方法1:
分析问题
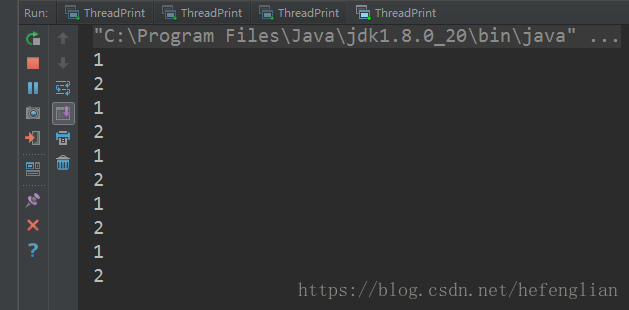
两个线程,可以想到的是多线程编程,共享变量,数据等,设想先让一个线程打印1,然后处于等待(wait)状态,接着另一个线程打印2,然后唤醒(notify)线程1,线程2再进入等待(wait)状态,线程1被唤醒后接着打印1,依次循环输出即可
代码
public class ThreadPrint {
static final Object object=new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
//线程1打印1
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <5 ; i++) {
synchronized (object){
System.out.println("1");
object.notify();//唤醒线程2
try{
object.wait();//线程1进入等待
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}).start();
//线程2
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
synchronized (object) {
System.out.println("2");
object.notify();//唤醒线程1
try {
object.wait();//线程2进入等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
方法2:
分析问题:
使用volatile保证数据的可见性,避免多线程访问同一个变量,它的值刷新不及时的问题;设想定义一个volatile修饰的boolean变量flag,当flag为true时,线程1打印1,同时修改flag的值,置为false,当flag为false时,线程2打印2,同时修改falg的值,置为true,依次循环即可
代码
package cn.alibaba.thread;
public class ThreadPrint2 {
volatile static boolean flag=true;//volatile
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1=new MyThread(1);
Thread t2=new MyThread(2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int printValue;
public MyThread(int printValue) {
this.printValue = printValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (flag) {
System.out.println("1");
} else {
System.out.println("2");
}
flag = !flag;
}
}
}
}
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/libinbin147256369/article/details/79909050