这篇文章主要讨论使用Elasticdump工具做数据的备份和type删除。
Elasticsearch的备份,不像MYSQL的myslqdump那么方便,它需要一个插件进行数据的导出和导入进行备份和恢复操作,也就是插件:Elasticdump
1、Elasticdump的安装:
[root@master mnt]# npm install elasticdump

2、使用
[root@master bin]# pwd
/mnt/elasticsearch-head-master/node_modules/elasticdump/bin
[root@master bin]# ./elasticdump --help elasticdump: Import and export tools for elasticsearch version: 4.7.0 Usage: elasticdump --input SOURCE --output DESTINATION [OPTIONS] --input Source location (required) --input-index Source index and type (default: all, example: index/type) --output Destination location (required) --output-index Destination index and type (default: all, example: index/type) --limit How many objects to move in batch per operation limit is approximate for file streams (default: 100) --size How many objects to retrieve (default: -1 -> no limit) --debug Display the elasticsearch commands being used (default: false) --quiet Suppress all messages except for errors (default: false) --type What are we exporting? (default: data, options: [data, settings, analyzer, mapping, alias]) --delete Delete documents one-by-one from the input as they are moved. Will not delete the source index (default: false) --headers Add custom headers to Elastisearch requests (helpful when your Elasticsearch instance sits behind a proxy) (default: '{"User-Agent": "elasticdump"}') --params Add custom parameters to Elastisearch requests uri. Helpful when you for example want to use elasticsearch preference (default: null) --searchBody Preform a partial extract based on search results (when ES is the input, default values are if ES > 5 `'{"query": { "match_all": {} }, "stored_fields": ["*"], "_source": true }'` else `'{"query": { "match_all": {} }, "fields": ["*"], "_source": true }'` --sourceOnly Output only the json contained within the document _source Normal: {"_index":"","_type":"","_id":"", "_source":{SOURCE}} sourceOnly: {SOURCE} (default: false) --ignore-errors Will continue the read/write loop on write error (default: false) --scrollTime Time the nodes will hold the requested search in order. (default: 10m) --maxSockets How many simultaneous HTTP requests can we process make? (default: 5 [node <= v0.10.x] / Infinity [node >= v0.11.x] ) --timeout Integer containing the number of milliseconds to wait for a request to respond before aborting the request. Passed directly to the request library. Mostly used when you don't care too much if you lose some data when importing but rather have speed. --offset Integer containing the number of rows you wish to skip ahead from the input transport. When importing a large index, things can go wrong, be it connectivity, crashes, someone forgetting to `screen`, etc. This allows you to start the dump again from the last known line written (as logged by the `offset` in the output). Please be advised that since no sorting is specified when the dump is initially created, there's no real way to guarantee that the skipped rows have already been written/parsed. This is more of an option for when you want to get most data as possible in the index without concern for losing some rows in the process, similar to the `timeout` option. (default: 0) --noRefresh Disable input index refresh. Positive: 1. Much increase index speed 2. Much less hardware requirements Negative: 1. Recently added data may not be indexed Recommended to use with big data indexing, where speed and system health in a higher priority than recently added data. --inputTransport Provide a custom js file to use as the input transport --outputTransport Provide a custom js file to use as the output transport --toLog When using a custom outputTransport, should log lines be appended to the output stream? (default: true, except for `$`) --awsChain Use [standard](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/a-new-and-standardized-way-to-manage-credentials-in-the-aws-sdks/) location and ordering for resolving credentials including environment variables, config files, EC2 and ECS metadata locations _Recommended option for use with AWS_ --awsAccessKeyId --awsSecretAccessKey When using Amazon Elasticsearch Service protected by AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), provide your Access Key ID and Secret Access Key --awsIniFileProfile Alternative to --awsAccessKeyId and --awsSecretAccessKey, loads credentials from a specified profile in aws ini file. For greater flexibility, consider using --awsChain and setting AWS_PROFILE and AWS_CONFIG_FILE environment variables to override defaults if needed --transform A javascript, which will be called to modify documents before writing it to destination. global variable 'doc' is available. Example script for computing a new field 'f2' as doubled value of field 'f1': doc._source["f2"] = doc._source.f1 * 2; --httpAuthFile When using http auth provide credentials in ini file in form `user=<username> password=<password>` --support-big-int Support big integer numbers --retryAttempts Integer indicating the number of times a request should be automatically re-attempted before failing when a connection fails with one of the following errors `ECONNRESET`, `ENOTFOUND`, `ESOCKETTIMEDOUT`, ETIMEDOUT`, `ECONNREFUSED`, `EHOSTUNREACH`, `EPIPE`, `EAI_AGAIN` (default: 0) --retryDelay Integer indicating the back-off/break period between retry attempts (milliseconds) (default : 5000) --parseExtraFields Comma-separated list of meta-fields to be parsed --fileSize supports file splitting. This value must be a string supported by the **bytes** module. The following abbreviations must be used to signify size in terms of units b for bytes kb for kilobytes mb for megabytes gb for gigabytes tb for terabytes e.g. 10mb / 1gb / 1tb Partitioning helps to alleviate overflow/out of memory exceptions by efficiently segmenting files into smaller chunks that then be merged if needs be. --s3AccessKeyId AWS access key ID --s3SecretAccessKey AWS secret access key --s3Region AWS region --s3Bucket Name of the bucket to which the data will be uploaded --s3RecordKey Object key (filename) for the data to be uploaded --s3Compress gzip data before sending to s3 --tlsAuth Enable TLS X509 client authentication --cert, --input-cert, --output-cert Client certificate file. Use --cert if source and destination are identical. Otherwise, use the one prefixed with --input or --output as needed. --key, --input-key, --output-key Private key file. Use --key if source and destination are identical. Otherwise, use the one prefixed with --input or --output as needed. --pass, --input-pass, --output-pass Pass phrase for the private key. Use --pass if source and destination are identical. Otherwise, use the one prefixed with --input or --output as needed. --ca, --input-ca, --output-ca CA certificate. Use --ca if source and destination are identical. Otherwise, use the one prefixed with --input or --output as needed. --inputSocksProxy, --outputSocksProxy Socks5 host address --inputSocksPort, --outputSocksPort Socks5 host port --help This page Examples: # Copy an index from production to staging with mappings: elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=http://staging.es.com:9200/my_index \ --type=mapping elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=http://staging.es.com:9200/my_index \ --type=data # Backup index data to a file: elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=/data/my_index_mapping.json \ --type=mapping elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=/data/my_index.json \ --type=data # Backup and index to a gzip using stdout: elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=$ \ | gzip > /data/my_index.json.gz # Backup the results of a query to a file elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=query.json \ --searchBody '{"query":{"term":{"username": "admin"}}}' ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Learn more @ https://github.com/taskrabbit/elasticsearch-dump
3、elasticsearchdump的使用
'#拷贝analyzer如分词 elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=http://staging.es.com:9200/my_index \ --type=analyzer '#拷贝映射 elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=http://staging.es.com:9200/my_index \ --type=mapping '#拷贝数据 elasticdump \ --input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \ --output=http://staging.es.com:9200/my_index \ --type=data
'#拷贝所有索引
elasticdump
--input=http://production.es.com:9200/
--output=http://staging.es.com:9200/
--all=true
# 备份到标准输出,且进行压缩(这里有一个需要注意的地方,我查询索引信息有6.4G,用下面的方式备份后得到一个789M的压缩文件,这个压缩文件解压后有19G):
elasticdump \
--input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \
--output=$ \
| gzip > /data/my_index.json.gz
# 把一个查询结果备份到文件中
elasticdump \
--input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \
--output=query.json \
--searchBody '{"query":{"term":{"username": "admin"}}}'
# Copy a single shard data:
elasticdump \
--input=http://es.com:9200/api \
--output=http://es.com:9200/api2 \
--params='{"preference" : "_shards:0"}'
# Backup aliases to a file
elasticdump \
--input=http://es.com:9200/index-name/alias-filter \
--output=alias.json \
--type=alias
# Import aliases into ES
elasticdump \
--input=./alias.json \
--output=http://es.com:9200 \
--type=alias
# Backup templates to a file
elasticdump \
--input=http://es.com:9200/template-filter \
--output=templates.json \
--type=template
# Import templates into ES
elasticdump \
--input=./templates.json \
--output=http://es.com:9200 \
--type=template
# Split files into multiple parts
elasticdump \
--input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \
--output=/data/my_index.json \
--fileSize=10mb
# Export ES data to S3
elasticdump \
--input=http://production.es.com:9200/my_index \
--s3Bucket "${bucket_name}" \
--s3AccessKeyId "${access_key_id}" \
--s3SecretAccessKey "${access_key_secret}" \
--s3RecordKey "${file_name}"
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
5943560 查看本文章


3、实例操作
1. 将es集群中的某个company的数据导出到文件中。
[root@master bin]# ./elasticdump --input http://192.168.200.100:9200/company --output /mnt/company.json Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:39:20 GMT | starting dump Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:39:20 GMT | got 2 objects from source elasticsearch (offset: 0) Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:39:20 GMT | sent 2 objects to destination file, wrote 2 Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:39:20 GMT | got 0 objects from source elasticsearch (offset: 2) Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:39:20 GMT | Total Writes: 2 Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:39:20 GMT | dump complete

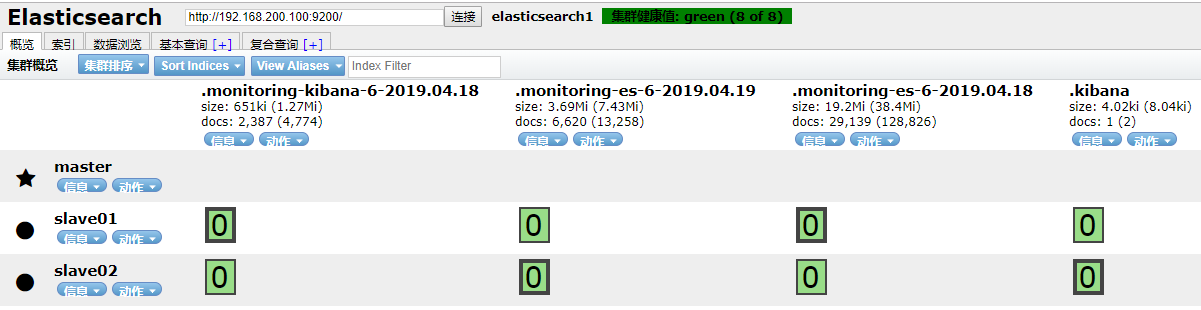
2、删除该index下的data
[root@master mnt]# curl -XDELETE '192.168.200.100:9200/company'
查看删除情况:
3、恢复:
[root@master bin]# ./elasticdump elasticdump --input /mnt/company.json --output "http://192.168.200.100:9200/company" Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:46:56 GMT | starting dump Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:46:56 GMT | got 2 objects from source file (offset: 0) Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:46:57 GMT | sent 2 objects to destination elasticsearch, wrote 2 Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:46:57 GMT | got 0 objects from source file (offset: 2) Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:46:57 GMT | Total Writes: 2 Fri, 19 Apr 2019 03:46:57 GMT | dump complete

