
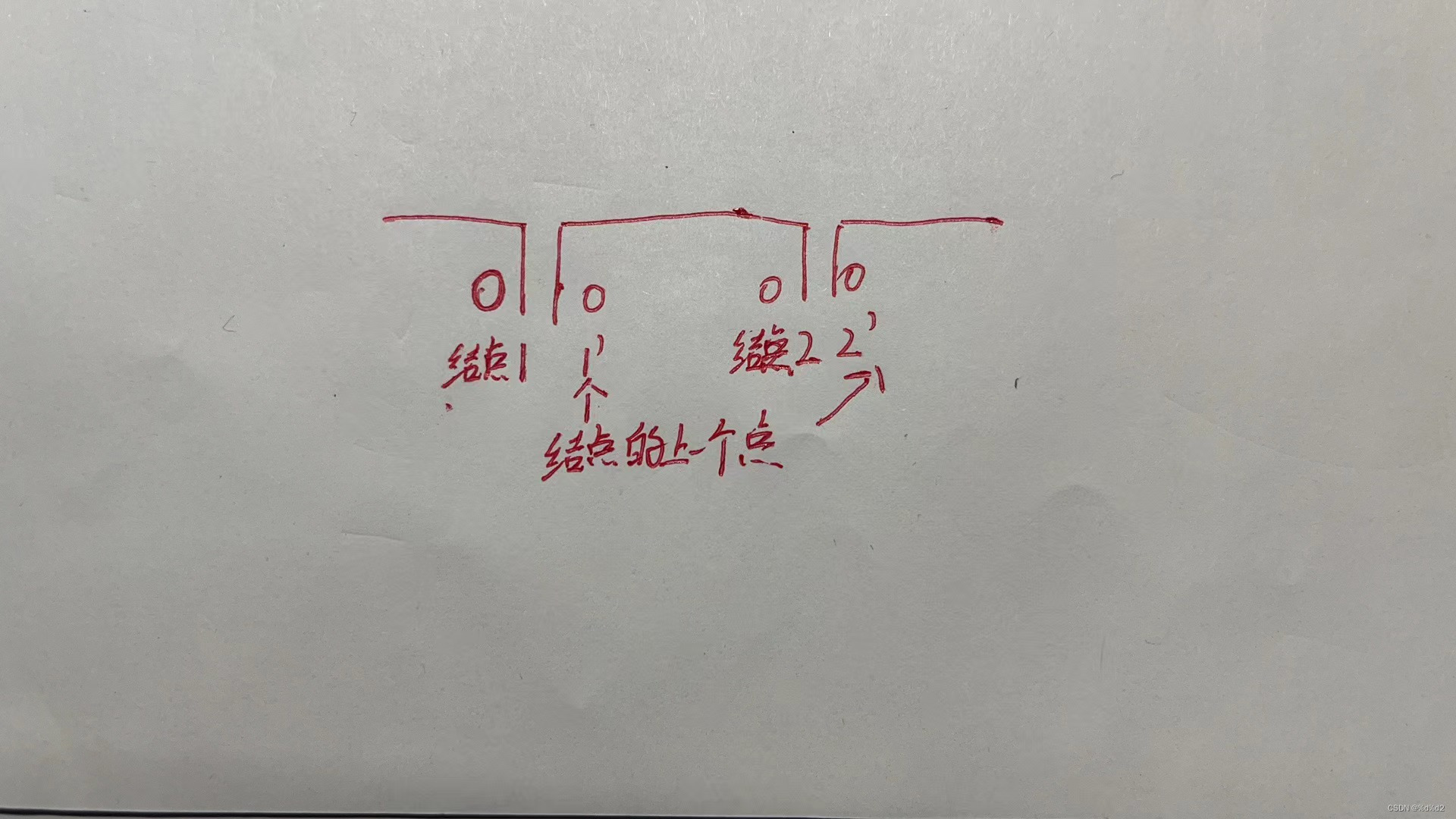
分析:pingpong(n) 递归返回 pingpong(n-1)+direction(n)
1.direction()作用是确定第n个数值正负,初始值都是1
n<8时 可以确定一定为正即 1
n>8时 递归统计有多少个结点n 及 结点的上一个点n+1
(这两点会转换正负)
(因为结点的上一个点n+1处与更大的结点之间的数正负性均相同
结点处同理如图)
def pingpong(n):
"""Return the nth element of the ping-pong sequence.
>>> pingpong(8)
8
>>> pingpong(10)
6
>>> pingpong(15)
1
>>> pingpong(21)
-1
>>> pingpong(22)
-2
>>> pingpong(30)
-2
>>> pingpong(68)
0
>>> pingpong(69)
-1
>>> pingpong(80)
0
>>> pingpong(81)
1
>>> pingpong(82)
0
>>> pingpong(100)
-6
>>> from construct_check import check
>>> # ban assignment statements
>>> check(HW_SOURCE_FILE, 'pingpong', ['Assign', 'AugAssign'])
True
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if n <= 8:
return n
return direction(n) + pingpong(n-1)
def direction(n):
if n < 8:
return 1
if (n-1) % 8 == 0 or num_eights(n-1):
return -1 * direction(n-1)
return direction(n-1)完整答案代码:
HW_SOURCE_FILE=__file__
def pascal(row, column):
"""Returns a number corresponding to the value at that location
in Pascal's Triangle.
>>> pascal(0, 0)
1
>>> pascal(0, 5) # Empty entry; outside of Pascal's Triangle
0
>>> pascal(3, 2) # Row 4 (1 3 3 1), 3rd entry
3
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if row<0 :
return 0
if row==0 and column==0:
return 1
elif column>row or column<0:
return 0
else:
return pascal(row-1,column)+pascal(row-1,column-1)
def compose1(f, g):
""""Return a function h, such that h(x) = f(g(x))."""
def h(x):
return f(g(x))
return h
def repeated(f, n):
"""Return the function that computes the nth application of func (recursively!).
>>> add_three = repeated(lambda x: x + 1, 3)
>>> add_three(5)
8
>>> square = lambda x: x ** 2
>>> repeated(square, 2)(5) # square(square(5))
625
>>> repeated(square, 4)(5) # square(square(square(square(5))))
152587890625
>>> repeated(square, 0)(5)
5
>>> from construct_check import check
>>> # ban iteration
>>> check(HW_SOURCE_FILE, 'repeated',
... ['For', 'While'])
True
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if n==0:
return lambda x:x
if n==1:
return f
return compose1(f,repeated(f,n-1))
def num_eights(x):
"""Returns the number of times 8 appears as a digit of x.
>>> num_eights(3)
0
>>> num_eights(8)
1
>>> num_eights(88888888)
8
>>> num_eights(2638)
1
>>> num_eights(86380)
2
>>> num_eights(12345)
0
>>> from construct_check import check
>>> # ban all assignment statements
>>> check(HW_SOURCE_FILE, 'num_eights',
... ['Assign', 'AugAssign'])
True
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if x==0:
return 0
if x%10==8:
return num_eights(x//10)+1
else:
return num_eights(x//10)
def pingpong(n):
"""Return the nth element of the ping-pong sequence.
>>> pingpong(8)
8
>>> pingpong(10)
6
>>> pingpong(15)
1
>>> pingpong(21)
-1
>>> pingpong(22)
-2
>>> pingpong(30)
-2
>>> pingpong(68)
0
>>> pingpong(69)
-1
>>> pingpong(80)
0
>>> pingpong(81)
1
>>> pingpong(82)
0
>>> pingpong(100)
-6
>>> from construct_check import check
>>> # ban assignment statements
>>> check(HW_SOURCE_FILE, 'pingpong', ['Assign', 'AugAssign'])
True
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if n <= 8:
return n
return direction(n) + pingpong(n-1)
def direction(n):
if n < 8:
return 1
if (n-1) % 8 == 0 or num_eights(n-1):
return -1 * direction(n-1)
return direction(n-1)