版权声明:版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38954835/article/details/88242526
Linux内核数据结构——哈希表
1、基本概念
In computing, a hash table (hash map) is a data structure that implements an associative array abstract data type, a structure that can map keys to values. A hash table uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found.
Ideally, the hash function will assign each key to a unique bucket, but most hash table designs employ an imperfect hash function, which might cause hash collisions where the hash function generates the same index for more than one key. Such collisions must be accommodated in some way.
(以上摘自wiki)
2、哈希函数的构造方法
2.1、设计原则
- 计算简单
- 散列地址分布均匀
2.3、常用方法
- 直接定址法
f(key) = a * key + b (a、b为常数) - 数字分析法
- 平方取中法
- 折叠法
- 除留余数法
f(key) = key mod p (p=<m) 通常p选=<m的最小质数或不包含小于20质因子的合数 - 随机数法
f(key) = random(key)
3、处理哈希冲突的方法
- 开放定址法
- 再散列函数法
- 链地址法
- 公共溢出区法
4、linux内核中数据结构——hlist
/*哈希表表头结构*/
struct hlist_head {
struct hlist_node *first;//指向头结点的指针
};
/*结点结构*/
struct hlist_node {
struct hlist_node *next, **pprev;//next指向下一结点的指针,pprev指向上一结点next指针的指针
};
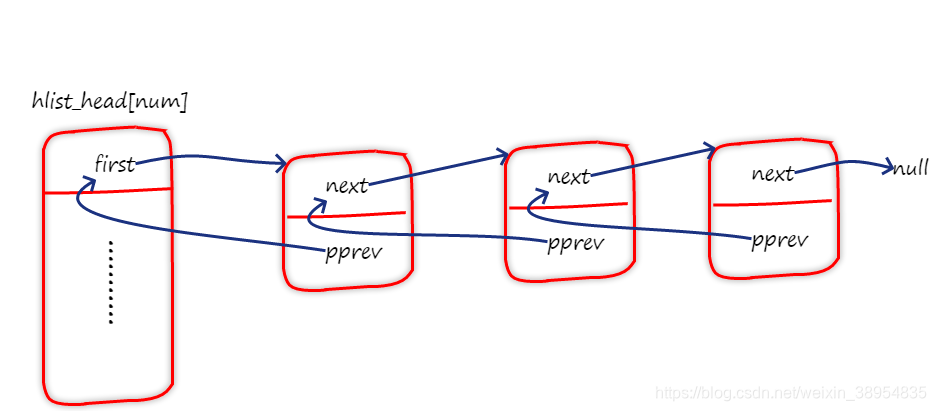
hlist采用链地址法解决哈希冲突
/*初始化hlist_head*/
#define HLIST_HEAD_INIT { .first = NULL }
#define HLIST_HEAD(name) struct hlist_head name = { .first = NULL }
#define INIT_HLIST_HEAD(ptr) ((ptr)->first = NULL)
/*初始化hlist_node*/
static void INIT_HLIST_NODE(struct hlist_node *h)
{
h->next = NULL;
h->pprev = NULL;
}
/*删除结点操作*/
static void __hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{
struct hlist_node *next = n->next;
struct hlist_node **pprev = n->pprev;
*pprev = next;
if (next)
next->pprev = pprev;
}
static void hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{
__hlist_del(n);
n->next = LIST_POISON1;
n->pprev = LIST_POISON2;
}
/*链表头部添加结点*/
static void hlist_add_head(struct hlist_node *n, struct hlist_head *h)
{
struct hlist_node *first = h->first;
n->next = first;
if (first)
first->pprev = &n->next;
h->first = n;
n->pprev = &h->first;
}
/*结点next前加入结点n*/
/* next must be != NULL */
static void hlist_add_before(struct hlist_node *n,
struct hlist_node *next)
{
n->pprev = next->pprev;
n->next = next;
next->pprev = &n->next;
*(n->pprev) = n;
}
/*结点next后加入结点n*/
static void hlist_add_after(struct hlist_node *n,
struct hlist_node *next)
{
next->next = n->next;
n->next = next;
next->pprev = &n->next;
if(next->next)
next->next->pprev = &next->next;
}
/*遍历hlist相关宏*/
#define hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr,type,member)
#define hlist_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1; }); \
pos = pos->next)
#define hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }); \
pos = n)
#define hlist_for_each_entry(tpos, pos, head, member) \
for (pos = (head)->first; \
pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \
pos = pos->next)