The Design of Knowledge Test Based on MATLAB —ComprehensiveTest
Abstract: MATLAB has become powerful tool for researchers and engineers in various fields such as Mathematics, fiance and many other calculated correlation fields. Mean while, this wonderful tool is also able to bring more joy to our lives by broadening people’s horizon and simulate their interests. This little curriculum design designed a kind of simple knowledge test called ComprehensiveTest, which is based on the GUI of MATLAB, for the purpose of both learning and joy.
Keyword: knowledge test; MATLAB; GUI designer
摘要: MATLAB在许多与计算有关的领域,诸如数学和金融等,已经成为了科研工作者们和工程师们的强大工具。与此同时,这件非凡的工具还可以通过开拓人们的视野和激发他们学习的兴趣来给我们的生活带来更多的乐趣。本次课程设计旨在寓学于乐,通过MATLAB的GUI界面设计了一种名为”ComprehensiveTest”的简易知识测试问卷。
关键字: 知识测试;MATLAB; 图形用户界面设计
I Introduction
1.1 Brief Introduction of The ComprehensiveTest
The knowledge questionnaire, ComprehensiveTest, including 3 main parts is designed based on the GUI of MATLAB. The 3 main parts are filling banks, listening dialogues and reading pictures. There are 17 questions in total and the full mark is 100 points. When you get into the program, you will be welcomed. Every time you finish a question, you will be able to check you answer by clicking the ‘RightAns’ button and look up you scores by clicking the ‘ShowScore’ button. The edit box will show you your score and one dialogue box will be popped up to give you some corresponding comments. Give wrong answers and get very low scores? Don’t worry, just write right answers again and the score will be calculated again. If you really could not give the right answers, don’t worry, simply click the following ‘RightAns’ button; and not only correct answers but also analyses and tips will be given. This knowledge test examines users both in reading and listening. Not only you may need some English knowledge but also you have to have a good command of Chinese and its culture. Do you want to have a try? The panel design is showed in the below picture 1.1.
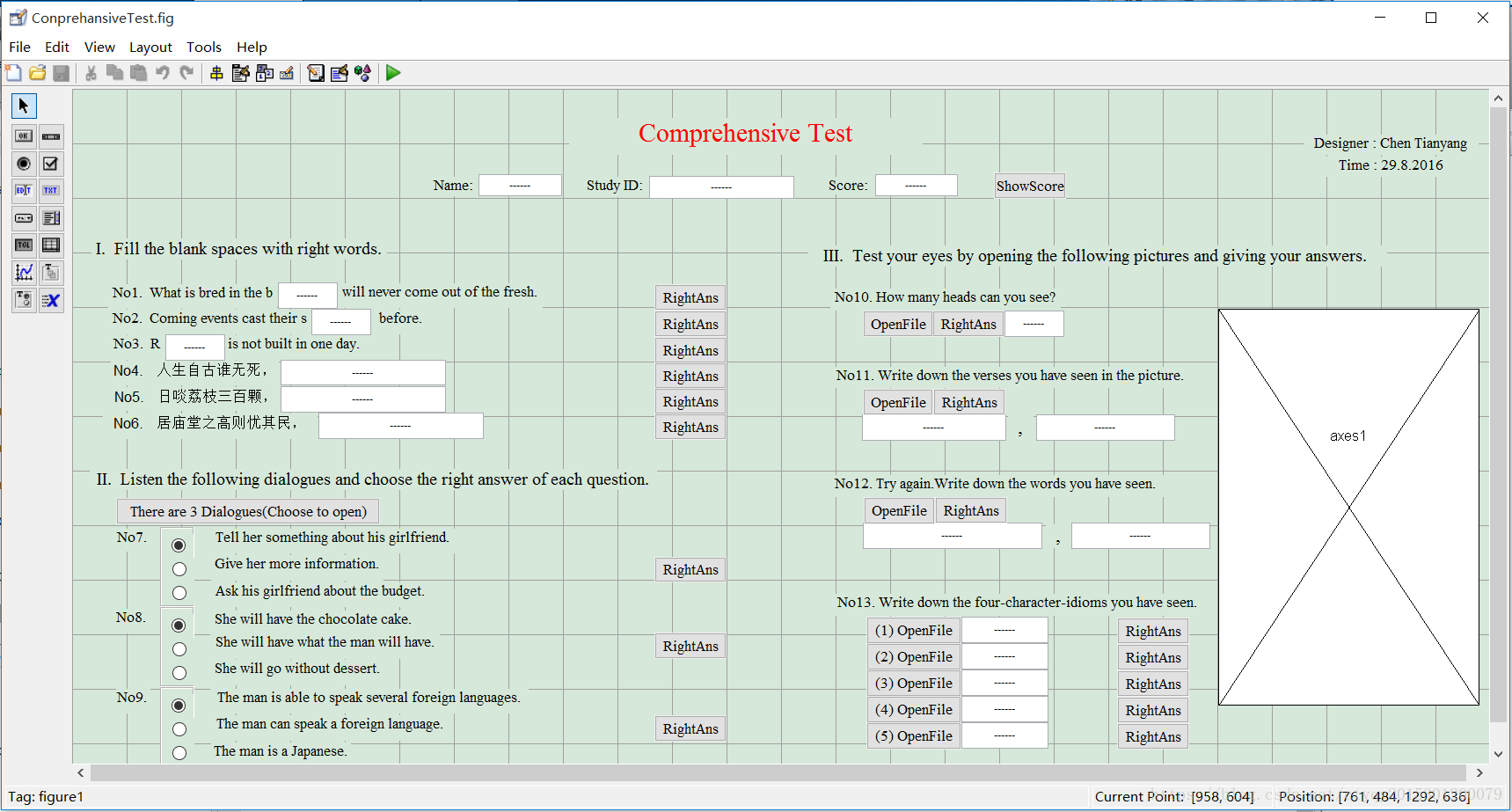
1.2 Detailed Introduction of 3 parts
1.2.1 Part1.Fill in Blanks
In this part, you will have to fill in 6 blanks, including 3 in English and 3 in Chinese. 5 points for each question. You will get 30 points if you answer all these questions correctly.
1.2.2 Prat2.Choose Correct Answers
In this part, you will have to listen 3 dialogues in English and choose one right answer out of 3. 5 points for each question. You will get 15 points if you answer all these questions correctly.
1.2.3 Part3.Read Pictures
In this part, you will have to read some pictures and give you answers. There are 8 questions and the full mark is 55 points. You must have a good command of Chinese and its culture if you want to get high scores in this part.
II Step And Result Analysis
In general, the program realized the pre-designed function. In this chapter, all the code will be analyzed by steps and modules to test the results.
2.1 The ‘Welcome’ Module
This is the first module of this program. On clicking the button ’run’, this module will do its duty, which includes show the Welcome Window and play welcome words.
2.1.1 Code Analysis
Talk is cheap, let’s see the code:
function varargout = ConprehansiveTest_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
smile1 = imread(‘smile1.jpg’);
%the response after the existing of the GUI Window
s = ‘Welcome To This Comprehensive Test!’;
hs = msgbox(s,‘Welcome!’,‘custom’,smile1);
ht = findobj(hs, ‘Type’, ‘text’); %change the size of words
set(ht, ‘FontSize’, 12, ‘Unit’, ‘normal’,‘FontName’,‘Times New Roman’);
%position [a b c d]determine the position of the msgbox, [a b] represent the coordinate of the point
% in the lower left quarter,c and d respectively express the width and height of the msgbox.
%It will show the former msgbox,setting proper coordinate will make the latter msgbox cover the former one.
set(hs,‘Position’,[480 380 280 80]);
fn = uigetfile(‘Welcome.wav’,‘Open File’);
[y,fs] = audioread(fn);
sound(y,fs);
varargout{1} = handles.output;
Firstly, the use of function ‘msgbox’ and ‘findobj’ is critical to change the size of words in the dialog box. Secondly, The function “set” is to change the size of the dialog box itself; ‘hs’ is the handle of the message box ’msgbox’. The 4 parameters decide the position and size of the dialog box. Finally, the welcome words will be heard.
2.1.2 Phenomenon Analysis
Firstly, after clicking the ‘run’ button, you will see a panel as picture 2.4 shows.
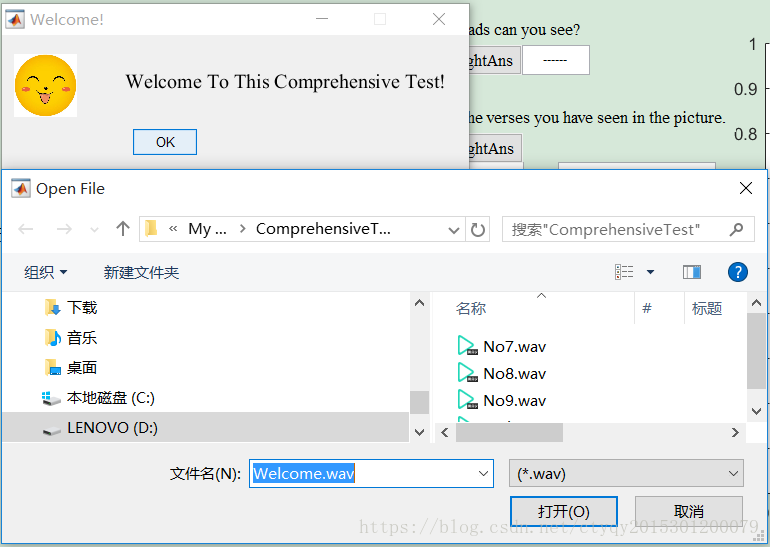
Then, you could click the button ”打开” and will hear the welcome words. Then, you click the button ‘OK’ and go into this program.
2.2 The Score Calculate Module
Every time you give an answer, The program will compare it with the right answer and decide whether you can get the points or how many you can get. This is the score calculate module. Every blank and radio have some codes to finish this important function. Here let’s analyze it.
2.2.1 Code Analysis
Let’s use the first question as a model.Here is the code:
function edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
global Score1
YourAns = get(handles.edit4,‘String’);
RightAns = ‘one’;
if strcmp(YourAns,RightAns) == 1
Score1 = 5;
else
Score1 = 0;
end
Score1 is one of the global variables, the value of it will be 0 or 5, lying on the user’s answer. This section of code will first get your answer that has been written down in the blank by the function ‘get’, and then compare it with the right answer ‘one’, which has been decided previously by the function ‘strcmp’, if they are same(the return number of function ‘strcmp’ is 1), the value of variable Score1 will be 5, otherwise it is 0. There is a variable called Score that represent the whole scores you have got. Actually, Score is the sum of all ScoreX, representing the score of each question. To realize it, we have to set lots of global variables to mark each question and sum them up in the end. The initial value of all ScoreX is 0.
Here is the code that set global variables:
function ConprehansiveTest_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
global Score Score1 Score2 Score3 Score4 Score5 Score6 Score7 Score8 Score9
global Score10 Score11 Score12 Score13 Score14 Score15 Score16 Score17 Score18 Score19
Score = 0;Score1 = 0;Score2 = 0;Score3 = 0;Score4 = 0;Score5 = 0;Score6 = 0;
Score7 = 0;Score8 = 0;Score9 = 0;Score10 = 0;Score11 = 0;Score12 = 0;Score13 = 0;
Score14 = 0;Score15 = 0;Score16 = 0;Score17 = 0;Score18 = 0;Score19 = 0;
The section of code above must be written in the function ‘ComprehensiveTest’ in order to initialize them.
Here is the code that sum ScoreX up:
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
global Score Score1 Score2 Score3 Score4 Score5 Score6 Score7 Score8 Score9 Score10 Score11 Score12 Score13 Score14 Score15 Score16 Score17 Score18 Score19
Score = Score1+Score2+Score3+Score4+Score5+Score6+Score7+Score8+Score9+…
Score10+Score11+Score12+Score13+Score14+Score15+Score16+Score17+Score18+Score19;
set(handles.edit3,‘String’,num2str(Score));
2.2.2 Phenomenon Analysis
Here is the phenomenon, you will see what the following picture shows:




Obviously, the score is dynamic and can be changed any time after clicking button ‘RightAns’.
2.3 Command Module
The program will give you different remarks depending on the final score you get. If you get a full mark, you well get an ‘Excellent’; and if your score is lower than 60, you will get a ‘Fail’. This is completed by dialogue boxes.
2.3.1 Code Analysis
The relevant code is:
Excellent = imread(‘Excellent.JPG’);
Good = imread(‘Good.JPG’);
JustSoSo = imread(‘JustSoSo.JPG’);
Pass = imread(‘Pass.jpg’);
Fail = imread(‘Fail.JPG’);
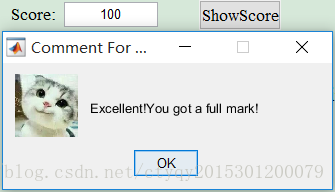
if Score == 100
msgbox(‘Excellent!You got a full mark!’,‘Comment For You:’,‘Custom’,Excellent);
elseif (Score >= 80 && Score < 100)
msgbox(‘Good!’,‘Comment For You:’,‘Custom’,Good);
elseif (Score >= 70 && Score < 80)
msgbox(‘JustSoSo!’,‘Comment For You:’,‘Custom’,JustSoSo);
elseif (Score >= 60 && Score < 70)
msgbox(‘Pass!’,‘Comment For You:’,‘Custom’,Pass);
elseif Score < 60
msgbox(‘Fail!You did not pass the test!’,‘Comment For You:’,‘Custom’,Fail);
end
It’s easy to understand the meaning of the section of the code above. This is just a combination of if-sentence and message boxes. What is special is that this message dialogue has its unique expressions, lively and amusingly.
2.3.2 Phenomenon Analysis
After you click button ‘ShowScore’, the popped message boxes will be different. What you will see are picture 2.4 to 2.8.
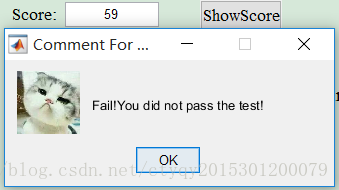 Pic2.4 Fail
Pic2.4 Fail
|
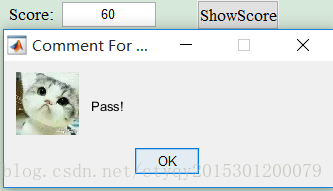 Pic2.5 Pass
Pic2.5 Pass
|
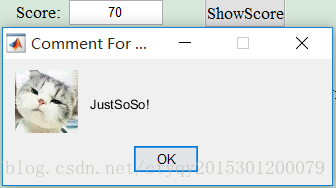 Pic2.6 JustSoSo
Pic2.6 JustSoSo
|
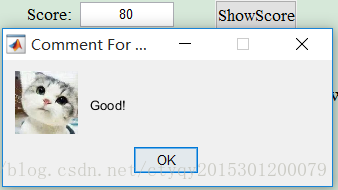 Pic2.7 Good
Pic2.7 Good
|
|
III Summary
3.1 Experiences
1. The necessity of edit_callback functions.
Some functions, like the callback of the edit boxes on the above of the interface to be filled with users’ names and student IDs, has their meaning to be. As long as you need to click them, even if no callback function is needed, they cannot be deleted. Otherwise the compile system of MATLAB will come into errors.
2. The usage of dialog boxes.
There are many kinds of dialog boxes in MATLAB, we can use different ones by changing a few words in some certain functions. What’s more, some extra elements can be added to them, like pictures and so on.
3.2 Hopes
1. Pop up ‘*TXT’ files.
In the second part, the program will pop up a TXT file inside MATLAB. This is not satisfactory enough because the popped file will cover the former interface. Can it be realized that one TXT file could be popped up outside the frame of MATLAB? This is worth learning and trying in the future.
2. Add music into message boxes.
In this program, music(sound) cannot be played without opening the Open-Interface, but this is cockamamie. Can it be realized that a piece of music could be played right after clicking? This is worth learning and trying in the future.
IV Additional Words
Here is the link of the codes of this project and the passwords is 866r. If you are interested in it, please feel free to download them immediately. What’s more, if you find something wrong or have better ideas or improvements, please contact me as soon as possible and I will be appreciate for your contribution.
REFERENCES
[1]. Matlab-GUI-fundation of programming.pdf.
[2]. http://www.ilovematlab.cn/matlab_jishuwenzhang_technical_articles/
[3]. http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4d633dc70100nvbo.html