源噪声功率通常以系统输入为参考,因此也必须考虑系统的功率增益Gs(如果Gs < 1,则为损耗)。
Source noise power isusually referenced to the input of a system so that the power gain Gs(or loss if Gs < 1) of the system must also be taken intoaccount.
也就是说,如果在接收机输出处观察到的输出功率谱密度(仍然假设在接收机带宽上为白色)是某个值Sn,则在其输入处噪声源的等效温度T′被定义为
That is, if theobserved output power spectral density (still assumed white over the receiverbandwidth) at the output of a receiver is some value Sn , then anequivalent temperature T′ of the noise source at its input is defined to be

接收机的总输出噪声功率是我们主要关注的对象。
The total outputnoise power at the receiver output is the primary quantity of interest.
在雷达系统中,产生这种噪声的因素包括外部噪声、固有的kT0βn热噪声以及由于天线结构和非理想接收机损耗而产生的附加热噪声。
In a radar system,the contributors to this noise include the external noise, the intrinsic kT0βnthermal noise, and additional thermal noise due to losses in the antennastructure and nonideal receivers.
详细的噪声分析将单个等效噪声温度分配给系统中的每一级组件;Curlander和McDonough(1991)对此给出了一个很好的介绍性描述。
Detailed noiseanalyses assign individual equivalent noise temperatures to each stage in thesystem; a good introductory description is given in Curlander and McDonough(1991).
当将系统作为一个整体考虑时,通常将总输出噪声功率表示为两部分噪声纸盒,第一部分是由接收机输入处的最小噪声密度kT0引起的,第二部分是由于非理想系统而产生的附加噪声,即:
When considering thesystem as a whole, it is common to express the total output noise power as thesum of the power that would be observed due to the minimum noise density kT0at the input and a second term that accounts for the additional noise due tothe nonideal system
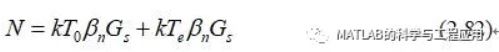
在这个方程中,Gs是整个接收系统的功率增益,包括天线损耗效应。
In this equation, Gsis now the power gain of the complete receiver system, including antenna losseffects.
用于计算高于理论最小值噪声的等效温度Te称为系统的有效温度。
The equivalenttemperature Te used to account for noise above the theoreticalminimum is called the effective temperature of the system.
噪声功率的噪声温度描述对于低噪声接收机最为有用。
The noise temperaturedescription of noise power is most useful for low-noise receivers.
雷达中常见的另一种描述是基于噪声系数Fn的概念,即系统输出时的实际噪声功率与最小功率kT0βnGs之比。
An alternativedescription common in radar is based on the idea of noise figure Fn, which is the ratio of the actual noise power at the output of a system to theminimum power kT0βnGs (Skolnik, 2001).
与噪声温度一样,各种噪声系数可以定义为仅包括接收机或整个天线和接收机系统的影响,等等。
As with noisetemperatures, various noise figures can be defined to include the effects ofjust the receiver, or of the entire antenna and receiver system, and so forth.
在这里,未经定义的噪声系数一词是指整个接收系统的噪声系数,因此
Here, the term noisefigure used without qualification will mean the noise figure of the completereceiver system, so that

——本文译自Mark A. Richards所著的《Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing(Second edition)》
更多精彩文章请关注微信号: