1.什么是Window
- 1.1、代码层面来看,Window是一个abstract类。
/**
* Abstract base class for a top-level window look and behavior policy. An
* instance of this class should be used as the top-level view added to the
* window manager. It provides standard UI policies such as a background, title
* area, default key processing, etc.
*
* <p>The only existing implementation of this abstract class is
* android.view.PhoneWindow, which you should instantiate when needing a
* Window.
*/
public abstract class Window {
...
}- 1.2、解释
- Window是为顶级View提供的一个抽象类,该实现类应该作为顶级的view被添加到WindowManager中
- WindowManager提供了标准的ui规则,比如:背景,标题等
- 仅仅有一个存在的实例PhoneWindow,当需要Window时,实例PhoneWindow即可。
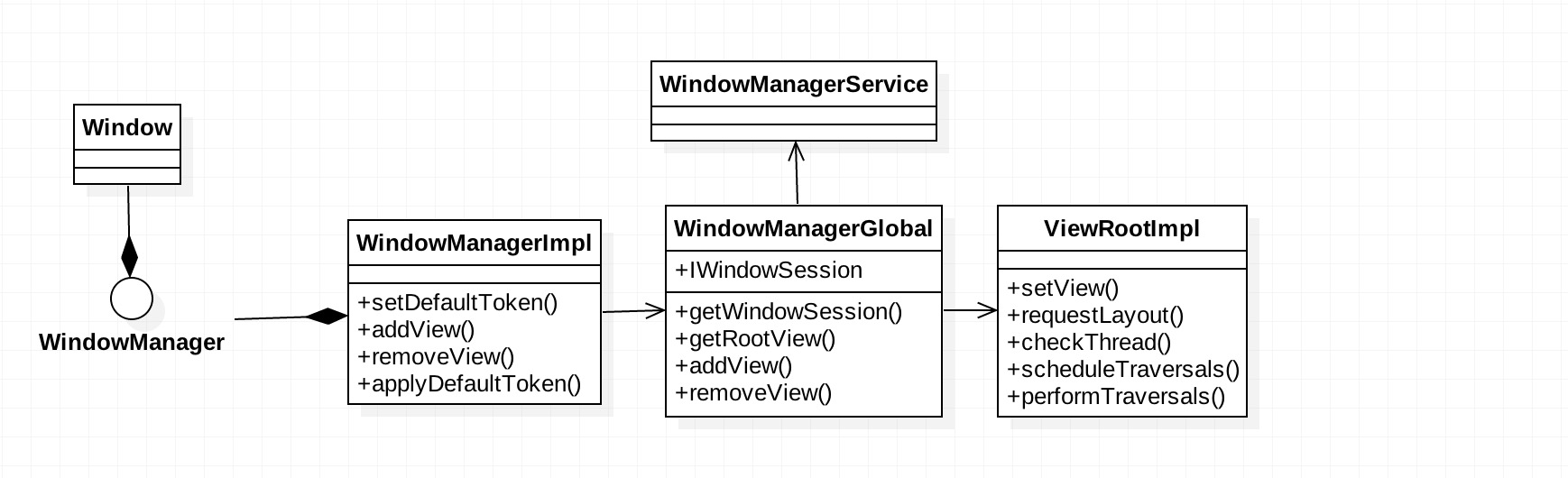
2.什么是WindowManager
- 2.1、直接看WindowManager interface的实现类
/**
* Provides low-level communication with the system window manager for
* operations that are bound to a particular context, display or parent window.
* Instances of this object are sensitive to the compatibility info associated
* with the running application.
*
* This object implements the {@link ViewManager} interface,
* allowing you to add any View subclass as a top-level window on the screen.
* Additional window manager specific layout parameters are defined for
* control over how windows are displayed. It also implements the {@link WindowManager}
* interface, allowing you to control the displays attached to the device.
*
* <p>Applications will not normally use WindowManager directly, instead relying
* on the higher-level facilities in {@link android.app.Activity} and
* {@link android.app.Dialog}.
*
* <p>Even for low-level window manager access, it is almost never correct to use
* this class. For example, {@link android.app.Activity#getWindowManager}
* provides a window manager for adding windows that are associated with that
* activity -- the window manager will not normally allow you to add arbitrary
* windows that are not associated with an activity.
*/
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
private final Display mDisplay;
private final Window mParentWindow;
private IBinder mDefaultToken;
public WindowManagerImpl(Display display) {
this(display, null);
}
private WindowManagerImpl(Display display, Window parentWindow) {
mDisplay = display;
mParentWindow = parentWindow;
}
public WindowManagerImpl createLocalWindowManager(Window parentWindow) {
return new WindowManagerImpl(mDisplay, parentWindow);
}
public WindowManagerImpl createPresentationWindowManager(Display display) {
return new WindowManagerImpl(display, mParentWindow);
}
/**
* Sets the window token to assign when none is specified by the client or
* available from the parent window.
*
* @param token The default token to assign.
*/
public void setDefaultToken(IBinder token) {
mDefaultToken = token;
}
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
@Override
public void updateViewLayout(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.updateViewLayout(view, params);
}
private void applyDefaultToken(@NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// Only use the default token if we don't have a parent window.
if (mDefaultToken != null && mParentWindow == null) {
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
// Only use the default token if we don't already have a token.
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (wparams.token == null) {
wparams.token = mDefaultToken;
}
}
}
@Override
public void removeView(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, false);
}
@Override
public void removeViewImmediate(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, true);
}
@Override
public Display getDefaultDisplay() {
return mDisplay;
}
}2.2、解释
- WindowManager 是用来提供低等级的通讯跟system window manager 。例如:绑定context/显示/父Window的操作
- 允许添加任何的View作为高等级的Window。
- 一般我们不会直接用WindowManager,通常在Activity、Dialog上使用
2.3、功能
- addView() 添加View
- updateViewLayout() 刷新布局
- applyDefaultToken()
- removeView()
- 以上所有操作均是通过单例类 WindowManagerGlobal 完成
3.什么是WindowManagerGlobal
- 3.1、WindowManagerGlobal是App中全局的窗口管理模块
- 3.2、WindowManagerGlobal 主要用来与WMS进行交互。
- 3.3、那么问题来了怎么跟WMS交互?
- 通过Binder进程间的通信获取WMS的session
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
// a. 获取WMS
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
// b.拉取session
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to open window session", e);
}
}
// c.返回WMS中的session
return sWindowSession;
}
}
public static IWindowManager getWindowManagerService() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowManagerService == null) {
// 进程间通信 binder使用
sWindowManagerService = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService("window"));
try {
sWindowManagerService = getWindowManagerService();
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(sWindowManagerService.getCurrentAnimatorScale());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get WindowManagerService, cannot set animator scale", e);
}
}
return sWindowManagerService;
}
}
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Start watching for system
// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.
// ...
// If this is a panel window, then
// a.实例该View的ViewRootImpl
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
// b.设置布局位置参数
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
// c.存储view,ViewRootImpl,params
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
}
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
// d.将view添加到(显示View)
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
}- 3.4、WMS 中的session 存储在了WindowManagerGlobal单例类的实例中,那么如何用到的呢。在addView()中,最后看到 root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView)了,那么ViewRootImpl到底是什么?
4.什么是ViewRootImpl
// 构造中WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession() 获取session
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
mDisplayManager.registerDisplayListener(mDisplayListener, mHandler);
mViewLayoutDirectionInitial = mView.getRawLayoutDirection();
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(view);
...
//a.请求layout
requestLayout();
//b.通过session去通知WMS显示mWindow
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
}
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
// 检测线程
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
// 各种通知
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
void checkThread() {
// 只能是当前ViewRootImpl
if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException(
"Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.");
}
}
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
// mTraversalRunnable 调用doTraversal()到 performTraversals()中进行View的绘制
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
private void performTraversals() {
// 各种view change状态检查
...
// measure
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec)
// 该dispatchOnGlobalLayout通常用来接收View measure完毕,获取view宽高
if (triggerGlobalLayoutListener) {
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = false;
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnGlobalLayout();
}
...
// draw
performDraw();
}// dispatchOnGlobalLayout的使用
view.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
//measure完毕
}
});- 4.1、ViewRootImpl 中获取WindowManagerGlobal中的session,改session 是通过Binder获取WMS中的,在ViewRootImpl进行线程检测、layout,measure,draw等一系列操作。最终ViewRootImpl通过session去通知WMS显示mWindow。
总结