stat函数和stat命令
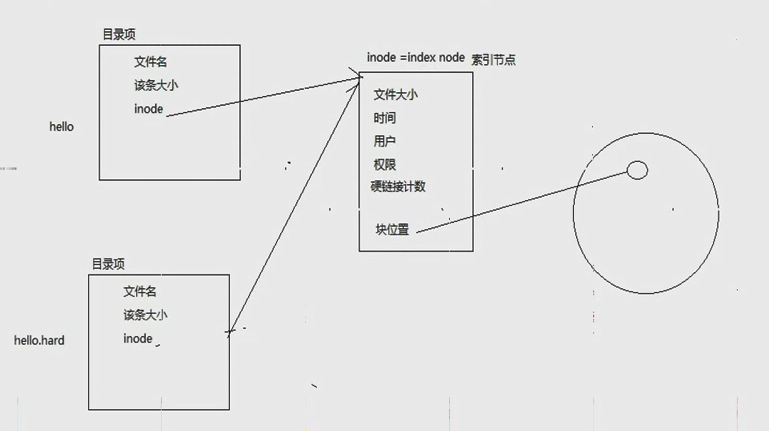
linux文件里的【inode = index node】解释:要理解inode必须了解磁盘和【目录项】,inode实际是连接【目录项】和磁盘的中间物质。
- 图里的大圈代表硬件的磁盘,里面的小圈代表某个文件存储在磁盘上了。
- 【inode = index node】的node(承载node信息的结构体是:stat,stat的定义在后面 )里面有:
- 文件大小
- 文件的最后修改时间
- 文件的所属用户
- 文件的权限
- 硬链接计数(ls -l 显示出来的数字)
- 块位置:指定文件存储在磁盘的具体位置。
- 下图中的hello是个普通文件,hello.hard是hello的硬链接
- 文件夹里放的就是每个文件的【目录项】如下图,【目录项】里有:
- 文件名
- 该目录项的大小
- 文件的类型
- inode
如何查看文件的【inode】呢?使用【-i】选项
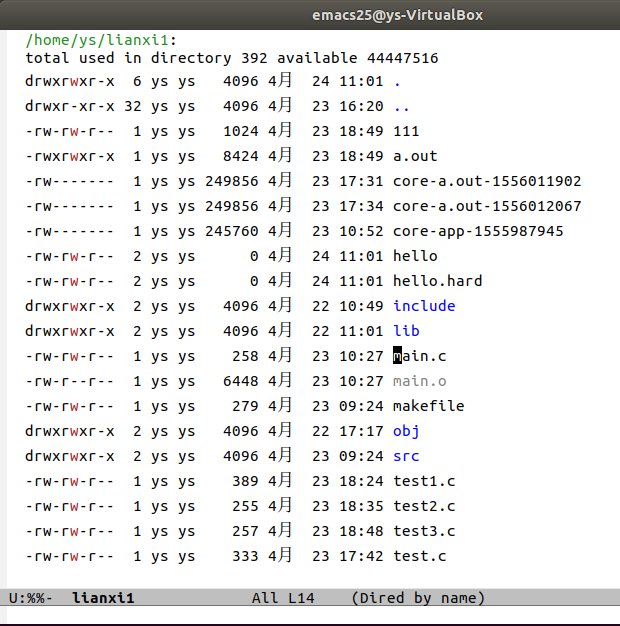
ls -li 文件名执行结果:
ys@ys-VirtualBox:~/lianxi1$ ls -li hello hello.hard 3801352 -rw-rw-r-- 2 ys ys 0 4月 24 11:01 hello 3801352 -rw-rw-r-- 2 ys ys 0 4月 24 11:01 hello.hard发现hello和hello.hard的inode(3801352)是相同的,也就说明了,只在磁盘上存了一份。
如何查看目录项呢?用emacs或者vim打开目录(lianxi1),截图如下。但是看不到文件的【inode】。
1,stat函数:取得指定文件的文件属性,文件属性存储在结构体stat里。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *statbuf);
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
struct stat 结构体:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
st_dev:设备ID,不太常用
st_ino:【inode】,【inode】是啥?不知道就看上面关于【inode】的解释
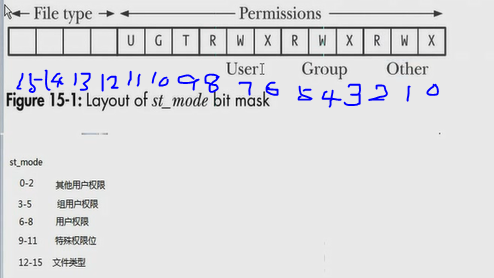
st_mode:文件的类型和权限,共16位,如下图。
0-11位控制文件的权限
12-15位控制文件的类型
0-2比特位:其他用户权限
3-5比特位:组用户权限
6-8比特位:本用户权限
9-11比特位:特殊权限
12-15比特位:文件类型(因为文件类型只有7中,所以用12-14位就够了
文件类型的宏如下(下面的数字是8进制):
- S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket
- S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link(软连接)
- S_IFREG 0100000 regular file(普通文件)
- S_IFBLK 0060000 block device(块设备文件)
- S_IFDIR 0040000 directory(目录)
- S_IFCHR 0020000 character device(字符设备文件)
- S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO(管道)
另一种文件类型的宏:
S_ISREG(m) is it a regular file?
S_ISDIR(m) directory?
S_ISCHR(m) character device?
S_ISBLK(m) block device?
S_ISFIFO(m) FIFO (named pipe)?
S_ISLNK(m) symbolic link? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)
S_ISSOCK(m) socket? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)文件权限的宏如下:
S_ISUID 04000 set-user-ID bit
S_ISGID 02000 set-group-ID bit (see below)
S_ISVTX 01000 sticky bit (see below)
S_IRWXU 00700 owner has read, write, and execute permission
S_IRUSR 00400 owner has read permission
S_IWUSR 00200 owner has write permission
S_IXUSR 00100 owner has execute permission
S_IRWXG 00070 group has read, write, and execute permission
S_IRGRP 00040 group has read permission
S_IWGRP 00020 group has write permission
S_IXGRP 00010 group has execute permission
S_IRWXO 00007 others (not in group) have read, write, and
execute permission
S_IROTH 00004 others have read permission
S_IWOTH 00002 others have write permission
S_IXOTH 00001 others have execute permissionst_nlink:硬连接计数
st_uid:这个文件所属用户的ID
st_gid:这个文件所属用户的组ID
st_rdev:特殊设备的ID,不太常用
st_size:文件的大小
st_blksize:不明是干啥的
st_blocks:不明是干啥的
struct timespec st_atim:最后访问的时间
struct timespec st_mtim:最后修改的时间
struct timespec st_ctim:最后状态改变的时间
struct timespec { __kernel_time_t tv_sec; /* seconds */当前时间到1970.1.1 00:00:00的秒数 long tv_nsec; /* nanoseconds *//纳秒数(不知道从哪到哪的) }; 1s 秒 = 1000ms 毫秒 1ms 毫秒 = 1000us 微秒 1us 微秒 = 1000ns 纳秒
pathname:文件名
返回值:0代表成功;-1代表失败,并设置error
例子:statbuf是结构体stat,可以看出来st_mode是个10进制的数字。
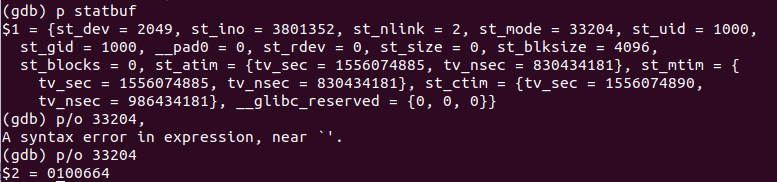
st_mode
用gdb显示st_mode,发现返回的st_mode是个10进制的数字,用gdb的【p/o】(o代表用8进制表示)命令把10进制的33204转换成了8进制的【0100664】,第一个0代笔是8进制,后三位的【100】代表文件类型,从上面的说明可以看出来【100】代表普通文件,最后三位的【664】代表这个文件的权限(本用户:rw-,组用户:rw-,其他用户:r--)。所以从st_mode里就可以得知文件的类型和权限设置(只使用了16个比特位,真的好节省空间,牛逼!)
st_uid
st_gid
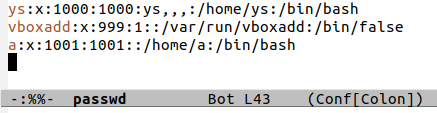
发现st_uid和st_gid是1000,但这个1000怎么和用户对应上呢,查看/etc/passwd文件,发现用于ys的uid和gid都是1000,所以就对应上了。
stat命令,是stat函数对应,执行结果如下:
ys@ys-VirtualBox:~/lianxi1$ stat hello
File: hello
Size: 11 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: 801h/2049d Inode: 3801352 Links: 2
Access: (0764/-rwxrw-r--) Uid: ( 1000/ ys) Gid: ( 1000/ ys)
Access: 2019-04-24 17:02:39.199461489 +0800
Modify: 2019-04-24 16:54:16.407461489 +0800
Change: 2019-04-24 17:03:44.927461489 +0800