前言
react的virtual dom非常强大,本篇文章将会简单讨论virtual dom的实现思路~具体步骤如下:
- 用js对象构造一个虚拟的dom树,插入到文档中
- 状态变更时,记录新树和旧树的差异
- 把上面的差异构建到真正的dom中

1.用js对象构建一个dom树
一个dom节点包含节点类型(tagName),所有属性(props,是一个对象),它的子节点(children一个数组)。
function Element(tagName,props,children){
this.tagName=tagName
this.props=props
this.children=children
}我们用上面的构造函数来构建一个dom树
const ul = new Element('ul',{id:'list'},[
new Element('li',{class:'item'},['item 1']),
new Element('li',{class:'item'},['item 1']),
new Element('li',{class:'item'},['item 1'])
])这个dom树渲染成html:
<ul id='list'>
<li class='item'>item 1</li>
<li class='item'>item 2</li>
<li class='item'>item 3</li>
</ul>我们再来编写一个方法,来真正的渲染dom
Element.prototype.render=function(){
// 根据tagName构建
const el=document.createElement(this.tagName)
const props=this.props
// 添加属性
const keys=Object.keys(props)
keys.forEach(key=>{
el.setAttribute(key,props[key])
})
// 添加子节点
const children=this.childen||[]
children.forEach(child=>{
const childEl=(child instanceof Element)
? child.render() // 是虚拟dom就递归render
: document.createTextNode(child) // 不是就构建文本节点
el.appendChild(childEl)
})
return el
}这时,我们再把ul插入到真正的节点中:
const rootEl=ul.render()
document.body.appendChild('#root')2.比较两颗虚拟dom树的差异
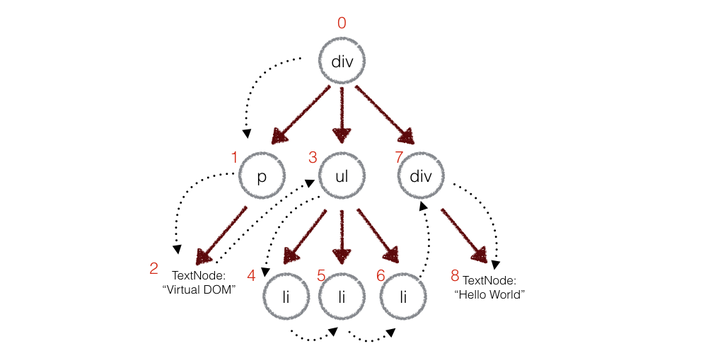
先对两棵树进行深度优先遍历,每个节点都会有一个唯一的标记;每遍历一个节点就把该节点和新树中的对应节点进行比较,有差异则记录到一个对象中(patches)。
function diff(oldTree,newTree){
const patches={}
let index=0
return patches // 每个节点的差异对象
}
function dpsWalk(oldNode,newNode,patches,index){
// 记录差异。。
patches[index]=[...]
diffChildren(oldNode.children,newNode.children,patches,index)
}
function diffChildren(oldChildren,newChildren,patches,index){
let leftNode=null
let currentNodeIndex=index // 节点的唯一标识
oldChildren.forEach((val,i)=>{
const newChild=newChildren[i]
currentNodeIndex=(leftNode&&leftNode.count) // 计算节点标识
? currentNodeIndex+leftNode.count+1
: currentNodeIndex+1
dfsWalk(child, newChild, patches,currentNodeIndex) // 深度遍历子节点
leftNode=child
})
}如在标记为3的节点发现差异,则:
patches[3]=[{difference},{difference},{difference}]差异类型
考虑到会有以下几种差异类型:
- 替换了原来的节点 - REPLACE 0
- 移动、删除、新增子节点 - REORDER 1
- 修改了节点的属性 - PROPS 2
- 文本节点:内容的更改 -TEXT 3
对于节点的替换,根据tagName是否相同来判断,记录:
patches[0]=[{
type:REPLACE,
node:newNode // (Element('div',props,children))
}]如果该节点,又新增了id属性,则记录为:
patches[0]=[{
type:REPLACE,
node:newNode // (Element('div',props,children))
},{
type:PROPS,
props:{
id:'container'
}
}]如果更新为文本节点,则:
patches[0]=[{
type:TEXT,
content:'new content'
}]如果只是更改了节点的顺序,但在实际上并没有改变了节点;如原来的父节点有div、p、ul,后来改变节点顺序为ul、div、p。如果按照同层顺序进行比较将都被标记为replace,这样dom开销就大了;而实际上只需要移动节点就可以达到,我们需要知道如何移动。这里可以抽象为字符串的编辑最小距离,采用动态规划来处理,具体算法详见我的博客用js实现编辑距离算法(Edit Distance)。
然后记录某个父节点的子节点操作:
patches[0]=[{
type:REORDER,
moves:[{remove or insert}]
}]3.把差异应用到真正的dom树上
算法是对dom树进行深度优先遍历,遍历时从patches对象中找到差异对象,然后根据不同的type分别对dom进行操作。
function dfswalk(node,walker,patches){
// 从patches拿出当前节点的差异
const currentPatches=patches[walker.index]
// 进行深度优先遍历
const len=node.childNodes?node.childNodes.length:0
for(let i=0;i<len;i++){
const child=node.childNodes[i]
walker.index++
dfswalk(child,walker,patches)
}
if(currentPatches){
// 有差异则对当前节点进行dom操作
applyPatches(node,currentPatches)
}
}
/*根据不同类型的差异对当前节点进行DOM操作*/
function applyPatches(node,currentPatches){
currentPatches.forEach((currentPatch)=>{
switch(currentPatch.type){
case REPLACE:
node.parentNode.replaceChild(currentPatch.node.render(),node)
break;
case REORDER:
reorderChildren(node, currentPatch.moves)
break;
case PROPS:
setProps(node,currentPatch.props)
break;
case TEXT:
node.textContent=currentPatch.textContent
break;
default:
throw new Error('Unknown patch type ' + currentPatch.type)
}
})
}以上并不是完整的代码,但基本的思路就是这样:构造element,找差异diff,把patches应用到dom上。查看完整的virtual-dom的代码参考github:simple-virtual-dom