尊重原创,转载请标明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/abcdef314159
在之前讲到Android Paint的使用详解的时候,其中setColorFilter(ColorFilter filter)方法没有讲,今天就来简单的分析一下,在Android中ColorFilter共有3个子类,ColorMatrixColorFilter,LightingColorFilter,PorterDuffColorFilter,今天先来看第一个ColorMatrixColorFilter,ColorMatrixColorFilter的构造方法很简单,一个是传入数组,一个是传入ColorMatrix类型的对象
public ColorMatrixColorFilter(ColorMatrix matrix) {
mMatrix.set(matrix);
update();
} public ColorMatrixColorFilter(float[] array) {
if (array.length < 20) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
mMatrix.set(array);
update();
} * [ a, b, c, d, e,
* f, g, h, i, j,
* k, l, m, n, o,
* p, q, r, s, t ]而图像的ARGB值存储在一个5*1的颜色分量矩阵中[R, G, B, A,1]。最终运算的结果是两矩阵相乘
R = a*R + b*G + c*B + d*A + e;
G = f*R + g*G + h*B + i*A + j;
B = k*R + l*G + m*B + n*A + o;
A = p*R + q*G + r*B + s*A + t; private final float[] mArray = new float[20]; /**
* Set this colormatrix to identity:
* <pre>
* [ 1 0 0 0 0 - red vector
* 0 1 0 0 0 - green vector
* 0 0 1 0 0 - blue vector
* 0 0 0 1 0 ] - alpha vector
* </pre>
*/
public void reset() {
final float[] a = mArray;
Arrays.fill(a, 0);
a[0] = a[6] = a[12] = a[18] = 1;
}[ 1 0 0 0 8
0 1 0 0 8
0 0 1 0 8
0 0 0 1 0 ]
表示个颜色分量计算完成之后要在加上8,其中最后一行是表示透明度的,一般不要修改。我们来演示一下
public class ColorFilterView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private int padding = 12;
float[] colorMatrix = {
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, //red
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, //green
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, //blue
0, 0, 0, 1, 0 //alpha
};
private ColorMatrixColorFilter mLightingColorFilter= new ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix);
public ColorFilterView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
mPaint.setColorFilter(mLightingColorFilter);
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap,
(i % 4) * (mBitmap.getWidth() + padding), (i / 4)
* (mBitmap.getHeight() + padding), mPaint);
}
}
}再来修改一下
float[] colorMatrix = {
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, //red
0, 1, 0, 0, 0, //green
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, //blue
0, 0, 0, 1, 0 //alpha
};最后在修改一下,让他还原正常图片
float[] colorMatrix = {
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, //red
0, 1, 0, 0, 0, //green
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, //blue
0, 0, 0, 1, 0 //alpha
};OK,上面的演示完了,我们看下面的一个矩阵。
[ 1 0 0 0 8
0 2 0 0 8
0 0 3 0 8
0 0 0 1 0 ] public void setScale(float rScale, float gScale, float bScale,
float aScale) {
final float[] a = mArray;
for (int i = 19; i > 0; --i) {
a[i] = 0;
}
a[0] = rScale;
a[6] = gScale;
a[12] = bScale;
a[18] = aScale;
}public class ColorFilterView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private ColorMatrix colorMatrix = new ColorMatrix();
private ColorMatrixColorFilter matrixColorFilter[] = new ColorMatrixColorFilter[24];
private int padding = 12;
public ColorFilterView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon);
for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
if (i < 8)
colorMatrix.setScale(i * .1f, i * .1f, i * .1f, i * .1f);
else if (i < 16)
colorMatrix.setScale(i * .1f, i * .1f, i * .1f, i * .1f);
else
colorMatrix.setScale(i * .1f, i * .1f, i * .1f, i * .1f);
matrixColorFilter[i] = new ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
mPaint.setColorFilter(matrixColorFilter[i]);
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap,
(i % 4) * (mBitmap.getWidth() + padding), (i / 4)
* (mBitmap.getHeight() + padding), mPaint);
}
}
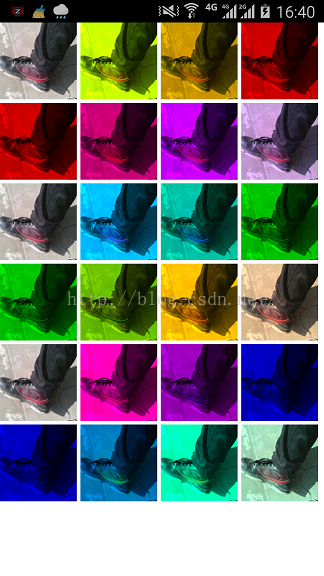
}我们看一下运行结果
再来修改一下
for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
if (i < 8)
colorMatrix.setScale(i * .1f, i * .3f, i * .9f, i * .1f);
else if (i < 16)
colorMatrix.setScale(i * .1f, i * .3f, i * .9f, i * .1f);
else
colorMatrix.setScale(i * .1f, i * .3f, i * .9f, i * .1f);
matrixColorFilter[i] = new ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix);
}再看另一个方法setRotate(int axis, float degrees),表示的是色相
/**
* Set the rotation on a color axis by the specified values.
* <p>
* <code>axis=0</code> correspond to a rotation around the RED color
* <code>axis=1</code> correspond to a rotation around the GREEN color
* <code>axis=2</code> correspond to a rotation around the BLUE color
* </p>
*/
public void setRotate(int axis, float degrees) {
reset();
double radians = degrees * Math.PI / 180d;
float cosine = (float) Math.cos(radians);
float sine = (float) Math.sin(radians);
switch (axis) {
// Rotation around the red color
case 0:
mArray[6] = mArray[12] = cosine;
mArray[7] = sine;
mArray[11] = -sine;
break;
// Rotation around the green color
case 1:
mArray[0] = mArray[12] = cosine;
mArray[2] = -sine;
mArray[10] = sine;
break;
// Rotation around the blue color
case 2:
mArray[0] = mArray[6] = cosine;
mArray[1] = sine;
mArray[5] = -sine;
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException();
}
} for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
if (i < 8)
colorMatrix.setRotate(0, i*50);
else if (i < 16)
colorMatrix.setRotate(1, i*50);
else
colorMatrix.setRotate(2, i*50);
matrixColorFilter[i] = new ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix);
}再来修改一下
for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
if (i < 8)
colorMatrix.setRotate(0, i*50);
else if (i < 16)
colorMatrix.setRotate(1, (i%8)*50);
else
colorMatrix.setRotate(2, (i%8)*50);
matrixColorFilter[i] = new ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix);
}看一下运行结果
再看另一个方法setSaturation(float sat),代表的是饱和度,其中0是灰色,1是正常
for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
if (i < 8)
colorMatrix.setSaturation(i*.2f);
else if (i < 16)
colorMatrix.setSaturation(i*.5f);
else
colorMatrix.setSaturation(i*2f);
matrixColorFilter[i] = new ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix);
}setConcat(ColorMatrix matA, ColorMatrix matB),两矩阵相乘
public void setConcat(ColorMatrix matA, ColorMatrix matB) {
float[] tmp;
if (matA == this || matB == this) {
tmp = new float[20];
} else {
tmp = mArray;
}
final float[] a = matA.mArray;
final float[] b = matB.mArray;
int index = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j += 5) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
tmp[index++] = a[j + 0] * b[i + 0] + a[j + 1] * b[i + 5] +
a[j + 2] * b[i + 10] + a[j + 3] * b[i + 15];
}
tmp[index++] = a[j + 0] * b[4] + a[j + 1] * b[9] +
a[j + 2] * b[14] + a[j + 3] * b[19] +
a[j + 4];
}
if (tmp != mArray) {
System.arraycopy(tmp, 0, mArray, 0, 20);
}
}再来看ColorFilter的另一个子类LightingColorFilter光线颜色过滤,就一个构造方法
public LightingColorFilter(int mul, int add) {
mMul = mul;
mAdd = add;
update();
}public class ColorFilterView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private LightingColorFilter mLightingColorFilter[] = new LightingColorFilter[8];
private int padding = 12;
public ColorFilterView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon);
//不变
mLightingColorFilter[0] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFFFFFFFF,
0x00000000);
//去掉红色
mLightingColorFilter[1] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFF00FFFF,
0x00000000);
//去掉绿色
mLightingColorFilter[3] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFFFF00FF,
0x00000000);
//去掉蓝色
mLightingColorFilter[4] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFFFFFF00,
0x00000000);
//增加红色
mLightingColorFilter[5] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFFFFFFFF,
0x00560000);
//增加绿色
mLightingColorFilter[6] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFFFFFFFF,
0x00006400);
//增加蓝色
mLightingColorFilter[7] = new LightingColorFilter(0xFFFFFFFF,
0x00000056);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
mPaint.setColorFilter(mLightingColorFilter[i]);
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap,
(i % 4) * (mBitmap.getWidth() + padding), (i / 4)
* (mBitmap.getHeight() + padding), mPaint);
}
}
}
再来看ColorFilter的最后一个子类PorterDuffColorFilter,他也是只有一个构造方法
/**
* Create a color filter that uses the specified color and Porter-Duff mode.
*
* @param color The ARGB source color used with the specified Porter-Duff mode
* @param mode The porter-duff mode that is applied
*
* @see Color
* @see #setColor(int)
* @see #setMode(android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode)
*/
public PorterDuffColorFilter(@ColorInt int color, @NonNull PorterDuff.Mode mode) {
mColor = color;
mMode = mode;
update();
}public class ColorFilterView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private int length = PorterDuff.Mode.values().length;
private PorterDuffColorFilter mLightingColorFilter[] = new PorterDuffColorFilter[length];
private int padding = 12;
public ColorFilterView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon);
int i = 0;
for (PorterDuff.Mode e : PorterDuff.Mode.values())
mLightingColorFilter[i++] = new PorterDuffColorFilter(Color.YELLOW,
e);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
mPaint.setColorFilter(mLightingColorFilter[i]);
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap,
(i % 4) * (mBitmap.getWidth() + padding), (i / 4)
* (mBitmap.getHeight() + padding), mPaint);
}
}
}
其中Mode是之前在讲到 Android Paint的使用详解的时候讲到的18种混合模式,OK,到此为止,已经分析完毕。