1.接口interface
1.1 接口基本使用
package com.daigua13;
/*
* 接口的成员特点:
* 只能有抽象方法
* 只能有常量
* 默认使用public&abstract修饰方法
* 只能使用public&abstract修饰方法
* 默认使用public static final来修饰成员变量
*
* 建议:建议大家手动的给上默认修饰符
*
* 注意:
* 接口不能创建对象(不能实例化)
* 类与接口的关系是实现关系,一个类实现一个接口必须实现它所有的方法
*/
public class InterfaceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat();
c.eat();
System.out.println(c.num);
System.out.println(Animal.num);
}
}
// 定义接口
interface Animal {
// 接口只能有常量用public static final修饰
public static final int num = 10;
// 抽象方法
public abstract void eat();
}
class Cat implements Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我是你爸爸!");
}
}
1.2 接口的多继承
package com.daigua13;
/*
*
* 类与类:继承关系,单一继承,多层继承
* 类与接口:实现关系,多实现
* 接口与接口的关系:继承关系,多继承
*/
public class InterfaceDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
interface InterA extends InterB {
public abstract void method();
}
interface InterB {
public abstract void function();
}
interface InterC extends InterA {
}
class Demo implements InterC {
@Override
public void method() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void function() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
1.3 运动员案例
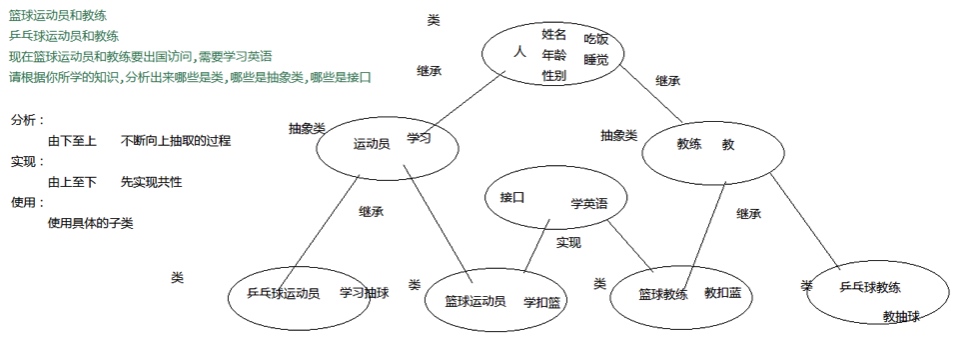 

package com.daigua13;
public class InterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Basketball b = new Basketball();
b.name = "Mike";
b.age = 50;
b.gender = "男";
b.studyEnglish();
b.study();
}
}
class Human {
String name;
int age;
String gender;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("睡觉");
}
}
abstract class Althlete extends Human {
// 抽象方法 学习
public abstract void study();
}
abstract class Coach extends Human {
// 抽象方法 教
public abstract void teach();
}
interface StudyEnglish {
public abstract void studyEnglish();
}
class PingPong extends Althlete {
@Override
public void study() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("学习抽球");
}
}
class Basketball extends Althlete implements StudyEnglish {
@Override
public void study() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("学扣篮");
}
@Override
public void studyEnglish() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("篮球运动员" + this.name + "学英语");
}
}
class BasketballCoach extends Coach {
@Override
public void teach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("教扣篮");
}
}
class PingPongCoach extends Coach {
@Override
public void teach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("教抽球");
}
}
2.final关键字
2.1 简单使用
package com.daigua13;
/*
* final: 修饰符,可以用于修饰类、成员方法和成员变量
* final所修饰的类:不能被继承,不能有子类
* final所修饰的方法:不能被重写
* final所修饰的变量:是不可以修改的,是常量
*
* 常量:
* 字面值常量:1,2,3
* 自定义常量:被final所修饰的成员变量,一旦初始化则不可改变
*
* 注意:自定义常量必须初始化,可以选择显示初始化或者构造初始化
*/
public class FinalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Animal a = new Animal();
// a.eat();
Dog d = new Dog();
// d.eat();
// d.num = 20;
System.out.println(d.NUM);
}
}
/* final */ class Animall {
public final void eat() {
System.out.println("吃东西");
}
}
class Dog extends Animall {
/* public void eat() {} */
final int NUM;
public Dog() {
NUM = 10;
}
}
3.多态
3.1基本使用
package com.daigua13;
/*
* 多态的前提:
* 子父类的继承关系
* 方法的重写
* 父类引用指向子类对象
*
* 动态绑定:运行期间调用的方法,是根据其具体的类型
*
*/
public class PolymorphismDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* Cat c = new Cat(); c.eat();
*/
// 父类引用 Animal a
// 指向 =
// 子类对象 new Cat()
Animal3 a = new Cat3();
a.eat();
}
}
class Animal3 {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃东西");
}
}
class Cat3 extends Animal3 {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
3.2多态成员特点(执行顺序)
package com.daigua13;
/*
*
* 多态的成员特点:
* 成员变量 编译时看的是左边,运行时看的左边
* 成员方法 编译时看的是左边,运行时看右边
* 静态方法 编译时看的是左边,运行时看的也是左边
*
*
* 编译时看的都是左边,运行时成员方法看的是右边,其他(成员变量和静态的方法)看的都是左边
*
*/
public class PolymorphicDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dad d = new Kid();
// System.out.println(d.num);
d.method();
d.function();// 使用变量去调用静态方法,其实相当于用变量类型的类名去调用
}
}
class Dad {
int num = 20;
public void method() {
System.out.println("我是父类方法");
}
public static void function() {
System.out.println("我是父类静态方法");
}
}
class Kid extends Dad {
int num = 10;
public void method() {
System.out.println("我是子类方法");
}
public static void function() {
System.out.println("我是子类静态方法");
}
}
3.3多态中向上转型与向下转型
package com.daigua13;
/*
*
* 多态中的向上转型和向下转型:
*
* 引用类型之间的转换
* 向上转型
* 由小到大(子类型转换成父类型)
* 向下转型
* 由大到小
* 基本数据类型的转换
* 自动类型转换
* 由小到大
* byte short char --- int --- long --- float --- double
* 强制类型转换
* 由大到小
*
*
*
*/
public class DuoTailDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal2 a = new Dog1();// 向上转型
a.eat();
Dog1 d = (Dog1) a;// 向下转型
d.swim();
}
}
class Animal2 {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃东西");
}
}
class Dog1 extends Animal2 {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("啃骨头");
}
public void swim() {
System.out.println("狗刨");
}
}
3.4 多态的优缺点
package com.itheima_01;
/*
*
* 多态的优缺点
* 优点:可以提高可维护性(多态前提所保证的),提高代码的可扩展性
缺点:无法直接访问子类特有的成员
*/
public class PoymorphicDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MiFactory factory = new MiFactory();
factory.createPhone(new MiNote());
factory.createPhone(new RedMi());
}
}
class MiFactory {
/*public void createPhone(MiNote mi) {
mi.call();
}
public void createPhone(RedMi mi) {
mi.call();
}*/
// 这里是对多态的体现
public void createPhone(Phone p) {
p.call();
}
}
interface Phone {
public void call();
}
//小米Note
class MiNote implements Phone{
public void call() {
System.out.println("小米Note打电话");
}
}
//红米
class RedMi implements Phone {
public void call() {
System.out.println("红米打电话");
}
}