1.0.0 Summary
Tittle:【Java】-NO.16.EBook.4.Java.1.010-【疯狂Java讲义第3版 李刚】- 异常
Style:EBook
Series:Java
Since:2017-09-29
End:....
Total Hours:...
Degree Of Diffculty:2
Degree Of Mastery:2
Practical Level:2
Desired Goal:2
Archieve Goal:....
Gerneral Evaluation:...
Writer:kingdelee
Related Links:
http://www.cnblogs.com/kingdelee/
1.异常
Check异常:编译阶段需要处理的异常(可以被修复的异常)。非RuntimeException及其子类的异常,都是Check异常。
Runtime异常:RuntimeException及其子类的异常,都是Runtime异常
1.2.catch之间是短路的,最多有且只有一个catch被执行,应从小到大依次写出。
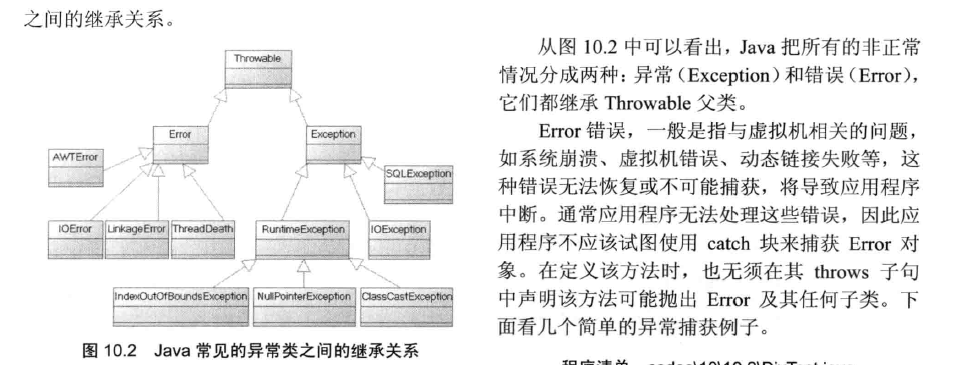
1.3 捕获多个异常时的变量时,变量默认是final,捕获一个异常时,变量没有final
// 1 捕获多个异常时的变量时,变量默认是final,捕获一个异常时,变量没有final
public class MultiExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int c = a / b;
System.out.println("您输入的两个数相除的结果是:" + c);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException | NumberFormatException
| ArithmeticException ie) {
System.out.println("程序发生了数组越界、数字格式异常、算术异常之一");
// 捕捉多异常时,异常变量默认有final修饰,
// 所以下面代码有错:
// ie = new ArithmeticException("test"); // ①
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("未知异常");
// 捕捉一个类型的异常时,异常变量没有final修饰
// 所以下面代码完全正确。
e = new RuntimeException("test"); // ②
}
}
}
1.4 异常输出,可以是以一段流的方式输出异常跟踪信息,也可以是以一句字符串的信息输出异常描述信息
// 1.异常输出,可以是以一段流的方式输出异常跟踪信息,也可以是以一句字符串的信息输出异常描述信息
public class AccessExceptionMsg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
// 返回异常描述信息
// a.txt (系统找不到指定的文件。)
System.out.println(ioe.getMessage());
// 异常跟踪信息
// java.io.FileNotFoundException: a.txt (系统找不到指定的文件。)
// at java.io.FileInputStream.open0(Native Method)
// at java.io.FileInputStream.open(FileInputStream.java:195)
// at java.io.FileInputStream.<init>(FileInputStream.java:138)
// at java.io.FileInputStream.<init>(FileInputStream.java:93)
// at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.AccessExceptionMsg.main(AccessExceptionMsg.java:20)
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.5 try后面的catch(除非try里边的方法已经要throw了,所以要么跟着catch要么在方法中throw出去)、finally都是可选的。即,可以try接finally或者try接catch,但不能只单独写try。
// 1.try后面的catch(除非try里边的方法已经要throw了,所以要么跟着catch要么在方法中throw出去)、finally都是可选的。即,可以try接finally或者try接catch,但不能只单独写try。
public class AccessExceptionMsg2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List list = null;
try
{
list.add(1);
}finally {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}
1.6 catch中的return仅表示该方法在此短路,最后仍继续执行finally的方法,并返回finally中的return(如果有的话)
1.7 catch只有使用System.exit(1);才不会执行finally
// 1.catch中的return仅表示该方法在此短路,最后仍继续执行finally的方法,并返回finally中的return(如果有的话)
// 2.下面的例子中,更好的表明return即表示结束,也表示结束并返回某值
public class FinallyTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = t1();
System.out.println("a:" + a);
}
public static int t1(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
boolean b = true;
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
System.out.println(ioe.getMessage());
// return语句强制方法返回
b = false;
return 1; // ①
// 使用exit来退出虚拟机
// System.exit(1); // ②
}
finally
{
// 关闭磁盘文件,回收资源
if (fis != null)
{
try
{
fis.close();
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("执行finally块里的资源回收!");
return 2;
}
// 编译失败
// System.out.println("111111");
// return 3;
}
}

1.8 异常要么处理,要么抛出给上一层调用者,若调用者依旧抛出,则直到main抛出被JVM捕获,输出异常,并中断程序
1.9 异常继承重写
1.重写方法的 两同两小一大 原则
1.1 两同:方法名相同 参数列表相同
1.2 两小:返回类型,异常 子类应比父类要小或者相同;
1.3 一大:修饰符 权限应该扩大或者相同
// 1.重写方法的 两同两小一大 原则
// 1.1 两同:方法名相同 参数列表相同
// 1.2 两小:返回类型,异常 子类应比父类要小或者相同;
// 1.3 一大:修饰符 权限应该扩大或者相同
class A{
A t1() throws Exception{
return new A();
}
}
class B extends A{
public B t1() throws IOException{
return new B();
}
}
1.10 抛出runtime异常,调用者可以不catch,但是程序一旦到达main之后就中断了
// 1.抛出check异常,调用者需要catch;抛出runtime异常,调用者可以不catch,但是程序一旦到达main之后就中断了
public class ThrowTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
// 调用声明抛出Checked异常的方法,要么显式捕获该异常
// 要么在main方法中再次声明抛出
throwChecked(-3);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
// 调用声明抛出Runtime异常的方法既可以显式捕获该异常,
// 也可不理会该异常
throwRuntime(3);
System.out.println("aa");
}
public static void throwChecked(int a)throws Exception
{
if (a > 0)
{
// 自行抛出Exception异常
// 该代码必须处于try块里,或处于带throws声明的方法中
throw new Exception("a的值大于0,不符合要求");
}
}
public static void throwRuntime(int a)
{
if (a > 0)
{
// 自行抛出RuntimeException异常,既可以显式捕获该异常
// 也可完全不理会该异常,把该异常交给该方法调用者处理
throw new RuntimeException("a的值大于0,不符合要求");
}
}
}
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: a的值大于0,不符合要求
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.ThrowTest.throwRuntime(ThrowTest.java:47)
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.ThrowTest.main(ThrowTest.java:29)
1.11 自定义异常
public class MyException extends Exception {
public MyException() {
}
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
1.12 catch and throw 企业对异常的使用 打印日志,在catch里将无法解决的异常抛出
// 1.企业打印异常的方式,将无法解决的异常抛出
public class AuctionTest {
private double initPrice = 30.0;
// 因为该方法中显式抛出了AuctionException异常,
// 所以此处需要声明抛出AuctionException异常
public void bid(String bidPrice) throws AuctionException {
double d = 0.0;
try {
d = Double.parseDouble(bidPrice);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 此处完成本方法中可以对异常执行的修复处理,
// 此处仅仅是在控制台打印异常跟踪栈信息。
e.printStackTrace();
// // 1.企业打印异常的方式,将无法解决的异常抛出
// 再次抛出自定义异常
throw new AuctionException("竞拍价必须是数值," + "不能包含其他字符!");
}finally {
System.out.println("aaa");
}
if (initPrice > d) {
throw new AuctionException("竞拍价比起拍价低," + "不允许竞拍!");
}
initPrice = d;
System.out.println("bbb");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AuctionTest at = new AuctionTest();
try {
at.bid("df");
} catch (AuctionException ae) {
// 再次捕捉到bid方法中的异常。并对该异常进行处理
System.err.println(ae.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
//aaa
//end
//java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "df"
//at sun.misc.FloatingDecimal.readJavaFormatString(FloatingDecimal.java:2043)
//at sun.misc.FloatingDecimal.parseDouble(FloatingDecimal.java:110)
//at java.lang.Double.parseDouble(Double.java:538)
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.AuctionTest.bid(AuctionTest.java:22)
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.AuctionTest.main(AuctionTest.java:42)
//竞拍价必须是数值,不能包含其他字符!
1.13 throw异常检查机制,虽然 throw的是Exception异常,但是在try中会检测实际的异常,FileInputStream的异常是FileNotFoundException,只需要抛出这个即可
// 1.throw异常检查机制,虽然 throw的是Exception异常,但是在try中会检测实际的异常,FileInputStream的异常是FileNotFoundException,只需要抛出这个即可
public class ThrowTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException
// Java 6认为①号代码可能抛出Exception,
// 所以此处声明抛出Exception
// throws Exception
// Java 7会检查①号代码可能抛出异常的实际类型,
// 因此此处只需声明抛出FileNotFoundException即可。
{
try
{
// new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("aaa.txt");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
throw ex; // ①
}
}
}
1.14 一旦发生catch,都会中断try块内的代码不让其继续往下执行,但可以继续执行try之外的代码;在catch中出现throw,则直接中断catch所在的方法不让其继续往下执行
// 1. 一旦发生catch,都会中断try块内的代码不让其继续往下执行,但可以继续执行try之外的代码;在catch中出现throw,则直接中断catch所在的方法不让其继续往下执行
public class SalException extends Exception {
public SalException() {
}
public SalException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
// 创建一个可以接受Throwable参数的构造器
public SalException(Throwable t) {
super(t);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new A().t();
} catch (TooBigException e) {
System.out.println("1");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("2");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("3");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main");
}
}
class A {
public void tt(){
}
// 一旦发生catch,都会中断try块内的代码不让其继续往下执行,但可以继续执行try之外的代码;在catch中出现throw,则直接中断catch所在的方法不让其继续往下执行
public void t() throws TooBigException, FileNotFoundException {
try {
t1(); // t2 t3 t4都没机会执行
t2();
t3();
t4();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// throw e;
} catch (TooBigException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// throw e;
}
System.out.println("aaaa");
}
public void t4(){
int [] a = {1, 2};
a[2] = 3;
}
private void t3() throws FileNotFoundException {
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("aa.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
}
}
private void t2() {
String a = null;
try {
System.out.println(a.length());
} catch (NullException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
}
}
public void t1() throws TooBigException {
int a = 10;
int b = 11;
if (b > a) {
throw new TooBigException(" b > a");
}
}
}
class FileException extends IOException{
public FileException() {
}
public FileException(String message) {
super(message);
System.err.println("file error");
}
public FileException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public FileException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
class NullException extends NullPointerException {
public NullException() {
}
public NullException(String s) {
super(s);
System.err.println("null~~~~~~~~~~");
}
}
class TooBigException extends Exception {
public TooBigException() {
}
public TooBigException(String message) {
super(message);
System.err.println("too big");
}
public TooBigException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public TooBigException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public TooBigException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
//too big
//aaaa
//main
//com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.TooBigException: b > a
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.A.t1(SalException.java:105)
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.A.t(SalException.java:60)
//at com.lee.test.java.ebook.crazy_java.u_10_exception.c_10_4_runtimeexception.SalException.main(SalException.java:35)
1.15 避免使用catch all,Throwable会捕获所有的异常,因为是顶级类,不易区分异常
catch (Throwable a){
a.printStackTrace();
}