版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/java_collect/article/details/85221643
有这样一个需求,在一张图片上画几条线并保存,如图所示:
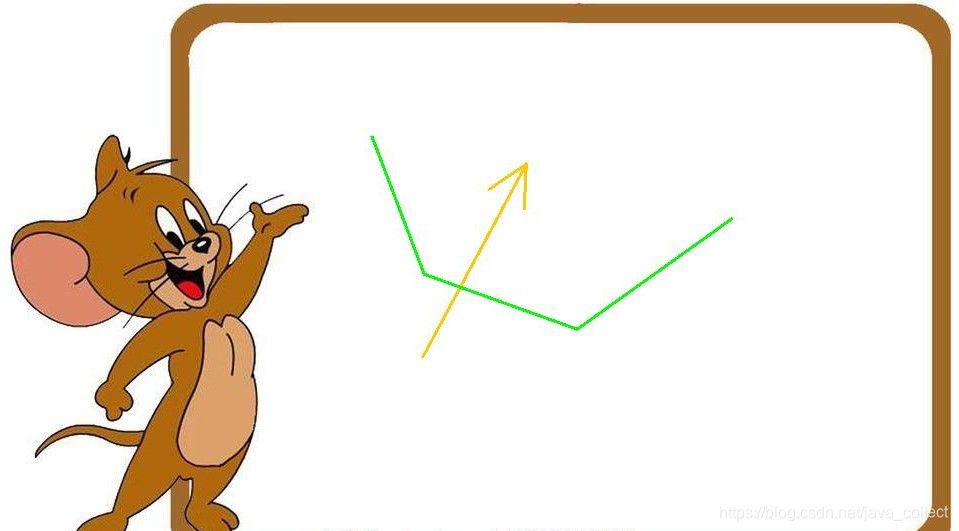
已知各个点的x,y坐标,坐标范围是[0.000,1],即将横纵方向分成1000份。
我们可以使用java.awt.Graphics2D的库来实现。
Graphics2D在Graphics类提供绘制各种基本的几何图形的基础上进行扩展,拥有更强大的二维图形处理能力,提供坐标转换、颜色管理以及文字布局等更精确的控制。Graphics2D类重要的属性包含以下几个
- stroke属性
控制线条的宽度、笔形样式、线段连接方式或短划线图案 - paint属性
控制填充效果 - transform属性
实现常用的图形平移、缩放和斜切等变换操作 - clip属性
实现剪裁效果 - composit属性
设置图形重叠区域的效果 - color
控制颜色,使用RGB构造 - Graphics2D类的绘图draw()
扩充了Graphics的许多方法,可以画线段、矩形、椭圆、圆弧、二次曲线甚至三次曲线等
相关代码如下:
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.Line2D;
import java.awt.geom.RoundRectangle2D;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 94977
* @create 2018/12/22
*/
public class JfreeChart {
/**
* 线宽,这里默认设置所有线宽都一样,也可根据需求分别设置
*/
private static final float STROKE_WIDTH = 3.0f;
/**
* 箭头的高度,单位像素
*/
private static final Integer ARROW_HEIGHT = 40;
/**
* 箭头底边的一半,单位像素
*/
private static final Integer ARROW_LENGTH = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File imgFile = new File("D:\\3.jpg");
File imgFile2 = new File("D:\\11.jpg");
BufferedImage srcimg = ImageIO.read(imgFile);
//Graphics2D对象相当于画笔
Graphics2D g2d = srcimg.createGraphics();
// 获取图片宽度
int width = srcimg.getWidth();
// 获取图片高度
int height = srcimg.getHeight();
// 设置线的型式
Stroke stroke = new BasicStroke(STROKE_WIDTH, // 线宽
BasicStroke.CAP_SQUARE, // 端点样式
BasicStroke.JOIN_BEVEL, // 接头样式
15.0f, // 拼接限制
null, // 虚线
5.0f); //虚线的设置
g2d.setStroke(stroke);
//画方向线
g2d.setColor(new Color(255, 200, 0));
List<CoordinateDto> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(new CoordinateDto(0.450,0.650));
list2.add(new CoordinateDto(0.550,0.300));
getDirectionLine(list2,width,height,g2d);
//画检测线,需至少两个点
g2d.setColor(Color.GREEN);
List<CoordinateDto> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new CoordinateDto(0.400,0.250));
list.add(new CoordinateDto(0.450,0.500));
list.add(new CoordinateDto(0.600,0.600));
list.add(new CoordinateDto(0.750,0.400));
for(int i = 0 ; i < list.size()-1; i++){
g2d.draw(getLine(list.get(i).getX(),list.get(i).getY(),list.get(i+1).getX(),list.get(i+1).getY(),width,height));
}
//g2d.fill3DRect(500,400,100,5,true);
//画一个矩形
//RoundRectangle2D rRect = new RoundRectangle2D.Double(13.0,30.0,100.0,70.0,10.0,10.0);
//g2d.draw(rRect);
//释放此图形的上下文并释放它所使用的所有系统资源
g2d.dispose();
ImageIO.write(srcimg, "JPG", imgFile2);
}
private static void getDirectionLine(List<CoordinateDto> list, int width, int height, Graphics2D g2){
CoordinateDto startPoint = list.get(0);
CoordinateDto endPoint = list.get(1);
int sx = (int)(startPoint.getX()*width);
int sy = (int)(startPoint.getY()*height);
int ex = (int)(endPoint.getX()*width);
int ey = (int)(endPoint.getY()*height);
drawAL(sx, sy, ex, ey, g2);
}
/**
* 画箭头
*/
private static void drawAL(int sx, int sy, int ex, int ey, Graphics2D g2) {
double H = ARROW_HEIGHT; // 箭头高度
double L = ARROW_LENGTH; // 底边的一半
int x3 = 0;
int y3 = 0;
int x4 = 0;
int y4 = 0;
double awrad = Math.atan(L / H); // 箭头角度
double arraow_len = Math.sqrt(L * L + H * H); // 箭头的长度
double[] arrXY_1 = rotateVec(ex - sx, ey - sy, awrad, true, arraow_len);
double[] arrXY_2 = rotateVec(ex - sx, ey - sy, -awrad, true, arraow_len);
double x_3 = ex - arrXY_1[0]; // (x3,y3)是第一端点
double y_3 = ey - arrXY_1[1];
double x_4 = ex - arrXY_2[0]; // (x4,y4)是第二端点
double y_4 = ey - arrXY_2[1];
Double X3 = new Double(x_3);
x3 = X3.intValue();
Double Y3 = new Double(y_3);
y3 = Y3.intValue();
Double X4 = new Double(x_4);
x4 = X4.intValue();
Double Y4 = new Double(y_4);
y4 = Y4.intValue();
//起始线
g2.drawLine(sx, sy, ex, ey);
//箭头
g2.drawLine(ex, ey, x3, y3);
g2.drawLine(ex, ey, x4, y4);
//三角形箭头
//GeneralPath triangle = new GeneralPath();
//triangle.moveTo(ex, ey);
//triangle.lineTo(x3, y3);
//triangle.lineTo();
//triangle.closePath();
//实心箭头
//g2.fill(triangle);
//非实心箭头
//g2.draw(triangle);
}
// 计算
private static double[] rotateVec(int px, int py, double ang,
boolean isChLen, double newLen) {
double mathstr[] = new double[2];
// 矢量旋转函数,参数含义分别是x分量、y分量、旋转角、是否改变长度、新长度
double vx = px * Math.cos(ang) - py * Math.sin(ang);
double vy = px * Math.sin(ang) + py * Math.cos(ang);
if (isChLen) {
double d = Math.sqrt(vx * vx + vy * vy);
vx = vx / d * newLen;
vy = vy / d * newLen;
mathstr[0] = vx;
mathstr[1] = vy;
}
return mathstr;
}
private static Line2D getLine(double x1 ,double y1,double x2 ,double y2, int width, int height){
return new Line2D.Double(x1*width,y1*height,x2*width,y2*height);
}
}
public class CoordinateDto {
private double x;
private double y;
//省略getter setter
}
主要使用的是Graphics2D.drawLine()方法,注意这个方法参数里坐标是以像素为单位,所以代码中对此进行了些转换。
相关链接:
stroke属性详解
对图像像素点的处理