版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/Anbang713/article/details/82890090
一、简介
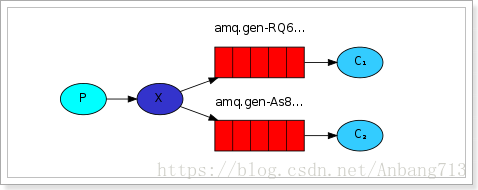
学习完《RabbitMQ-简单队列》和《RabbitMQ-Work模式》,今天我们一起学习订阅模式。如下图所示:
解读:
1、1个生产者,多个消费者。
2、每一个消费者都有自己的一个队列。
3、生产者没有将消息直接发送到队列,而是发送到了交换机(x)。
4、每个队列都要绑定到交换机。
5、生产者发送的消息,经过交换机到达队列,实现一个消息被多个消费者获取的目的。
二、编码实现
2.1、生产者
向交换机发送消息。(注意:消息发送到没有队列绑定的交换机时,消息将丢失,因为交换机没有存储消息的能力,消息只能存在在队列中。)
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明exchange
channel.exchangeDeclare(QueueUtil.EXCHANGE_NAME_FANOUT, "fanout");
// 消息内容
String message = "Hello World!";
channel.basicPublish(QueueUtil.EXCHANGE_NAME_FANOUT, "", null, message.getBytes());
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}2.2、消费者1
public class Receiver1 {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QueueUtil.QUEUE_NAME_FANOUT1, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QueueUtil.QUEUE_NAME_FANOUT1, QueueUtil.EXCHANGE_NAME_FANOUT, "");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QueueUtil.QUEUE_NAME_FANOUT1, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println("Receiver1 Received:" + message);
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}2.3、消费者2
public class Receiver2 {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QueueUtil.QUEUE_NAME_FANOUT2, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QueueUtil.QUEUE_NAME_FANOUT2, QueueUtil.EXCHANGE_NAME_FANOUT, "");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QueueUtil.QUEUE_NAME_FANOUT2, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println("Receiver2 Received:" + message);
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}三、测试
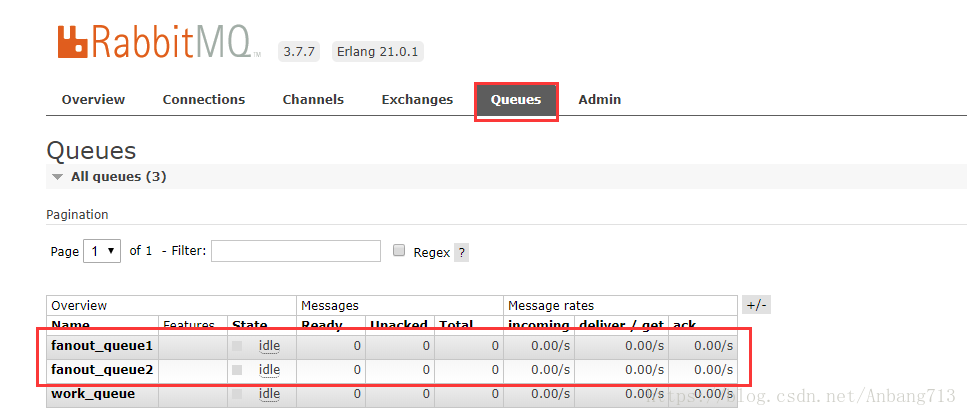
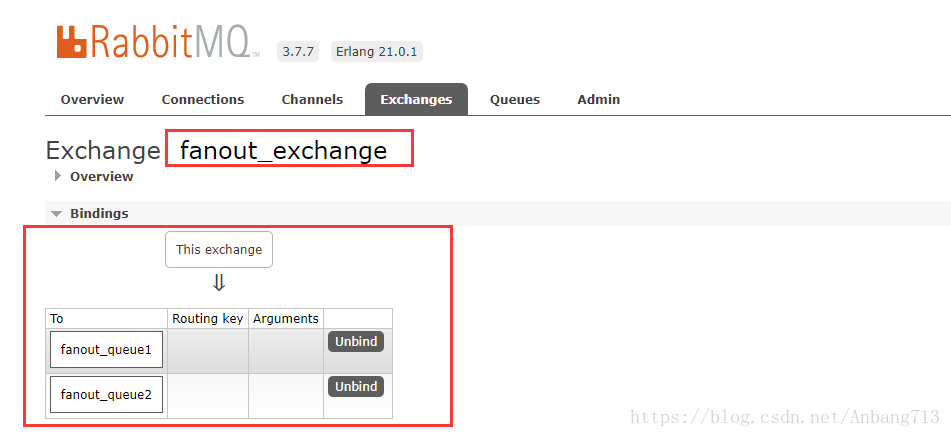
启动消费者1和消费者2,我们在管理工具中查看队列和交换机的绑定关系: