Algorithm N
Algorithm N (Natural two-way merge sort). Records R1,…,RN are sorted
using two areas of memory, each of which is capable of holding N records. For
convenience, we shall say that the records of the second area are RN+1, …, R2N,
although it is not really necessary that RN+1 be adjacent to RN. The initial
contents of RN+1, … , R2N are immaterial. After sorting is complete, the ‘keys
will be in order, K1 <= … <= KN.
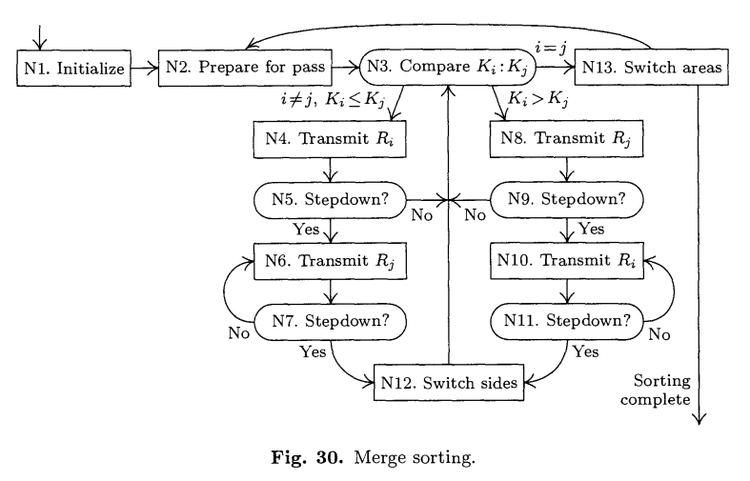
N1. [Initialize.] Set s <– 0. (When s = 0, we will be transferring records from
the (R1,…, RN) area to the (RN+1, … , R2N) area; when s = 1, we will
be going the other way.)
N2. [Prepare for pass.] If s = 0, set i <– 1, j <– N, k <– N+1, I <– 2N; if
s = 1, set i <– N+1, j <– 2N, k <– 1, I <– N. (Variables i, j, k, I point to
the current positions in the “source files” being read and the “destination
files” being written.) Set d <– 1, f <– 1. (Variable d gives the current
direction of output; f is set to zero if future passes are necessary.)
N3. [Compare Ki:Kj.] If Ki > Kj, go to step N8. If i = j, set Rk <– Ri and
go to N13.
N4. [Transmit Ri.] (Steps N4-N7 are analogous to steps M3-M4 of Algo-
rithm M.) Set Rk <– Ri, k <– k+d.
N5. [Stepdown?] Increase i by 1. Then if Ki-1 <= Ki, go back to step N3.
N6. [Transmit Rj.] Set Rk <– Rj, k <– k+d.
N7. [Stepdown?] Decrease j by 1. Then if Kj+1 <= Kj, go back to step N6;
otherwise go to step N12.
N8. [Transmit Rj.] (Steps N8-N11 are dual to steps N4-N7.) Set Rk <– Rj,
k <– k+d.
N9. [Stepdown?] Decrease j by 1. Then if Kj+1 <= Kj, go back to step N3.
N10. [Transmit Ri] Set Rk <– Ri, k <– k+d.
N11. [Stepdown?] Increase i by 1. Then if Ki-1 <= Ki, go back to step N10.
N12. [Switch sides.] Set f <– 0, d <– -d, and interchange k <–> I. Return to
step N3.
N13. [Switch areas.] If = 0, set s <– 1-s and return to N2. Otherwise sorting
is complete; if s = 0, set (R1,…, RN) <– (RN+1, … , R2N). (This last
copying operation is unnecessary if it is acceptable to have the output in
(RN+1, … , R2N) about half of the time.) |
Flow diagram
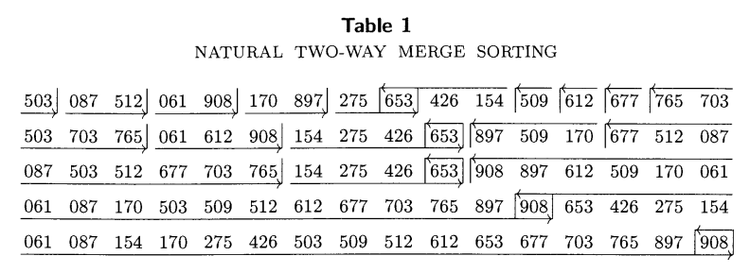
Data table
Java program
In this program, R1,…,RN were simplified to K1,…,KN.
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 1O1O
* Date: 12/3/13
* Time: 10:01 PM
* :)~
* Natural Two-way Merge Sort:Sorting by Merging:Internal Sorting
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 16;
int[] K = new int[33];
int temp;
/*Prepare the data*/
K[1] = 503;
K[2] = 87;
K[3] = 512;
K[4] = 61;
K[5] = 908;
K[6] = 170;
K[7] = 897;
K[8] = 275;
K[9] = 653;
K[10] = 426;
K[11] = 154;
K[12] = 509;
K[13] = 612;
K[14] = 677;
K[15] = 765;
K[16] = 703;
/*Output unsorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Unsorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
System.out.println();
/*Kernel of the Algorithm!*/
int s = 0;
int i = -1;
int j = -1;
int k = -1;
int l = -1;
int d;
int f;
do{ /*N2*/
if(s == 0){
i = 1;
j = N;
k = N+1;
l = 2*N;
}else if(s == 1){
i = N+1;
j = 2*N;
k = 1;
l = N;
}
d = 1;
f = 1;
do{ /*N3*/
if(K[i] > K[j]){
K[k] = K[j]; /*N8*/
k += d;
j--;
if(K[j+1] <= K[j]){ /*N9*/
continue;
}else {
do{
K[k] = K[i]; /*N10*/
k += d;
i++;
}while (K[i-1] <= K[i]);
f = 0;
d = -d;
temp = k;
k = l;
l = temp;
}
}else if(i != j && K[i] <= K[j]){
K[k] = K[i]; /*N4*/
k += d;
i++; /*N5*/
if(K[i-1] <= K[i]){
continue;
}else {
do{
K[k] = K[j]; /*N6*/
k += d;
j--;
}while (K[j+1] <= K[j]);
f = 0;
d = 0-d;
temp = k;
k = l;
l = temp;
}
}else if(i == j){
K[k] = K[i];
if(f == 0){
s = 1 - s;
}
break;
}
}while (true);
}while (f == 0);
if(s == 0){
for(int m=1; m<=N; m++){
K[m] = K[N+m];
}
}
/*Output sorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Sorted Ks:");
for(int m=1; m<=N; m++){
System.out.println(m+":"+K[m]);
}
}
}Outputs
Unsorted Ks:
1:503
2:87
3:512
4:61
5:908
6:170
7:897
8:275
9:653
10:426
11:154
12:509
13:612
14:677
15:765
16:703
Sorted Ks:
1:61
2:87
3:154
4:170
5:275
6:426
7:503
8:509
9:512
10:612
11:653
12:677
13:703
14:765
15:897
16:908Reference
<< The art of computer programming: Sorting and Searching >> VOLUME 3, DONALD E. KNUTH