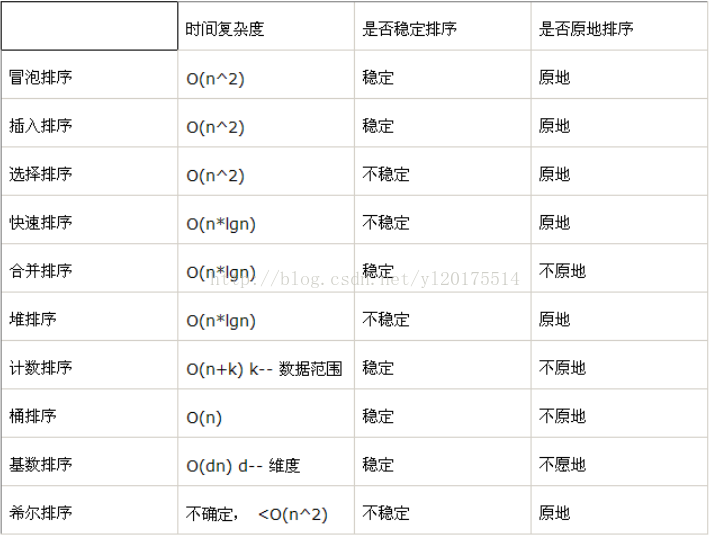
冒泡排序、选择排序、快速排序、插入排序、希尔排序、归并排序、堆排序
Java排序算法
1)分类:
1)插入排序(直接插入排序、希尔排序)
2)交换排序(冒泡排序、快速排序)
3)选择排序(直接选择排序、堆排序)
4)归并排序
5)分配排序(箱排序、基数排序)
所需辅助空间最多:归并排序
所需辅助空间最少:堆排序

平均速度最快:快速排序
不稳定:快速排序,希尔排序,堆排序。
1)选择排序算法的时候
1.数据的规模 ; 2.数据的类型 ; 3.数据已有的顺序
一般来说,当数据规模较小时,应选择直接插入排序或冒泡排序。任何排序算法在数据量小时基本体现不出来差距。考虑数据的类型,比如如果全部是正整数,那么考虑使用桶排序为最优。 考虑数据已有顺序,快排是一种不稳定的排序(当然可以改进),对于大部分排好的数据,快排会浪费大量不必要的步骤。数据量极小,而起已经基本排好序,冒泡是最佳选择。我们说快排好,是指大量随机数据下,快排效果最理想。而不是所有情况。
3)总结:
——按平均的时间性能来分:
1)时间复杂度为O(nlogn)的方法有:快速排序、堆排序和归并排序,其中以快速排序为最好;
2)时间复杂度为O(n2)的有:直接插入排序、起泡排序和简单选择排序,其中以直接插入为最好,特别是对那些对关键字近似有序的记录序列尤为如此;
3)时间复杂度为O(n)的排序方法只有,基数排序。
当待排记录序列按关键字顺序有序时,直接插入排序和起泡排序能达到O(n)的时间复杂度;而对于快速排序而言,这是最不好的情况,此时的时间性能蜕化为O(n2),因此是应该尽量避免的情况。简单选择排序、堆排序和归并排序的时间性能不随记录序列中关键字的分布而改变。
——按平均的空间性能来分(指的是排序过程中所需的辅助空间大小):
1) 所有的简单排序方法(包括:直接插入、起泡和简单选择)和堆排序的空间复杂度为O(1);
2) 快速排序为O(logn ),为栈所需的辅助空间;
3) 归并排序所需辅助空间最多,其空间复杂度为O(n );
4)链式基数排序需附设队列首尾指针,则空间复杂度为O(rd )。
——排序方法的稳定性能:
1) 稳定的排序方法指的是,对于两个关键字相等的记录,它们在序列中的相对位置,在排序之前和 经过排序之后,没有改变。
2) 当对多关键字的记录序列进行LSD方法排序时,必须采用稳定的排序方法。
3) 对于不稳定的排序方法,只要能举出一个实例说明即可。
4) 快速排序,希尔排序和堆排序是不稳定的排序方法。
/**
* 七种排序算法Java版
* @author Administrator
*/
public class Sort {
/**
* 打印数组
* @param data
*/
public static void displayData(int[] data) {
for (int d : data) {
System.out.print(d + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 冒泡排序算法,时间复杂度O(n2),算法具有稳定性,堆排序和快速排序算法不具有稳定性,即排序后相同元素的顺序会发生变化
* @param src
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] src) {
if (src.length > 0) {
int length = src.length;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length - i; j++) {
if (src[j] > src[j + 1]) {
int temp = src[j];
src[j] = src[j + 1];
src[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 快速排序,时间复杂度O(nlogn),最坏时间复杂度O(n2),平均时间复杂度O(nlogn),算法不具稳定性
* @param src
* @param begin
* @param end
*/
public static void quickSort(int[] src, int begin, int end) {
if (begin < end) {
int key = src[begin];
int i = begin;
int j = end;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && src[j] > key) {
j--;
}
if (i < j) {
src[i] = src[j];
i++;
}
while (i < j && src[i] < key) {
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
src[j] = src[i];
j--;
}
}
src[i] = key;
quickSort(src, begin, i - 1);
quickSort(src, i + 1, end);
}
}
/**
* 选择排序,分为简单选择排序、树形选择排序(锦标赛排序)、堆排序 此算法为简单选择排序
* @param a
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] a) {
int length = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex != i) {
int temp = a[minIndex];
a[minIndex] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
}
/**
* 插入排序,适用于少量数据的排序,时间复杂度O(n2),是稳定的排序算法,原地排序
* @param a
*/
public static void insertSort(int[] a) {
int length = a.length;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
int temp = a[i];
int j = i;
for (; j > 0 && a[j - 1] > temp; j--) {
a[j] = a[j - 1];
}
a[j] = temp;
}
}
/**
* 归并排序算法,稳定排序,非原地排序,空间复杂度O(n),时间复杂度O(nlogn)
* @param a
* @param low
* @param high
*/
public static void mergeSort(int a[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
mergeSort(a, low, (low + high) / 2);
mergeSort(a, (low + high) / 2 + 1, high);
merge(a, low, (high + low) / 2, high);
}
}
/**
* 归并排序辅助方法,合并
*
* @param a
* @param low
* @param mid
* @param high
*/
private static void merge(int[] a, int low, int mid, int high) {
int[] b = new int[high - low + 1];
int s = low;
int t = mid + 1;
int k = 0;
while (s <= mid && t <= high) {
if (a[s] <= a[t])
b[k++] = a[s++];
else
b[k++] = a[t++];
}
while (s <= mid)
b[k++] = a[s++];
while (t <= high)
b[k++] = a[t++];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
a[low + i] = b[i];
}
}
/**
* 希尔排序的一种实现方法
*
* @param a
*/
public static void shellSort(int[] a) {
int temp;
for (int k = a.length / 2; k > 0; k /= 2) {
for (int i = k; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j >= k; j -= k) {
if (a[j - k] > a[j]) {
temp = a[j - k];
a[j - k] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 堆排序,最坏时间复杂度O(nlog2n),平均性能接近于最坏性能。由于建初始堆所需的比较次数多,故堆不适合记录较少的比较 堆排序为原地不稳定排序
*
* @param array
*/
public static void heapSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
makeHeap(array, i);
}
for (int i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[0];
array[0] = temp;
rebuildHeap(array, i);
}
}
/**
* 堆排序辅助方法---创建堆
*
* @param array
* @param k
*/
private static void makeHeap(int[] array, int k) {
int current = k;
while (current > 0 && array[current] > array[(current - 1) / 2]) {
int temp = array[current];
array[current] = array[(current - 1) / 2];
array[(current - 1) / 2] = temp;
current = (current - 1) / 2;
}
}
/**
* 堆排序辅助方法---堆的根元素已删除,末尾元素已移到根位置,开始重建
*
* @param array
* @param size
*/
private static void rebuildHeap(int[] array, int size) {
int currentIndex = 0;
int right = currentIndex * 2 + 2;
int left = currentIndex * 2 + 1;
int maxIndex = currentIndex;
boolean isHeap = false;
while (!isHeap) {
if (left < size && array[currentIndex] < array[left]) {
maxIndex = left;
}
if (right < size && array[maxIndex] < array[right]) {
maxIndex = right;
}
if (currentIndex == maxIndex) {
isHeap = true;
} else {
int temp = array[currentIndex];
array[currentIndex] = array[maxIndex];
array[maxIndex] = temp;
currentIndex = maxIndex;
right = currentIndex * 2 + 2;
left = currentIndex * 2 + 1;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int data[] = { 2, -1, 5, 4, 6, 8, 7, -3 };
Sort.displayData(data);
Sort.bubbleSort(data);
Sort.displayData(data);
}
}