异步编程
实例一:同步编程VS异步线程
分别用同步和异步方式计算一个数的平方。为了显示效果定义两个方法,其中一个方法延迟执行
编码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AsyncDemo
{
public partial class FrmMain : Form
{
public FrmMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 同步执行按钮
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnClick1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.lblCount1.Text = this.ExerTask1(10).ToString();
this.lblCount2.Text = this.ExerTask2(10).ToString();
}
//[2]根据委托定义方法
private int ExerTask1(int num)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(5000);//延迟5秒执行
return num * num;
}
private int ExerTask2(int num)
{
return num * num;
}
private void FrmMain_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 异步执行
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnClick2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//[3]异步调用
CalculateDelegate objCalculateDelegate = ExerTask1;//创建委托对象并指向第一个方法
IAsyncResult result = objCalculateDelegate.BeginInvoke(10, null, null);//异步调用任务
//委托类型的BeginInvoke(<输入和输出变量>(委托方法中的参数),AsyncCallback callback,object asyncState)方法:异步调用的核心
//第一个参数10,表示委托对应的实参
//第二个参数callback:回调函数,表示异步调用后自动调用的函数
//第三个参数asyncState:用于向回调函数提供参数信息
//返回值:IAsyncResult 异步操作状态接口,封装了异步执行中的参数
this.lblCount1.Text = "正在计算,请稍等...";
//同时执行另一个方法
this.lblCount2.Text = this.ExerTask2(10).ToString();
//获取异步执行结果
int res = objCalculateDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
//委托类型的EndInvok()方法:借助于IAsync接口对象,不断的查询异步调用是否结束
//该方法知道异步调用的方法所有参数,所以,异步调用完毕后,取出异步调用的结果作为返回值
this.lblCount1.Text = res.ToString();
}
}
//[1]声明委托
public delegate int CalculateDelegate(int num);
}
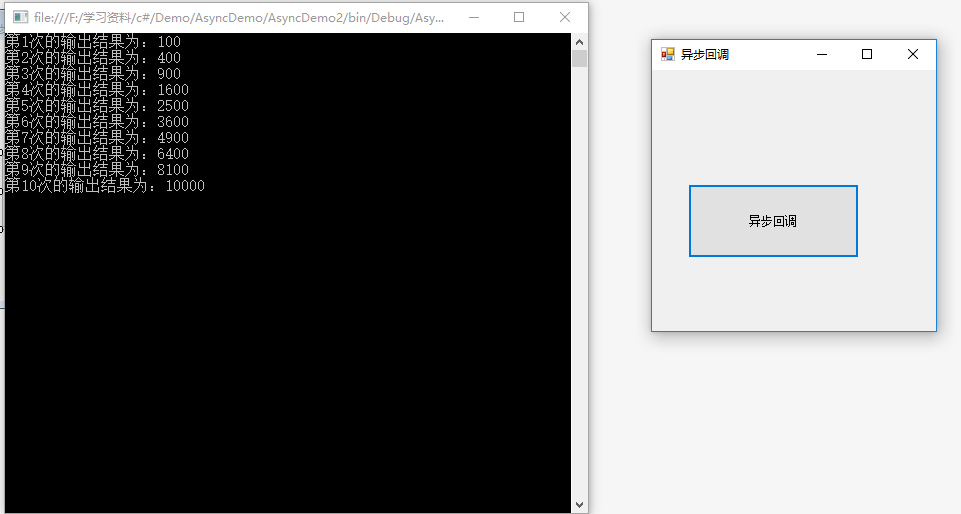
实例二:演示异步回调函数的应用,控制台延迟显示数字平方计算值10次
执行结果:
编码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AsyncDemo2
{
/// <summary>
/// 演示异步回调函数的应用,控制台延迟显示数字平方计算值10次
/// </summary>
public partial class FrmMain : Form
{
public FrmMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
//[3]初始化委托变量
this.objCal = new CalculateDelegate(Calculate);
}
//[2]根据委托定义方法
private int Calculate(int num,int ms)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(ms);
return num * num;
}
//[3]创建委托对象
CalculateDelegate objCal = null;
/// <summary>
/// 异步调用回调函数 同时执行多个任务
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnAsyncCallback_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//[4]异步调用
for(int i = 1; i < 11; i++)
{
//开始异步执行,并封装回调函数
objCal.BeginInvoke(10 * i, 1000 * i, CalCallback, i);
//最后一个参数i给回调函数的字段AsyncState赋值,这个字段是object类型
}
}
//[5]编写回调函数
private void CalCallback(IAsyncResult result)
{
int res = objCal.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("第{0}次的输出结果为:{1}", result.AsyncState.ToString(), res.ToString());
}
}
//[1]声明委托
public delegate int CalculateDelegate(int num, int ms);
}
异步编程总结:
1.异步编程是建立在委托基础之上的编程方法。
2.异步调用的每个方法都是在独立的线程中执行的。因此,本质上就是一种多线程程序,也可以说是一种简化的多线程技术
3.比较适合在后台运行较为耗费时间的《简单任务》,并且要求任务之间是独立的,任务中不要有直接访问可视化控件的内容
4.如果后台任务必须按照特定顺序执行,或者访问特定的共享资源,异步编程不太适合,而应该选择多线程开发技术
多线程
实例三:在控制台同时显示两个线程的输出内容
运行结果:
代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace TheadTest
{
/*
*进程:一个正在运行的程序就是一个进程,操作系统根据进程分配各种资源(内存...)
*线程:操作系统为了提高效率会将一个进程分为多个线程,并按照线程来分配CPU执行时间
*线程特点:在具有多个CPU的计算机中,可以并行执行。1CPU 12线程 轮循假多线程
*Thread类:表示托管线程,每个Thead对象都代表一个托管线程,每个托管线程都对应一个函数。
*ProcessThread类型:和操作系统本地线程一致
*TheadStart()方法定义:public delegate void ThreadStart();
*/
public partial class FrmThead : Form
{
public FrmThead()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//任务一:循环输出一个结果
private void btnThead1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread objThread1 = new Thread(delegate ()
{
int a = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine((a+i)+" ");
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
});//匿名方法定义委托方法
objThread1.IsBackground = true;//定义为后台线程
objThread1.Start();
}
//任务二
private void btnThead2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread objThread2 = new Thread(()=>
{
int a = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("-----------a"+i+"------------");
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
});//Lamada定义委托方法
objThread2.IsBackground = true;//定义为后台线程
objThread2.Start();
}
}
}
实例四:跨线程可视化控件。两个线程的控件不能直接访问需要借助Invoke()方法
代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CrossThreadVistControl
{
public partial class FrmCrossThreadVist : Form
{
public FrmCrossThreadVist()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnThread1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread objthread1 = new Thread(() =>
{
int a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
a += i;
if (this.lblCount1.InvokeRequired)//判断是否调用Invoke方法
{
//Invoke()方法第一个参数是返回值为void的委托,第二个参数是委托对应方法传递参数
//Action是有一个参数但是没有返回值的委托集合变量
this.lblCount1.Invoke(new Action<string>(s => { this.lblCount1.Text = s; }), a.ToString());
}
Thread.Sleep(200);
}
});
objthread1.IsBackground = true;
objthread1.Start();
}
private void btnThread2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread objthread2 = new Thread(() =>
{
int a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
a += i;
if (this.lblCount2.InvokeRequired)//判断是否调用Invoke方法
{
this.lblCount2.Invoke(new Action<string>(s => { this.lblCount2.Text = s; }), a.ToString());
}
Thread.Sleep(200);
}
});
objthread2.IsBackground = true;
objthread2.Start();
}
}
}