Once Petya read a problem about a bracket sequence. He gave it much thought but didn't find a solution. Today you will face it.
You are given string s. It represents a correct bracket sequence. A correct bracket sequence is the sequence of opening ("(") and closing (")") brackets, such that it is possible to obtain a correct mathematical expression from it, inserting numbers and operators between the brackets. For example, such sequences as "(())()" and "()" are correct bracket sequences and such sequences as ")()" and "(()" are not.
In a correct bracket sequence each bracket corresponds to the matching bracket (an opening bracket corresponds to the matching closing bracket and vice versa). For example, in a bracket sequence shown of the figure below, the third bracket corresponds to the matching sixth one and the fifth bracket corresponds to the fourth one.
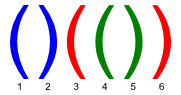
You are allowed to color some brackets in the bracket sequence so as all three conditions are fulfilled:
- Each bracket is either not colored any color, or is colored red, or is colored blue.
- For any pair of matching brackets exactly one of them is colored. In other words, for any bracket the following is true: either it or the matching bracket that corresponds to it is colored.
- No two neighboring colored brackets have the same color.
Find the number of different ways to color the bracket sequence. The ways should meet the above-given conditions. Two ways of coloring are considered different if they differ in the color of at least one bracket. As the result can be quite large, print it modulo1000000007 (109 + 7).
The first line contains the single string s (2 ≤ |s| ≤ 700) which represents a correct bracket sequence.
Print the only number — the number of ways to color the bracket sequence that meet the above given conditions modulo 1000000007(109 + 7).
(())
12
(()())
40
()
4
题目大意:
给一个给定合法的括号序列,给该序列每个括号上色,上色有三个要求
1、只有三种上色方案,不上色,上红色,上蓝色
2、每对匹配的括号必须只能给其中的一个上色
3、相邻的两个不能上同色,可以都不上色
分析:
区间dp,假设不上色为0,上红色为1,上蓝色为2,我们可以设置状态:
dp[cl][cr][l][r]:在l-1处染cl颜色,在r+1处染cr颜色,那么区间[l,r]的染色情况数。
既然是区间dp,就应该找能够分割区间的依据,那么就是对于区间[l,r],找到位置l处的'('所以对应的')'的位置match[l],设为R,那么就可以递归求解[l+1,R-1]和[R+1,r],然后递归的时候分别对两个区间的两边的颜色cl、cr讨论一下就好了,因为题目的限制条件多,所以这里的情况反而不多了。
用栈预处理出match数组即可。
/****************
*PID:149d div2
*Auth:Jonariguez
*****************
dp[cl][cr][l][r]:在l-1处染cl颜色,在r+1处染cr颜色,那么区间[l,r]的染色情况数
cl={0,1,2}
答案为dp[0][0][1][n]
记忆化搜索
*/
#define lson k*2,l,m
#define rson k*2+1,m+1,r
#define rep(i,s,e) for(i=(s);i<=(e);i++)
#define For(j,s,e) For(j=(s);j<(e);j++)
#define sc(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define In(x) scanf("%I64d",&x)
#define pf(x) printf("%d",x)
#define pfn(x) printf("%d\n",(x))
#define Pf(x) printf("%I64d",(x))
#define Pfn(x) printf("%I64d\n",(x))
#define Pc printf(" ")
#define PY puts("YES")
#define PN puts("NO")
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef int Ll;
Ll quick_pow(Ll a,Ll b,Ll MOD){a%=MOD;Ll res=1;while(b){if(b&1)res=(res*a)%MOD;b/=2;a=(a*a)%MOD;}return res;}
const int maxn=700+10;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
LL dp[3][3][maxn][maxn];
char str[maxn];
int match[maxn];
LL DP(int cl,int cr,int l,int r){
if(l==r+1 && cl==cr && cl!=0) return 0;
if(l>=r) return 1;
if(dp[cl][cr][l][r]>=0) return dp[cl][cr][l][r];
LL &ans=dp[cl][cr][l][r];
ans=0;
int R=match[l];
if(cl){
ans=(ans+DP(3-cl,0,l+1,R-1)*DP(0,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
ans=(ans+DP(0,1,l+1,R-1)*DP(1,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
ans=(ans+DP(0,2,l+1,R-1)*DP(2,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
}else {
ans=(ans+DP(1,0,l+1,R-1)*DP(0,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
ans=(ans+DP(2,0,l+1,R-1)*DP(0,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
ans=(ans+DP(0,1,l+1,R-1)*DP(1,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
ans=(ans+DP(0,2,l+1,R-1)*DP(2,cr,R+1,r)%MOD)%MOD;
}
// printf("cl=%d cr=%d l=%d r=%d ans=%d\n",cl,cr,l,r,ans);
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
while(scanf("%s",str+1)!=EOF){
n=strlen(str+1);
for(i=0;i<=n;i++) match[i]=n+2; //即无穷大
stack<int> s;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(str[i]=='(')
s.push(i);
else {
match[s.top()]=i;
s.pop();
}
}
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
printf("%I64d\n",DP(0,0,1,n));
}
return 0;
}