一、Spring的相关配置
1.1 Bean元素
- class属性:被管理对象的完整类名
- name属性:给Bean起个名字,能重复,能使用特殊字符.后来属性
- id属性:给Bean起个名字,不能重复,不能使用特殊字符.早期属性
- scope属性
- singleton:默认值,单例对象.项目一启动就创建对象,而且容器只创建一次
- prototype:多例原型.被标识为多例的对象,每次在获得才会创建.每次创建都是新的对象(整合struts2时,ActionBean必须配置为多例的.)
- request(了解):web项目中,Spring创建一个Bean的对象,将对象存入到request域中。.对象与request生命周期一致.
- session(了解):web项目中,Spring创建一个Bean的对象,将对象存入到session域中。,对象与session生命周期一致.
- 生命周期属性(了解)
- init-method:指出初始化方法,spring会在对象创建之后立即调用
- destory-method:指出销毁方法,spring在关闭并销毁所有容器中的对象之前调用.
1.2 spring创建对象的方式
【方式一:无参数的构造方法】
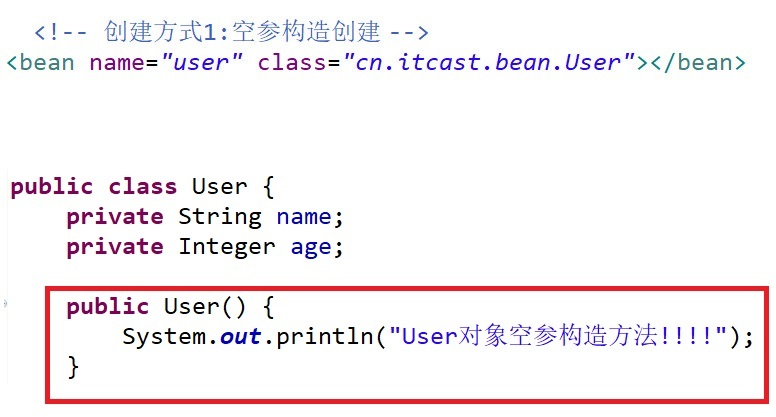
spring容器启动后就创建User对象。如果对象中提供了带参构造,而没有提供无参构造,这样讲无法创建对象,程序会报错:
警告: Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'user' defined in class path resource [applicationContext.xml]: Instantiation of bean failed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failed to instantiate [cn.itcast.domain.User]: No default constructor found; nested exception is java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: cn.itcast.domain.User.<init>()
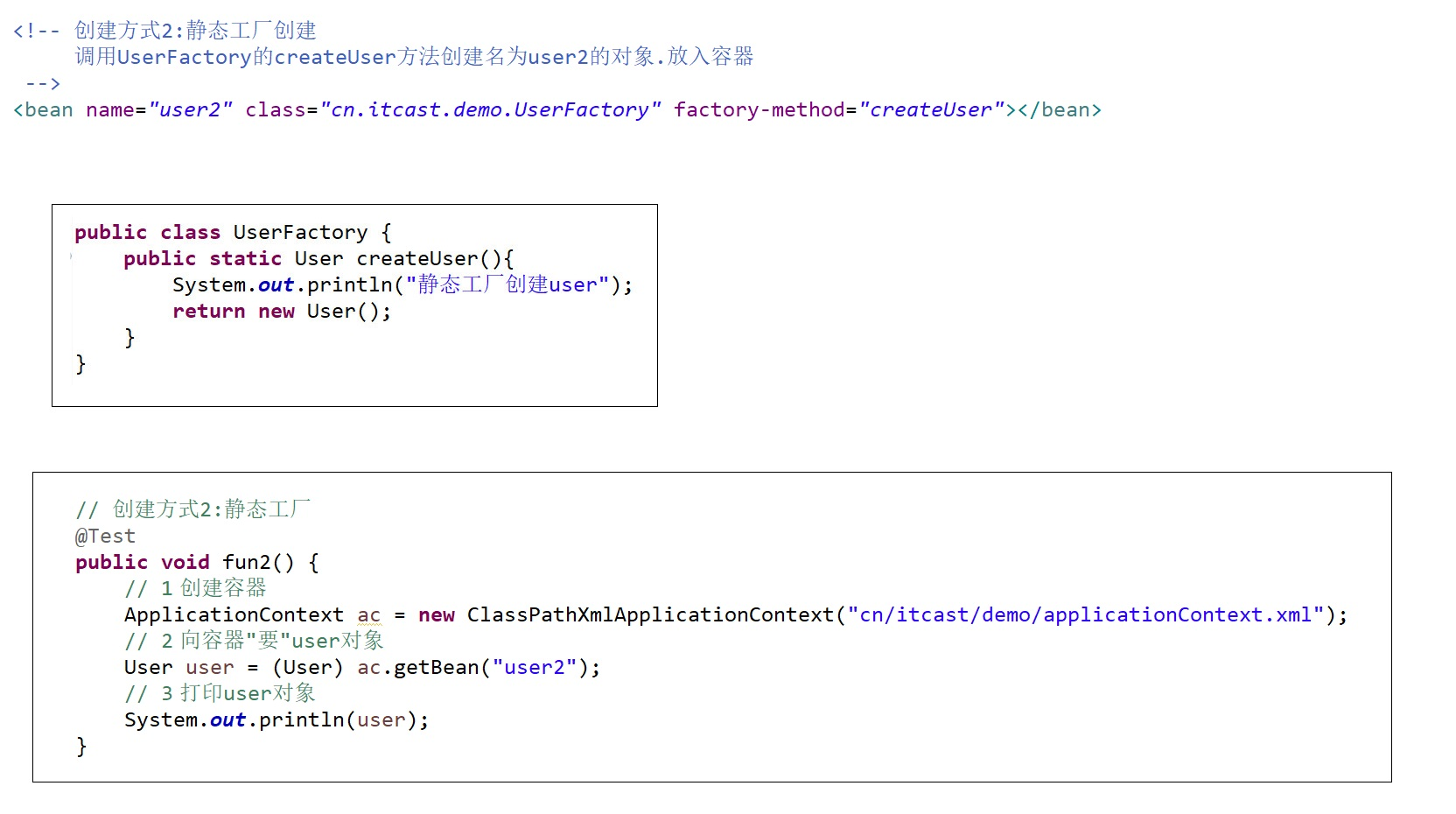
【方式二:静态工厂创建】(了解)
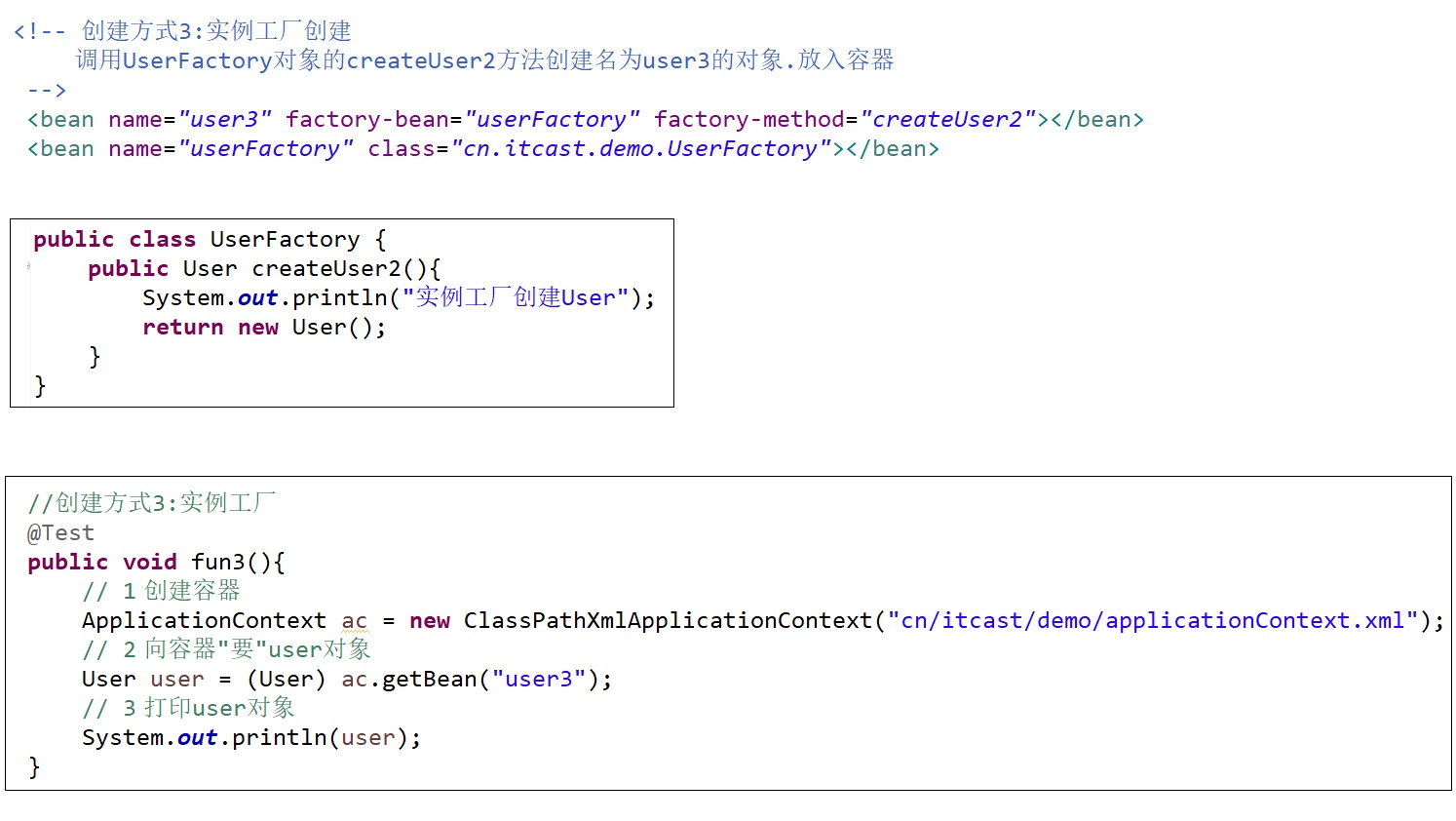
【方式三:实例工厂创建】(了解)
1.3 Spring的分模块配置
<!-- 导入其他spring配置文件 --> <import resource="cn/itcast/demo/applicationContext.xml"/>
1.4 管理容器在项目中的生命周期
【让spring容器随项目的启动而创建,随项目的关闭而销毁】
在web.xml中配置
<!-- 可以让spring容器随项目的启动而创建,随项目的关闭而销毁 --> <listener> <!-- 注意:引入此类前,要导入spring-web-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar --> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 指定加载spring配置文件的位置 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param>
【在Action中获得容器中的Service对象】
public String execute() throws Exception { // 获得spring容器=>从Application域获得即可 // 1.获得servletContext对象 ServletContext servletContext = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); // 2.从servletContext中获得applicationContext容器 WebApplicationContext applicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext); // 3.从容器中获得CustomerService CustomerService service = (CustomerService)applicationContext.getBean("customerService"); return NONE; }
错误示例:(这样会导致每次请求都会创建新的容器)
// 创建容器 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CustomerService service = (CustomerService)applicationContext.getBean("customerService");
二、属性注入
2.1 注入方式
【set方法注入】

【构造函数注入】

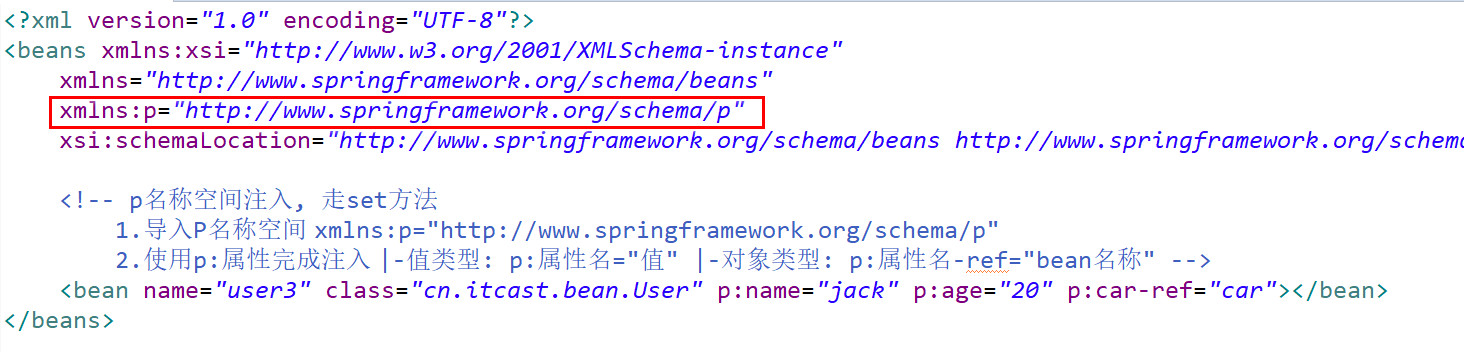
【p名称空间注入】(了解)
【spel注入】(了解)

2.2 复杂类型的注入
【数组】

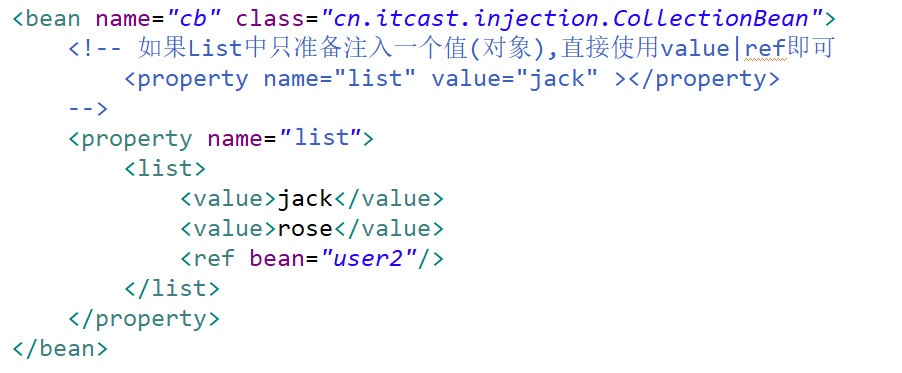
【list】
【map】

【Properties】

三、spring与Junit整合测试
首先要导入Junit测试包:![]()
测试代码如下:
// 帮我们创建容器 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) // 指定创建容器时使用哪个配置文件 @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class Demo { // 将名为user的对象注入到user变量中 @Resource(name="user") private User user; @Test public void fun1() throws Exception { // 1.创建容器对象 // ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 2.向容器"要"user对象 // User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user"); // 3.打印user对象 System.out.println(user); } }