【bean配置】
在XML文件中通过bean节点来配置bean
1 <!-- 2 配置bean 3 class: bean的全类名,通过反射的方式在IOC容器中创建bean,所以要求bean中必须有无参的构造器。 4 id:标识容器中的bean,id唯一。 5 --> 6 <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.hk.beans.HelloWorld"> 7 <property name="name" value="Spring"></property> 8 </bean>
id:bean的名称。
--在IOC容器中必须是唯一的。
--若id没有指定,Spring自动将对应类名作为bean的名字。
--id可以指定多个名字,名字之间可用逗号,分号,或空格分隔。
【注】:
当bean中不存在无参构造器,存在有参构造器时,运行程序,会出现以下错误:

【Spring容器】
--ApplicationContext代表容器,但实际上它是一个接口。
--在Spring IOC容器读取bean配置创建bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化。只有在容器实例化后,才可以从IOC容器中获取bean实例并使用。
--Spring提供了两种类型的IOC容器实现。
(1)BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现。
(2)ApplicationContext:提供了更多的高级特性。是BeanFactory的子接口。
BeanFactory是Spring框架的基础设施,面向Spring本身;
ApplicationContext面向使用Spring框架的开发者,几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用ApplicationContext而非底层的BeanFactory。
无论使用何种方式,配置文件是相同的。
【ApplicationContext】
1.ApplicationContext的主要实现类:
--ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下加载配置文件。
--FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统中加载配置文件。
2.ConfigurableApplicationContext(子接口)扩展于ApplicationContext,新增加两个主要方法:refresh()和close(),让ApplicationContext具有启动、刷新和关闭上下文的能力。
3.ApplicationContext在初始化上下文的时候就实例化所有单例的bean。
4.WebApplicationContext是专门为WEB应用而准备的,它允许从相对于WEB根目录的路径中完成初始化工作。
【从IOC容器中获取bean】
1.调用ApplicationContext的getBean()方法。该方法是在ApplicationContext的父接口BeanFactory中定义实现的。
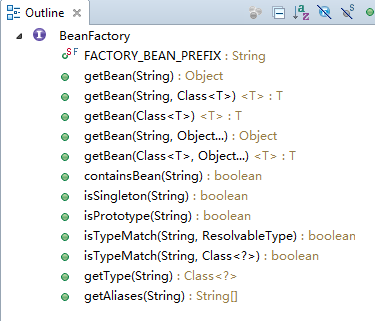
由图中可知,还可以由类型获取bean。
1 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 2 HelloWorld helloWorld = ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
缺点!!:如果在IOC容器中此类型不唯一(有两个或以上相同类型的bean时),会出错。
---小结:
1 //2. 从IOC容器中获取Bean实例 2 //方式一:利用id定位到IOC容器中的bean 3 //HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloWorld"); 4 //方式二:利用类型返回IOC容器中的bean,但要求IOC容器中必须只能有一个该类型的bean 5 HelloWorld helloWorld = ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
【依赖注入的方式】
Spring支持3种依赖注入的方式:
--属性输入
--构造器注入
--工厂方式(很少使用,不推荐)
1.属性注入
(1)概述:属性注入即通过setter方法注入Bean的属性值或以来的对象。
(2)属性注入使用<property>元素,使用name属性指定Bean的属性名称,value属性或<value>子节点指定属性值。
(3)属性注入是实际应用中最常用到的注入方式。
1 <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.hk.beans.HelloWorld"> 2 <property name="name" value="Spring"></property> 3 </bean>
2.构造方法注入
(1)通过构造方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了Bean实例在实例化后就可以使用。
(2)构造器注入在<constructor-arg>元素里声明属性,<constructor-arg>中没有name属性。
Car.java:
1 package com.hk.beans; 2 3 public class Car { 4 private String brand; 5 private String corp; 6 private double price; 7 private int maxSpeed; 8 9 public Car(String brand, String corp, double price) { 10 super(); 11 this.brand = brand; 12 this.corp = corp; 13 this.price = price; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public String toString() { 18 return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", corp=" + corp + ", price=" + price 19 + ", maxSpeed=" + maxSpeed + "]"; 20 } 21 22 public Car(String brand, String corp, int maxSpeed) { 23 super(); 24 this.brand = brand; 25 this.corp = corp; 26 this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed; 27 } 28 }
配置文件代码:
1 <!-- 通过构造方法来配置bean的属性 --> 2 <bean id="car" class="com.hk.beans.Car"> 3 <constructor-arg value="BWM" index="0"></constructor-arg> 4 <constructor-arg value="ShangHai" index="1"></constructor-arg> 5 <constructor-arg value="100000" type="double"></constructor-arg> 6 </bean> 7 8 <!-- 使用构造器注入属性值可以指定参数的位置和参数的类型!以区分重载的构造器! --> 9 <bean id="car2" class="com.hk.beans.Car"> 10 <constructor-arg value="bieke" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg> 11 <constructor-arg value="BeiJing" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg> 12 <constructor-arg value="150" type="int"></constructor-arg> 13 </bean>
(测试)Main.java:
1 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 2 3 Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car"); 4 System.out.println(car); 5 6 car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car2"); 7 System.out.println(car);
运行结果;
