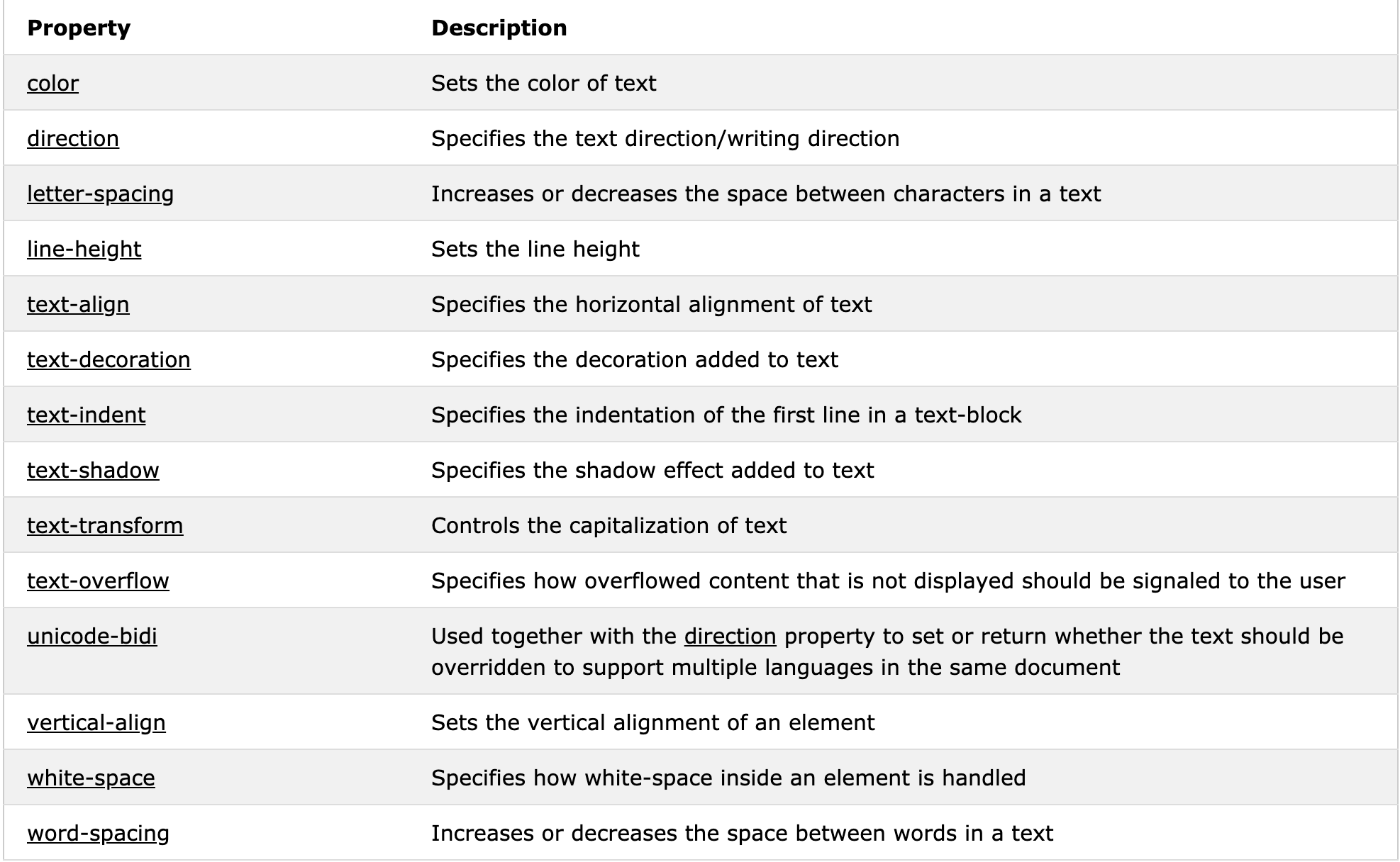
1、CSS Text
text color, text align...
Text Decoration
The text-decoration property is used to set or remove decorations from text.
The value text-decoration: none; is often used to remove underlines from links:
h1 { text-decoration: overline; } h2 { text-decoration: line-through; } h3 { text-decoration: underline; }
Text Transformation
The text-transform property is used to specify uppercase and lowercase letters in a text.
It can be used to turn everything into uppercase or lowercase letters, or capitalize the first letter of each word:
p.uppercase { text-transform: uppercase; } p.lowercase { text-transform: lowercase; } p.capitalize { text-transform: capitalize; }
Text Indentation
The text-indent property is used to specify the indentation of the first line of a text:
p { text-indent: 50px; }
Letter Spacing
The letter-spacing property is used to specify the space between the characters in a text.
The following example demonstrates how to increase or decrease the space between characters:
h1 { letter-spacing: 3px; } h2 { letter-spacing: -3px; }

Line Height
The line-height property is used to specify the space between lines:
Text Direction
he direction property is used to change the text direction of an element:
p { direction: rtl; }
This is right-to-left text direction
<head> <style> p.ex1 { direction: rtl; } </style> </head> <body> <p>This is the default text direction.</p> <p class="ex1"><bdo dir="rtl">This is right-to-left text direction.</bdo></p> </body>
Word Spacing
The word-spacing property is used to specify the space between the words in a text.
Text Shadow
The text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
The following example specifies the position of the horizontal shadow (3px), the position of the vertical shadow (2px) and the color of the shadow (red):
h1 {
text-shadow: 3px 2px red;
}
2、CSS Fonts
Font Family
The font family of a text is set with the font-family property.
The font-family property should hold several font names as a "fallback" system. If the browser does not support the first font, it tries the next font, and so on.
Start with the font you want, and end with a generic family, to let the browser pick a similar font in the generic family, if no other fonts are available.
Note: If the name of a font family is more than one word, it must be in quotation marks, like: "Times New Roman".
More than one font family is specified in a comma-separated list:
p { font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif; } p.sansserif { font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; }
Font Style
The font-style property is mostly used to specify italic text.
This property has three values:
- normal - The text is shown normally
- italic - The text is shown in italics
- oblique - The text is "leaning" (oblique is very similar to italic, but less supported)
Font Size
The font-size property sets the size of the text.
Being able to manage the text size is important in web design. However, you should not use font size adjustments to make paragraphs look like headings, or headings look like paragraphs.
Always use the proper HTML tags, like <h1> - <h6> for headings and <p> for paragraphs.
The font-size value can be an absolute, or relative size.
Absolute size:
- Sets the text to a specified size
- Does not allow a user to change the text size in all browsers (bad for accessibility reasons)
- Absolute size is useful when the physical size of the output is known
Relative size:
- Sets the size relative to surrounding elements
- Allows a user to change the text size in browsers
Note: If you do not specify a font size, the default size for normal text, like paragraphs, is 16px (16px=1em).
Set Font Size With Pixels(16px)
Set Font Size With Em(1em)
To allow users to resize the text (in the browser menu), many developers use em instead of pixels.
The em size unit is recommended by the W3C.
1em is equal to the current font size. The default text size in browsers is 16px. So, the default size of 1em is 16px.
The size can be calculated from pixels to em using this formula: pixels/16=em
h1 { font-size: 2.5em; /* 40px/16=2.5em */ } h2 { font-size: 1.875em; /* 30px/16=1.875em */ } p { font-size: 0.875em; /* 14px/16=0.875em */ }
Responsive Font Size
The text size can be set with a vw unit, which means the "viewport width".
That way the text size will follow the size of the browser window:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <body> <h1 style="font-size:10vw;">Responsive Text</h1> <p style="font-size:5vw;">Resize the browser window to see how the text size scales.</p> <p style="font-size:5vw;">Use the "vw" unit when sizing the text. 10vw will set the size to 10% of the viewport width.</p> <p>Viewport is the browser window size. 1vw = 1% of viewport width. If the viewport is 50cm wide, 1vw is 0.5cm.</p> </body> </html>
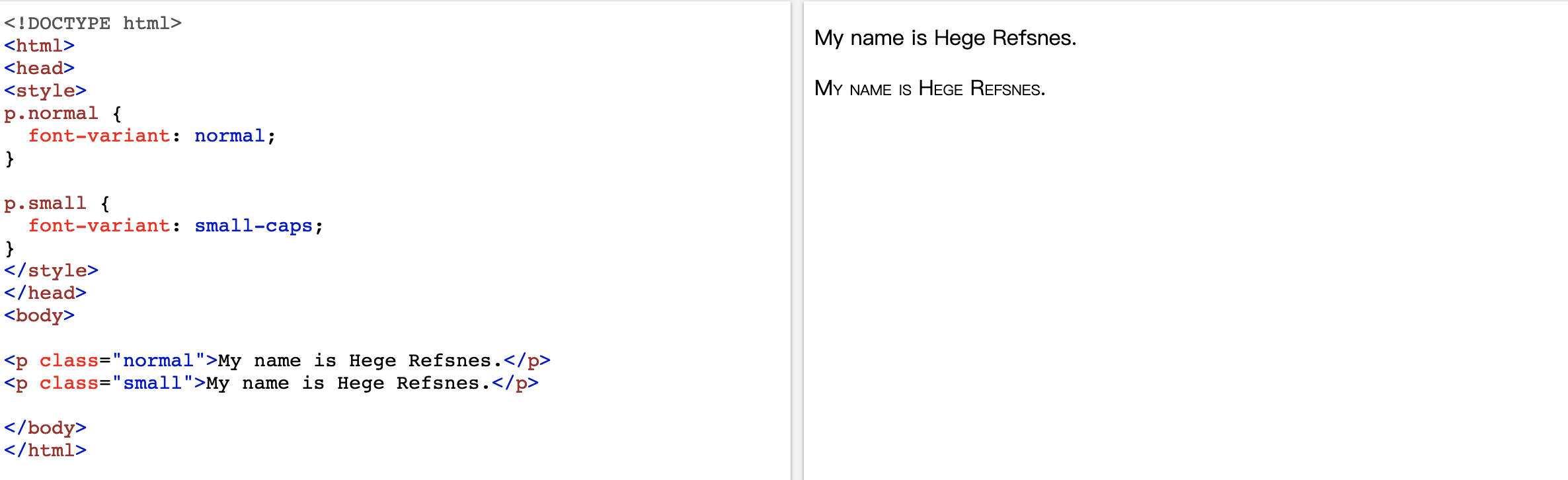
Font Variant
he font-variant property specifies whether or not a text should be displayed in a small-caps font.
In a small-caps font, all lowercase letters are converted to uppercase letters. However, the converted uppercase letters appears in a smaller font size than the original uppercase letters in the text.
3、CSS Icons
The simplest way to add an icon to your HTML page, is with an icon library, such as Font Awesome.
Add the name of the specified icon class to any inline HTML element (like <i> or <span>).
All the icons in the icon libraries below, are scalable vectors that can be customized with CSS (size, color, shadow, etc.)
Font Awesome Icons
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://use.fontawesome.com/releases/v5.7.0/css/all.css" integrity="sha384-lZN37f5QGtY3VHgisS14W3ExzMWZxybE1SJSEsQp9S+oqd12jhcu+A56Ebc1zFSJ" crossorigin="anonymous"> </head> <body> <i class="fas fa-cloud"></i> <i class="fas fa-heart"></i> <i class="fas fa-car"></i> <i class="fas fa-file"></i> <i class="fas fa-bars"></i> </body> </html>
Bootstrap Icons
To use the Bootstrap glyphicons, add the following line inside the <head> section of your HTML page
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <i class="glyphicon glyphicon-cloud"></i> <i class="glyphicon glyphicon-remove"></i> <i class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></i> <i class="glyphicon glyphicon-envelope"></i> <i class="glyphicon glyphicon-thumbs-up"></i> </body> </html>
Google Icons
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/icon?family=Material+Icons"> </head> <body> <i class="material-icons">cloud</i> <i class="material-icons">favorite</i> <i class="material-icons">attachment</i> <i class="material-icons">computer</i> <i class="material-icons">traffic</i> </body> </html>