摘要:
- 怎样建立datapath?需要哪些elements?如何连接这些elements?
- 怎样控制datapath?8bits的control linel包含了哪些signals?
- pipeline!
- 其他提高性能的方法,如并行、循环展开。
4.7-4.9、4.11待看。
内容:
elements盘点——
1.Instruction memory——a memory unit to store the instructions of a program and supply instructions given an address.
2.PC(Program Counter)——a register that holds the address of the current instruction.
3. An adder to increment the PC to the address of the next instruction.
以上三个elements组成了instruction fetch的datapath。
4.Register file——A register file is a collection of registers in which any register can be read or written by specifying the number of the register in the file.
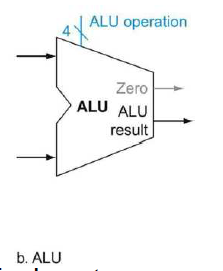
5.ALU
6.Data memory unit——A state element with inputs for the address and the write data, and a single output for the read result.
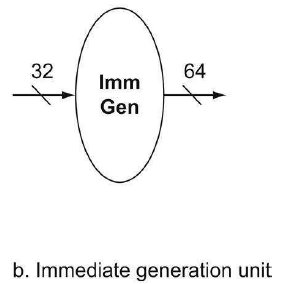
7.Immediate generation unit——sign-extend the 12-bit offset field in the instruction to a 64-bit signed value.
8.Control unit——2bits ALUOp、RegWrite、ALUSrc、PCSrc、MemRead、MemWrite和MemtoReg。
以上8个elements组成一个麻雀虽小五脏俱全的datapath——
一图说明pipeline如何起作用:
Pipeline Hazards: structural hazard, data hazard and control hazard.
Figure 4.17 之 single-cycle——
Figure 4.31 之 pipeline version——
在pipeline中加入control之后——
4.10讲instruction-level parallelism (ILP)的技巧,还建议去看Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach,这部分看得似懂非懂还有待琢磨。循环展开的技巧在CSAPP Chap.5中刚看过。
4.12用了循环展开去优化Matrix Multiply程序。