if scores[i] <= 0:
break
#f.write(item+' '+str(label+1)+' '+str(score)+' '+str(int(box[0]))+' '+str(int(box[1]))+' '+str(int(box[2]))+' '+str(int(box[3]))+' \n')
f.write(item+' '+str(int(labels[i])+1)+' '+str(float(scores[i]))+' '+str(boxes[i][0])+' '+str(boxes[i][1])+' '+str(boxes[i][2])+' '+str(boxes[i][3])+' \n')实现逐行写
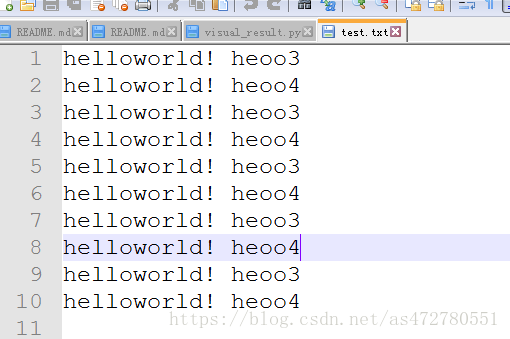
f = open('test.txt','w')
for i in range(5):
f.write('hello world!' + ',' + 'heoo 3' +'\n')
f.write('hello world!' + ' ' + 'heoo4' +'\n')
f.close()
print('write finish!') 实现逐行读
fp = open('test.txt', 'r')
lines = fp.readlines()
fp.close()
for i, line in enumerate(lines):
temp = line.split(' ')
print (temp[0])
print (temp[1])
#print (temp[2])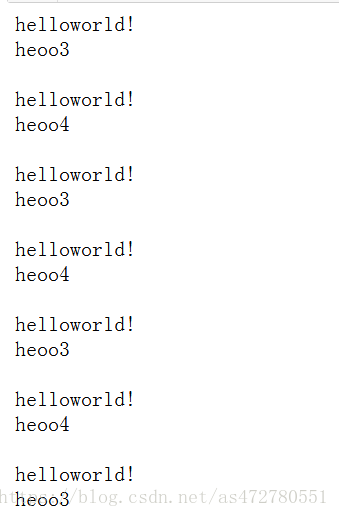
fp = open('test.txt', 'r')
lines = fp.readlines()
fp.close()
for i, line in enumerate(lines):
temp = line.split(' ')
#print (%(temp[0],temp[1]),end = ',')
print ("sum of " + str(temp[0]) + " and " + str(temp[0]) + " is ",end= " ")
#print (temp[1],end = ',')
#print (temp[2],end = ' ')a = 10
b = 20
c = a + b
#Normal string concatenation
print("sum of", a , "and" , b , "is" , c)
#convert variable into str
print("sum of " + str(a) + " and " + str(b) + " is " + str(c))
# if you want to print in tuple way
print("Sum of %s and %s is %s: " %(a,b,c))
#New style string formatting
print("sum of {0} and {1} is {2}".format(a,b,c))
#in case you want to use repr()
print("sum of " + repr(a) + " and " + repr(b) + " is " + repr(c))