版权声明:版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/zxzxzx0119/article/details/86634460
LeetCode - 40. Combination Sum II && LeetCode - 216. Combination Sum III (DFS)
做这题之前可以先做LeetCode - 39.Combination Sum,并知道dfs求解组合数的模板。
LeetCode - 40. Combination Sum II
题目链接
题目
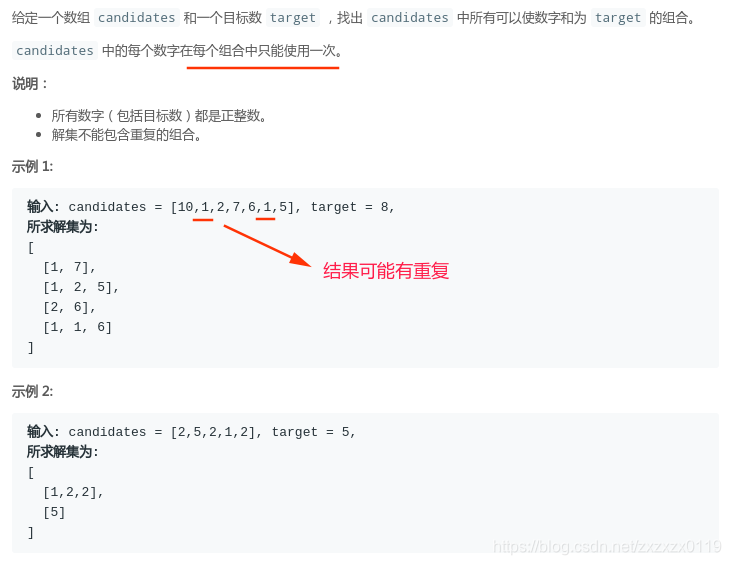
解析
这题和LeetCode - 39 . Combination Sum不同的地方在于:
- LeetCode - 39 . Combination Sum数组没有重复的元素,但是你可以使用同一个位置的元素去组成
target; - 而此题,数组中可能存在重复的元素,但是你不能使用同一个位置的元素;
- 由于这一题可以使用不同位置上值相同的元素,所以
dfs得到的结果res中可能存在重复的答案,例如第一个示例中,如果不去重,答案会是[1, 7], [1, 7], [1, 2, 5], [1, 2, 5], [2, 6], [1, 1, 6],可以看到有两个重复的答案。所以需要去重。下面给出两种代码实现去重的方式。
① 其实只需要在LeetCode - 39 . Combination Sum的基础上加上一行代码,当有连续重复(在排序之后)的值时,跳过即可,即while(i+1 < nums.length && nums[i] == nums[i+1]) i++;。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>>res;
//不同点: 不能使用同一个位置上的元素,但是不同位置上可能有相同值的元素,所以-->需要考虑重复答案的问题
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
if(candidates == null || candidates.length == 0)
return res;
Arrays.sort(candidates); //先排序 ,既可以剪枝,由导致相邻相等的元素在一起
dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0, new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int curSum, int cur, List<Integer>curr){
if(curSum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
return;
}
for(int i = cur; i < nums.length; i++){
if(curSum + nums[i] > target)
break; // 因为排序了,所以这里是break,不是continue,剪枝
curr.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, target, curSum + nums[i], i+1, curr); // notice is i+1
curr.remove(curr.size()-1);
while(i+1 < nums.length && nums[i] == nums[i+1]) i++; //only add this;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
int[] candidates = {10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5};
int target = 8;
out.println(new Solution().
combinationSum2(candidates, target)
);
}
}
② 或者在递归之前判断一下和前面的nums[i-1]是不是相同,即:if(i != cur && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>>res;
//不同点: 不能使用同一个位置上的元素,但是不同位置上可能有相同值的元素,所以-->需要考虑重复答案的问题
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
if(candidates == null || candidates.length == 0)
return res;
Arrays.sort(candidates); //先排序 ,既可以剪枝,由导致相邻相等的元素在一起
dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0, new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int curSum, int cur, List<Integer>curr){
if(curSum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
return;
}
for(int i = cur; i < nums.length; i++){
if(curSum + nums[i] > target)
break;
if(i != cur && nums[i] == nums[i-1])// judge this
continue;
curr.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, target, curSum + nums[i], i+1, curr); // notice is i+1
curr.remove(curr.size()-1);
}
}
}
LeetCode - 216. Combination Sum III
题目链接
题目
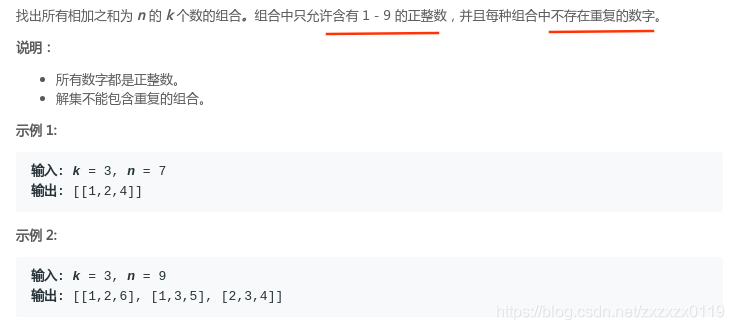
解析
这题其实也挺简单的,还是组合数的模板稍微改动一下。只不过将枚举数组中的元素改成for(int i = cur; i <= 9; i++){,即枚举
cur ~ 9,而cur一开始自然是从1开始的。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0, k, 1, 0, n, new ArrayList<>());// d is depth
return res;
}
private void dfs(int d, int k, int cur, int curSum, int target, List<Integer>curr){
if(d == k){
if(curSum == target)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
return;
}
for(int i = cur; i <= 9; i++){
if(curSum + i > target)
break;
curr.add(i);
dfs(d + 1, k, i + 1, curSum + i, target, curr);
curr.remove(curr.size() - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
int k = 3, n = 9;
out.println(new Solution().
combinationSum3(3, 9)
);
}
}
因为这里的数只从1 ~ 9,所以这题还有一种做法就是利用二进制枚举2 ^ 9种可能。
- 其中如果二进制(总共
9位)某位i上值为1,则说明取了i+1(因为二进制位数从0开始,但是这里是1~9(即从1开始));如果i位置上为0,则没有取i+1; - 枚举所有的二进制数(
0 ~ 2^9),然后每个数,对应哪些位置上是有数的(值为1),如果有,就累加,最后看是不是等于n即可;
例如:
二进制(0 ~ 2^9) |
对应集合 |
|---|---|
| 000000000 | [ ] |
| 000000001 | [ 1 ] |
| 000100011 | [ 1, 2, 6] |
| 010101101 | [ 1, 3, 4, 6, 8] |
| 111111110 | [ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] |
| 111111111 | [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] |
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int mask = 0; mask < (1 << 9); mask++){
List<Integer>cur = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
// if( (mask & (1 << (i-1))) != 0){
if( (( mask >> (i-1) ) & 1) == 1){// same as above
sum += i;
cur.add(i);
}
if(sum == n && cur.size() == k)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
int k = 3, n = 9;
out.println(new Solution().
combinationSum3(3, 9)
);
}
}