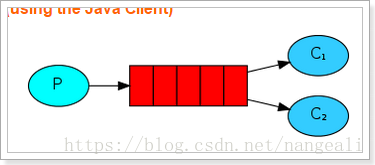
Work模式
一个生产者、多个消费者
多个消费者,共同监听一个队列
一个消息,只能被一个消费者获取
Send
发送者
package cn.itcast.rabbitmq.work;
import cn.itcast.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Send {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
// 消息内容
String message = "" + i;
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(i * 10);
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}Recv
消费者1
package cn.itcast.rabbitmq.work;
import cn.itcast.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
public class Recv {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
//channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
//休眠
Thread.sleep(10);
// 返回确认状态
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}Recv2
消费者2
package cn.itcast.rabbitmq.work;
import cn.itcast.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
public class Recv2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
//channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成状态
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
// 休眠1秒
Thread.sleep(1000);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}测试
查看队列
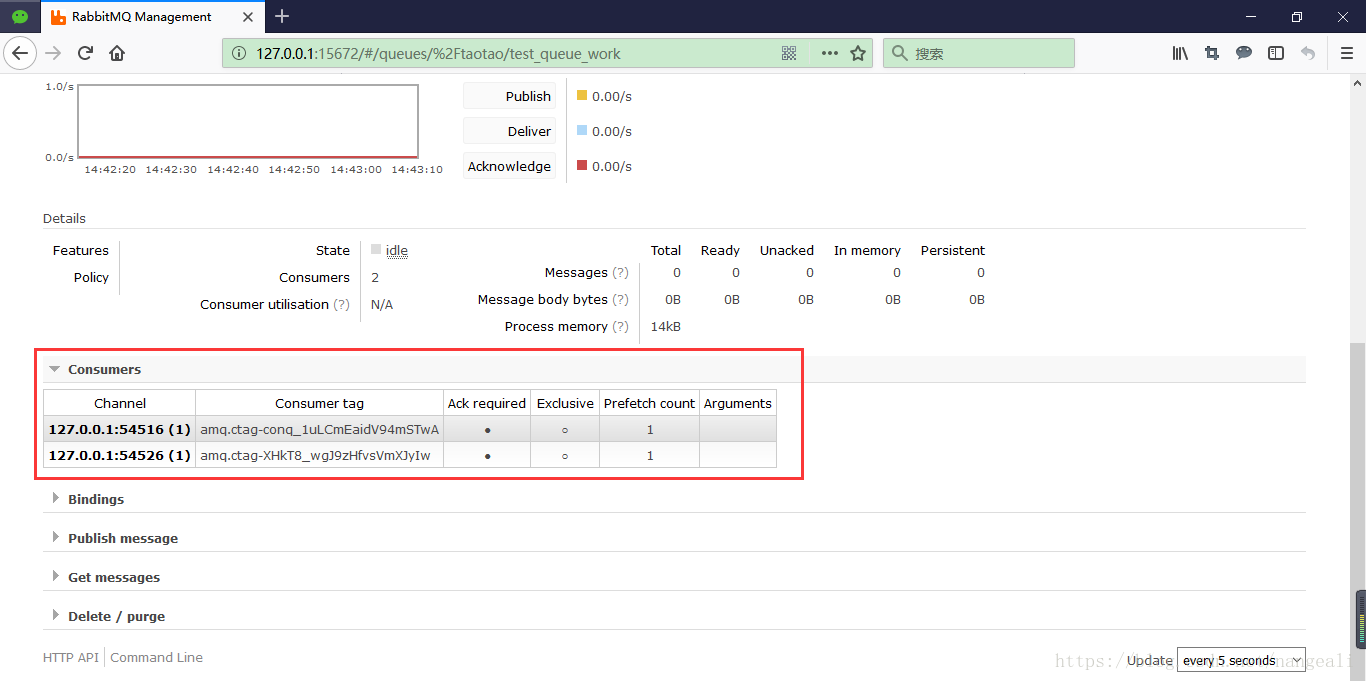
查看消费者
消费者1
接收消息,休眠10毫秒
消费者2
接收消息,休眠1000毫秒
测试结果
消费者1
获取了25条
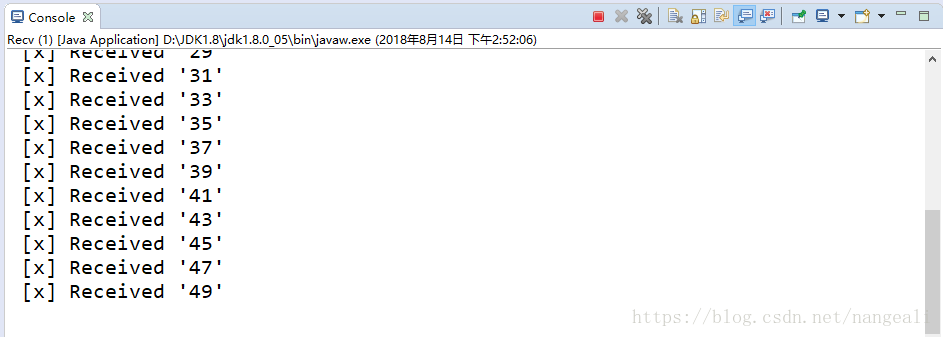
消费者2
获取了25条
消费者1,消费者2
获得了相同数量的消息