版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33706673/article/details/84799852
1.strlen()函数
功能:函数返回字符串str 的长度( 即空值结束符之前字符数目,不包括控制结束符)。
语法:
#include <string.h>
size_t strlen( char *str );
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char *str1 = "hello world\n";
char *str2 = "你好 中国!\n";
printf("str1 len=%u,str2 len=%u\n",strlen(str1),strlen(str2));
return 0;
}
结果:
![]()
注意:
1.strlen返回是size_t类型,即unsigned int,在头文件stddef.h中定义
2.中文字符长度为三个字节
2.不受限的字符串函数strcpy(),strcat(),strcmp();
2.1 strcpy()
功能:复制字符串src 中的字符到字符串dest,包括空值结束符。返回值为指针dest
语法:
#include <string.h>
char *strcpy( char *to, const char *from );
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char str1[40] = "hello world,hello china";
char *str2 = "你好 中国!";
strcpy(str1,str2);
printf("str1=%s,str2=%s\n",str1,str2);
return 0;
}
结果:
![]()
注意:
1.使用strcpy函数时因为没有长度限制,一定要确保str1的内存长度大于或者等于str2
2.如果st1里面有字符会被覆盖str2内容的长度,包括字符串结束符。
2.2strcat()
功能:函数将字符串str2 连接到str1的末端,并返回指针str1
语法:
#include <string.h>
char *strcat( char *str1, const char *str2 );
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char str1[40] = "hello world,hello china";
char *str2 = "你好 中国!";
strcat(str1,str2);
printf("str1=%s,str2=%s\n",str1,str2);
return 0;
}
![]()
2.3 strcmp();
功能:比较字符串str1 and str2, 返回值如下:
| 返回值 |
解释 |
| less than 0(小于0) |
str1 is less than str2 |
| equal to 0(等于0) |
str1 is equal to str2 |
| greater than 0(大于0) |
str1 is greater than str2 |
语法:
#include <string.h>
int strcmp( const char *str1, const char *str2 );
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char str1[40] = "hello world,hello china";
char *str2 = "你好 中国!";
printf("strcmp result=%d\n",strcmp(str1,str2));
return 0;
}
![]()
3.长度受限的字符串函数 strncpy(),strncat(),strncmp();
因为这三个函数与上面的函数功能一样,只是多了一个长度的控制,其他的都是一样的,所以这里不在分开说明:
语法:
char *strncpy( char *to, const char *from, size_t count );
char *strncat( char *str1, const char *str2, size_t count );
int strncmp( const char *str1, const char *str2, size_t count );
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
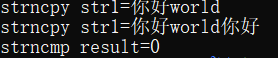
{
char str1[40] = "hello world";
char *str2 = "你好 中国!";
strncpy(str1,str2,6);
printf("strncpy str1=%s\n",str1);
strncat(str1,str2,6);
printf("strncpy str1=%s\n",str1);
printf("strncmp result=%d\n",strncmp(str1,str2,6));
return 0;
}