4.文件流类
void open(const char * filename ,openmode mode);
filename 是文件名,如果缺少路径,则默认为当前目录。
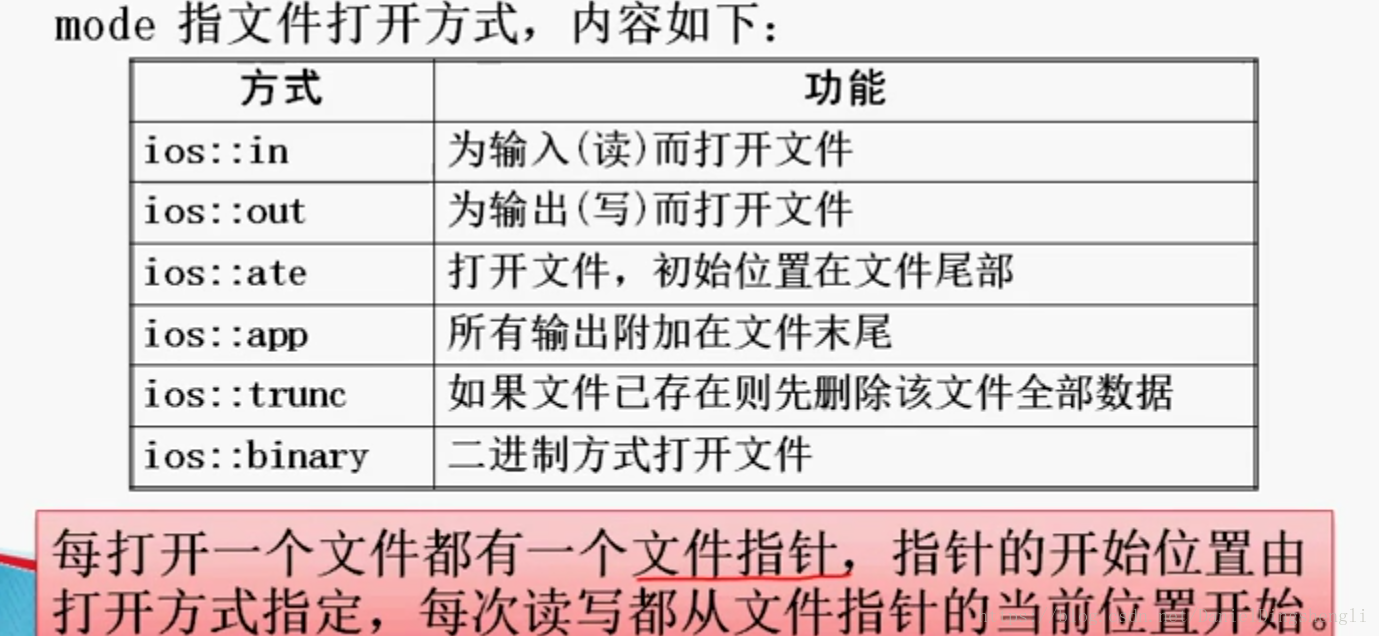
例子:ifstream file1; ,ios::in);//ios::in可以省略,因为ifstream本来是用来输入的;
file1.open("grade.txt
ofstream file2;
file2.open(“c:\msg.txt”);
以二进制输入方式打开文件c:\abc.bmp
fstream file3;
file3.open(“c:\abc.bmp”,ios::binary|ios::in);
用构造函数来打开二进制文件,用于输出
ofstream file(“example.bin”,ios::out|ios::binary);
5.文件的关闭
关闭文件操作包括把缓冲区数据完整地写入文件,添加文件结束标志,切断流对象和外部文件的连接。
当一个流对象的生存期结束,系统也会自动关闭文件。
若流对象的生存期没有结束,用close()关闭文件后,该流对象可以重用。
6.文本文件读写
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
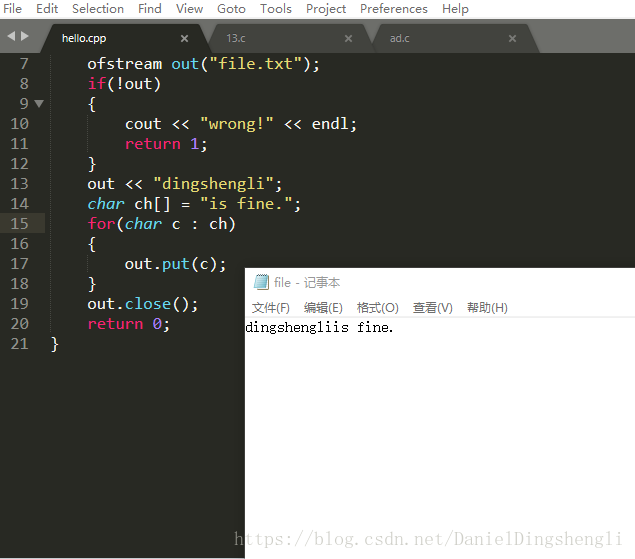
ofstream out("file.txt");//没有则会创建
if(!out)
{
cout << "wrong!" << endl;
return 1;
}
out << "dingshengli";
char ch[] = "is fine.";
for(char c : ch)
{
out.put(c);
}
out.close();
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
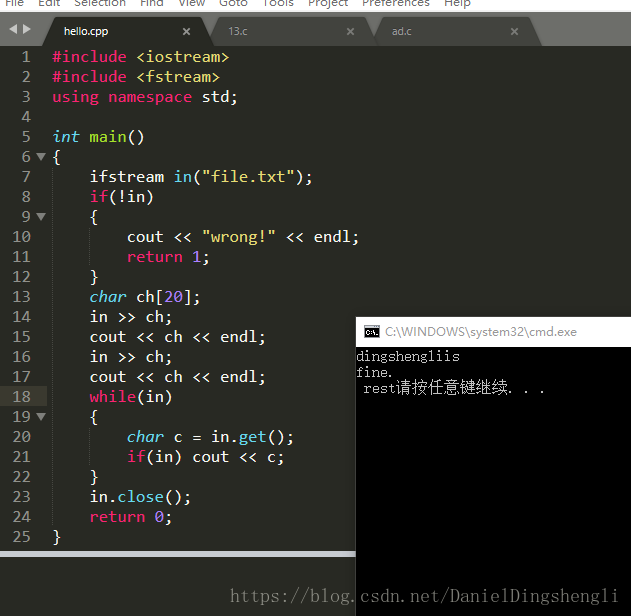
ifstream in("file.txt");
if(!in)
{
cout << "wrong!" << endl;
return 1;
}
char ch[20];
in >> ch;
cout << ch << endl;
in >> ch;
cout << ch << endl;
while(in)
{
char c = in.get();//get会读取空格
if(in) cout << c;
}
in.close();
return 0;
}判断读到达文件尾部
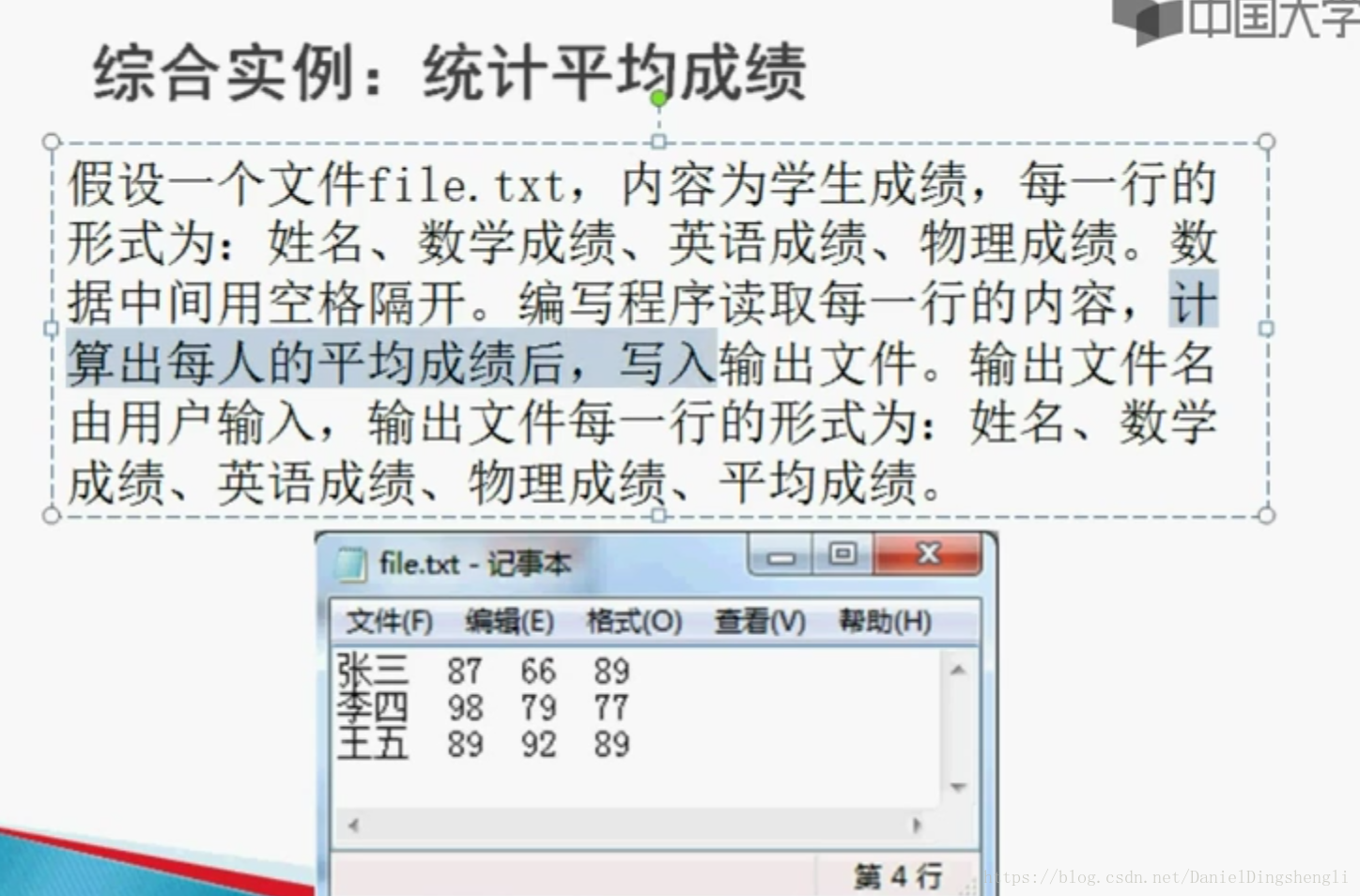
7.实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
//一行一行地处理
int main()
{
char ch[2];
int math,eng,phy;
ifstream fin("file.txt");
ofstream fout("res.txt");
if(!fin||!fout)
{
cout << "wrong" << endl;
}
while(fin)
{
fin >> ch >> math >> eng >> phy;
if(fin)
{
float avg = 1.0*(math+eng+phy)/3;
fout << ch << '\t' << math << '\t' << eng << '\t' << phy << '\t' << avg << endl;
}
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
return 0;
}8.二进制文件的读写


实例:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
private:
char Name[10];
char Class[10];
char Sex;
int Age;
public:
Student(){};
Student(char *Name,char *Class,char Sex,int age);
void Showme()
{
cout << Name << '\t' << Class << '\t' << Sex << '\t' << Age << endl;
}
};
Student::Student(char *Name,char *Class,char Sex,int age)
{
strcpy(this->Name,Name);
strcpy(this->Class,Class);
this->Sex = Sex;
Age = age;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
Student stu[3] =
{
Student("Wangxiao","电气11",'m',22),
Student("Liuda","机械01",'f',24),
Student("Liwenhua","生物12",'m',21),
};
ofstream file1("file.dat",ios::binary);
if(!file1)
{
cout << "Error!" << endl;
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
file1.write((char*)&stu[i],sizeof(stu[i]));
}
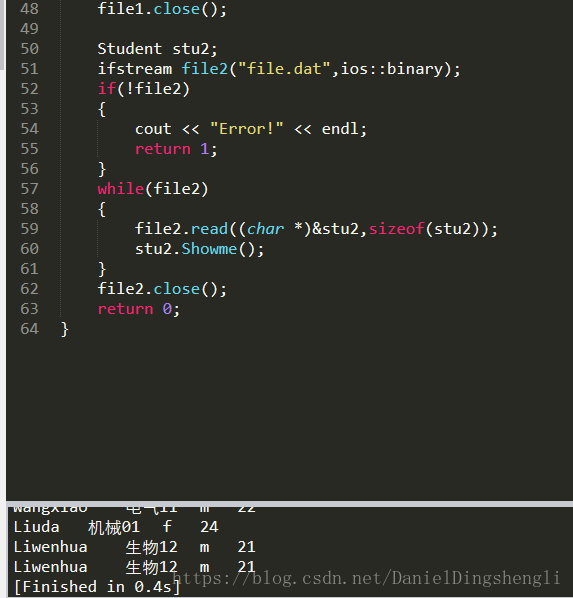
file1.close();
Student stu2;
ifstream file2("file.dat",ios::binary);
if(!file2)
{
cout << "Error!" << endl;
return 1;
}
while(file2)
{
file2.read((char *)&stu2,sizeof(stu2));
stu2.Showme();
}
file2.close();
return 0;
}8.B 二进制文件的顺序读写、随机读写
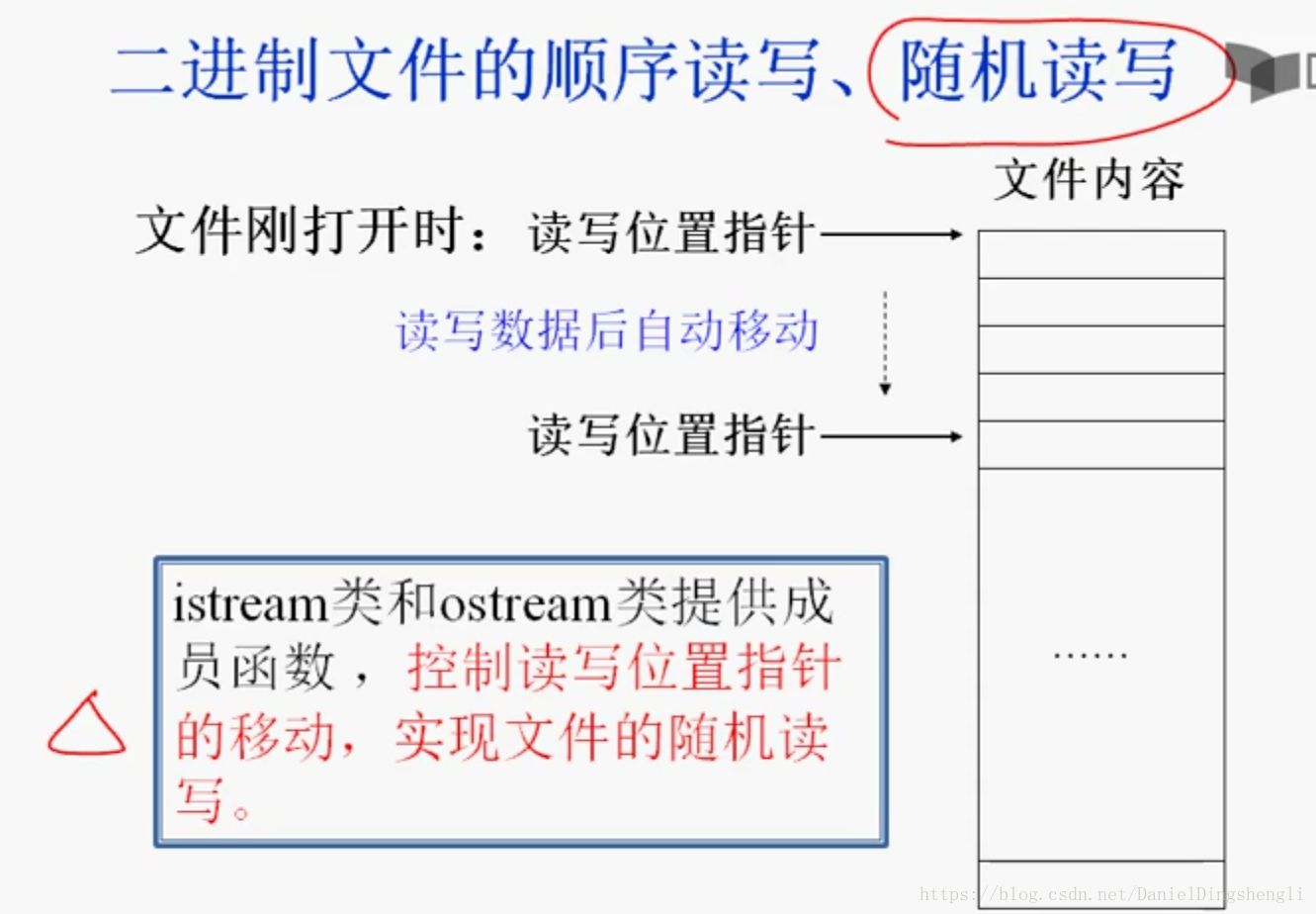

例如
iostream input;
input.seekg(-10,ios::end);//读指针从流的结尾,向前移动10个字节8.C实例
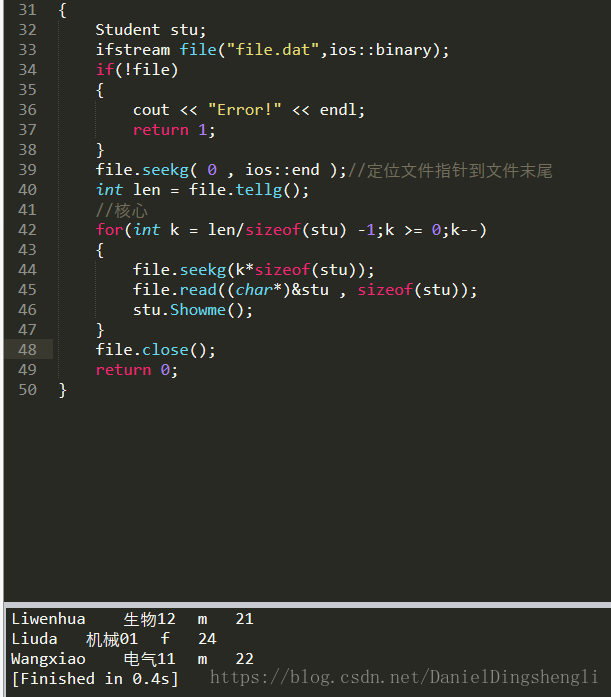
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
Student stu;
ifstream file("file.dat",ios::binary);
if(!file)
{
cout << "Error!" << endl;
return 1;
}
file.seekg( 0 , ios::end );//定位文件指针到文件末尾
int len = file.tellg();
//核心
for(int k = len/sizeof(stu) -1;k >= 0;k--)
{
file.seekg(k*sizeof(stu));
file.read((char*)&stu , sizeof(stu));
stu.Showme();
}
file.close();
return 0;
}