前提:多表数据

create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(16), work varchar(16) ); create table emp( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(16), salary float, dep_id int ); insert into dep values(1, '市场部', '销售'), (2, '教学部', '授课'), (3, '管理部', '开车'); insert into emp(name, salary, dep_id) values('egon', 3.0, 2),('yanghuhu', 2.0, 2),('sanjiang', 10.0, 1),('owen', 88888.0, 2),('liujie', 8.0, 1),('yingjie', 1.2, 0);
一:笛卡尔积(交叉连接)
需求:查看每位员工的部门的所有信息 select * from emp; +----+----------+--------+--------+ | id | name | salary | dep_id | +----+----------+--------+--------+ | 1 | egon | 3 | 2 | | 2 | yanghuhu | 2 | 2 | | 3 | sanjiang | 10 | 1 | | 4 | owen | 88888 | 2 | | 5 | liujie | 8 | 1 | | 6 | yingjie | 1.2 | 0 | +----+----------+--------+--------+ select * from dep; +----+-----------+--------+ | id | name | work | +----+-----------+--------+ | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 3 | 管理部 | 开车 | +----+-----------+--------+ 子查询,最终结果只能显示单表的信息,但需求是同时能够显示两张表的信息==>先将两张表合成一张表 select * from emp where dep_id in (select id from dep); +----+----------+--------+--------+ | id | name | salary | dep_id | +----+----------+--------+--------+ | 1 | egon | 3 | 2 | | 2 | yanghuhu | 2 | 2 | | 3 | sanjiang | 10 | 1 | | 4 | owen | 88888 | 2 | | 5 | liujie | 8 | 1 | +----+----------+--------+--------+ 笛卡尔积:集合 X{a, b} * Y{o, p, q} => Z{{a, o}, {a, p}, {a, q}, {b, o}, {b, p}, {b, q}} 交叉查询:select * from emp, dep; | select * from emp course join dep; ''' 做了筛选,结果<==完整数据,非笛卡尔积 select * from emp, dep where db2.emp.dep_id = db2.dep.id; # 同sql语句上表现是从两张表拿数据 +----+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+ | id | name | salary | dep_id | id | name | work | +----+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+ | 1 | egon | 3 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 2 | yanghuhu | 2 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 3 | sanjiang | 10 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | | 4 | owen | 88888 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 5 | liujie | 8 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | +----+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+ 注意:同时查询两张表形成新的表,可以称之为虚拟表,原表与表之间可能存在重复字段,同时使用时需要明确所属表,必要时还需明确所需数据库 '''
二:多表连接=>虚拟的单表
2.1内连接
inner join on 内连接: 结果为两张表有对应关系的数据(emp有dep没有,emp没有dep有的记录均不会被虚拟表展示) 语法:左表 inner join 右表 on 两表有关联的字段的条件,on就是产生对于关系的(连接的依据) eg:select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id; +----+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+ | id | name | salary | dep_id | id | name | work | +----+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+ | 1 | egon | 3 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 2 | yanghuhu | 2 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 3 | sanjiang | 10 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | | 4 | owen | 88888 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 5 | liujie | 8 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | +----+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+
2.2左连接
left join on 左连接:在内连接的基础上还保留左表特有的记录 语法:左表 left join 右表 on 两表有关联的字段条件 eg:select emp.name '员工', dep.name '部门', dep.work '职责' from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id; +----------+-----------+--------+ | 员工 | 部门 | 职责 | +----------+-----------+--------+ | sanjiang | 市场部 | 销售 | | liujie | 市场部 | 销售 | | egon | 教学部 | 授课 | | yanghuhu | 教学部 | 授课 | | owen | 教学部 | 授课 | | yingjie | NULL | NULL | +----------+-----------+--------+
左表: 右表:
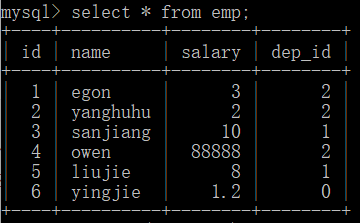
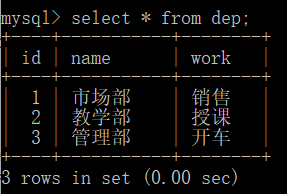

2.3右连接
right join on 右连接:在内连接的基础上还保留右表特有的记录 语法:左表 right join 右表 on 两表有关联的字段的条件 eg:select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
+------+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+
| id | name | salary | dep_id | id | name | work |
+------+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+
| 1 | egon | 3 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 |
| 2 | yanghuhu | 2 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 |
| 3 | sanjiang | 10 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 |
| 4 | owen | 88888 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 |
| 5 | liujie | 8 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 管理部 | 开车 |
+------+----------+--------+--------+----+-----------+--------+
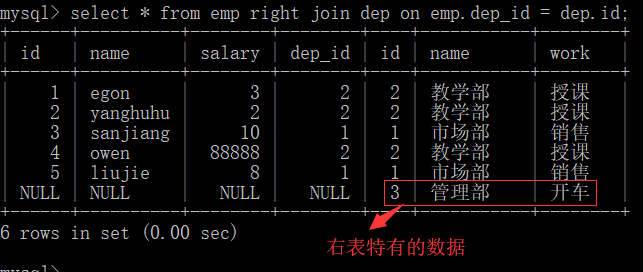
在连接语法join前面就是左表,之后就是右表
采用的是left关键词就是左连接,right关键词就是右连接,inner关键词就是内连接
2.4全连接
全连接:在内连接的基础上分别保留着左表及右表特有的记录 语法:mysql没有full join on 语法,但是可以通过去重达到效果 eg: select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id union select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id; +------+----------+--------+--------+------+-----------+--------+ | id | name | salary | dep_id | id | name | work | +------+----------+--------+--------+------+-----------+--------+ | 3 | sanjiang | 10 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | | 5 | liujie | 8 | 1 | 1 | 市场部 | 销售 | | 1 | egon | 3 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 2 | yanghuhu | 2 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 4 | owen | 88888 | 2 | 2 | 教学部 | 授课 | | 6 | yingjie | 1.2 | 0 | NULL | NULL | NULL | | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 管理部 | 开车 | +------+----------+--------+--------+------+-----------+--------+
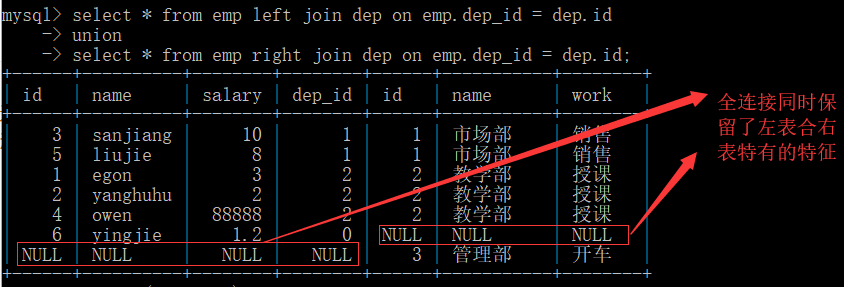

''' 1.查询每一位员工对应的工作职责 # 每一位员工 => 左表为emp表, 那么左表的所有数据均需要被保留, 所有采用左连接 => 左表为dep表, 那么右表的所有数据均需要被保留, 所有采用右连接 # select emp.name, dep.work from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id; select emp.name, dep.work from dep right join emp on emp.dep_id = dep.id; +----------+--------+ | name | work | +----------+--------+ | sanjiang | 销售 | | liujie | 销售 | | egon | 授课 | | yanghuhu | 授课 | | owen | 授课 | | yingjie | NULL | +----------+--------+ 2.查询每一个部门下的员工们及员工职责 # select max(dep.name), max(dep.work), group_concat(emp.name) from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id group by dep_id; # 分析过程 # 每一个部门 => dep的信息要被全部保留, 需要分组 # 员工职责 => dep.work, 由于分组不能直接被查询 => 需要用聚合函数处理 # 员工们 => emp.name做拼接 => group_concat(emp.name) # 分组的字段 => 部门 => emp.dep_id => emp.dep_id可以直接被查询,但没有显示意义 => dep.name用来显示 => dep.name需要用聚合函数处理 select max(dep.name), max(dep.work), group_concat(emp.name) from dep left join emp on emp.dep_id = dep.id group by emp.dep_id; # 注: on在where条件关键词之左 '''
三:Navicat
1.安装Navicat 2.连接数据库,并建库 3.创建表、设置字段、插入数据 4.新建查询
四:Python使用mysql
模块pymysql
按照并导入pymysql:pip3 install pymysql
通过pymysql操作数据库分四步
1.建立连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, db='db2', user='root', password='root') 2.设置字典类型游标 cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 3.执行sql语句并使用执行结果 # 书写sql语句 sql = 'select * from emp' # 执行sql语句, 有返回值, 返回值为得到的记录行数 line = cursor.execute(sql) print(line) # 使用执行的结果: fetchone()当前游标往后获取一行记录 fetchall()当前游标往后所有的记录 scroll(num, mode="relative|absolute") relative: 游标从当前位置往后移动num行 ablolute: 游标从头往后移动num行, 一般可以结合line来使用能定位到任意位置 tag = cursor.fetchone() # 第一条 print(tag) print(tag['salary']) tag = cursor.fetchone() # 第二条 print(tag) cursor.scroll(1, mode='relative') # 偏移第三条 # cursor.scroll(line - 1, mode='absolute') # 指针绝对, 游标永远从头开始偏移 tags = cursor.fetchall() # 第四条到最后 print(tags) 4.断开连接 cursor.close() conn.close()

''' 过程: 1. 建立连接 2. 设置一个可以执行sql语句的对象 - 游标 3. 通过该对象执行sql语句得到执行结果 4. 端口连接 ''' import pymysql # 1. 建立连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, db='db2', user='root', password='root') # 2. 设置游标 cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 设置游标的具体类型, DictCursor拿到字段名 # 3. 执行sql语句 sql = 'select * from emp' res = cursor.execute(sql) # 结果的行数 print(res) # 需求: 具体的一条条记录 tag = cursor.fetchone() print(tag) print(tag['salary']) tag = cursor.fetchone() print(tag) # cursor.scroll(1, mode='relative') # 指针相对于上一次位置往后偏移1条记录 cursor.scroll(res - 1, mode='absolute') # 指针绝对, 游标永远从头开始偏移 tags = cursor.fetchall() print(tags) cursor.close() conn.close()
五:pymysql处理sql注入
什么是sql注入: 通过书写sql包含(注释相关的)特殊字符,让原有的sql执行顺序发生改变,从而改变执行得到的sql 目的: 绕过原有的sql安全认证,达到对数据库攻击的目的 没有处理sql注入的写法: sql = 'select * from user where usr="%s" and pwd="%s"' % (usr, pwd) res = cursor.execute(sql) # sql注入 # 1.知道用户名: abc" -- hehe | ooo # select * from user where usr="abc" -- hehe" and pwd="ooo" # 2.不知道用户名 aaa" or 1=1 -- hehe | 000 # select * from user where usr="aaa" or 1=1 -- hehe" and pwd="000" # 处理sql注入: sql = 'select * from user where usr=%s and pwd=%s' res = cursor.execute(sql, (usr, pwd))

''' sql语法中 注释: /**/ | -- | # 什么是sql注入: 通过书写sql包含(注释相关的)特殊字符, 让原有的sql执行顺序发生改变, 从而改变执行得到的sql 目的: 绕过原有的sql安全认证, 达到对数据库攻击的目的 ''' import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root', db='db2') cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 登录 # 得到用户输入的账户密码 usr = input("请输入用户名: ") #abc pwd = input("请输入密码: ") #123 # sql注入 # 1.知道用户名: abc" -- hehe | ooo # select * from user where usr="abc" -- hehe" and pwd="ooo" # 2.不知道用户名 aaa" or 1=1 -- hehe | 000 # select * from user where usr="aaa" or 1=1 -- hehe" and pwd="000" # 处理方式 # 对输入的账户密码做完全处理 => 不可能形成达到sql注入的特殊语法 => 正则 # 和数据库的账户密码进行配对 # sql = 'select * from user where usr="%s" and pwd="%s"' % (usr, pwd) # select * from user where usr="abc" and pwd="123" # res = cursor.execute(sql) # pymysql已经处理了sql注入 sql = 'select * from user where usr=%s and pwd=%s' res = cursor.execute(sql, (usr, pwd)) # print(res) if res: print('login success') else: print('login failed') cursor.close() conn.close()
六:增、删、改
增: 增加sql的语句: sql1 = 'insert into user(usr, pwd) values (%s, %s)' 在内存中一次插入一条: cursor.execute(sql1, ("opq", "123")) 在内存中插入多条 cursor.executemany(sql1, [("aaa", "000"), ("bbb", "111")]) 将内存中的数据提交到硬盘中: conn.commit() 删: sql2 = 'delete from user where usr=%s' cursor.execute(sql2, ("aaa")) conn.commit() 改: sql3 = 'update user set pwd=%s where usr=%s' res = cursor.execute(sql3, ("222", "bbb")) conn.commit()

import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root', db='db2') cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 增 # sql1 = 'insert into user(usr, pwd) values (%s, %s)' # cursor执行sql语句,在内存中完成了对数据的插入, 但不能将数据存放到硬盘 # 会将id完成自增 # 插入单条 # res = cursor.execute(sql1, ("opq", "123")) # 插入多条 #res = cursor.executemany(sql1, [("aaa", "000"), ("bbb", "111")]) # print(res) # 将内存中的数据提交给硬盘, 完成真实意义上的数据存储 # conn.commit() # 删 # sql2 = 'delete from user where usr=%s' # res = cursor.execute(sql2, ("aaa")) # print(res) # conn.commit() # 改 sql3 = 'update user set pwd=%s where usr=%s' res = cursor.execute(sql3, ("222", "bbb")) conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
