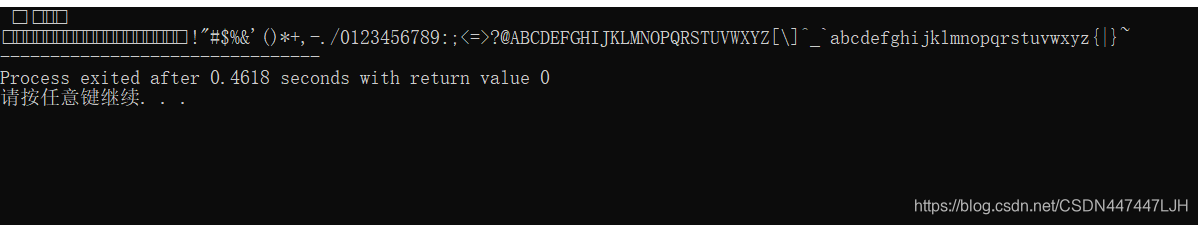
//将ASCII值在1-127之间的字符写入硬盘文件,文件读取这些字符时,显示出来
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char ch;
if((fp=fopen("demo.bin","wb"))==NULL)//二进制写方式打开文件
{
printf("Failure to open demo.bin!\n");
exit(0);
}
for(int i=0;i<128;i++)
{
fputc(i,fp);
}
fclose(fp);
if((fp=fopen("demo.bin","rb"))==NULL)//二进制读方式打开文件
{
printf("Failure to open demo.bin!\n");
exit(0);
}
//相同替换
//ch=fgetc(fp); 函数feof()判断是否读到文件末尾 +若fp已正确定义并指向某个文件,当未遇到该文件结束标志时函数feof(fp)的值为0,否则为非0值
//while(!feof(fp))
//{
// putchar(ch);
// ch=fgetc(fp);
// }
while((ch=fgetc(fp))!=EOF) //文件中读取字符
{
putchar(ch);//显示字符
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
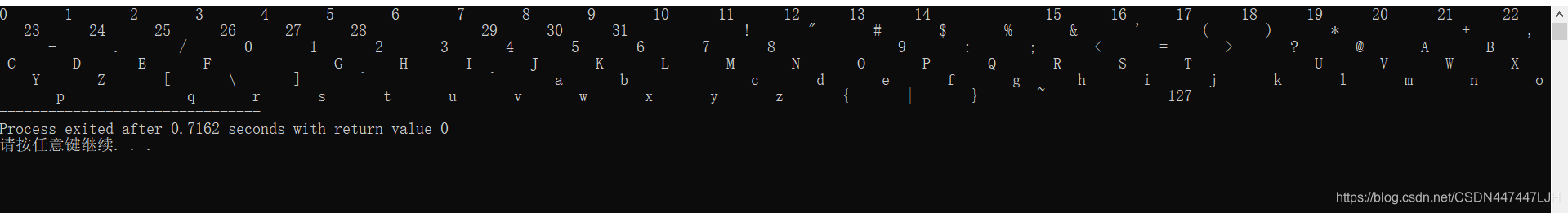
//将ASCII值在1-127之间的字符写入硬盘文件,从文件中读取这些字符时,判断是否可打印
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<ctype.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char ch;
if((fp=fopen("demo.bin","wb"))==NULL)//二进制写方式打开文件
{
printf("Failure to open demo.bin!\n");
exit(0);
}
for(int i=0;i<128;i++)
{
fputc(i,fp);//将字符ASCII值写入文件
}
fclose(fp);
if((fp=fopen("demo.bin","rb"))==NULL)//二进制读方式打开文件
{
printf("Failure to open demo.bin!\n");
exit(0);
}
//相同替换
//ch=fgetc(fp); 函数feof()判断是否读到文件末尾
//while(!feof(fp))
//{
// putchar(ch);
// ch=fgetc(fp);
// }
while((ch=fgetc(fp))!=EOF) //文件中读取字符
{
if(isprint(ch)) //判断是否为可打印字符
printf("%c\t",ch);
else
printf("%d\t",ch);//可打印,显示ASCII值
//putchar(ch);//显示字符
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
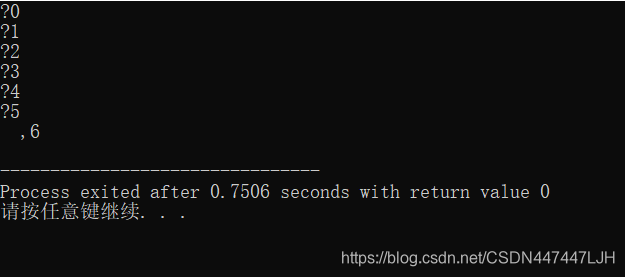
 //文件中数据读出时的相关情况
//文件中数据读出时的相关情况
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int ch;
FILE *fp;
long pos;//显示文件数据输出时,“位于文件中的位置”
if((fp=fopen("demo.1.txt","r"))==NULL)
{
printf("Failure to open demo.1.txt!\n");
exit(0);
}
//ch=fgetc(fp);
pos=ftell(fp);
ch=fgetc(fp);
while(!feof(fp))
//使用 while(!feof(fp))效果更好,EOF在文件读取结束和读取出错时都将返回相同的结果
//判断读取是否出错,使用ferror判断
{
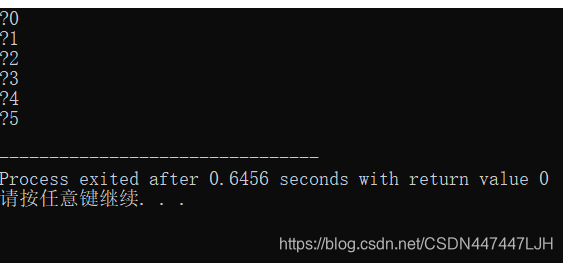
printf("%c,%ld\n",ch,pos);
pos=ftell(fp);
ch=fgetc(fp);
//putchar(ch);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int ch;
FILE *fp;
long pos;//显示文件数据输出时,“位于文件中的位置”
if((fp=fopen("demo.1.txt","r"))==NULL)
{
printf("Failure to open demo.1.txt!\n");
exit(0);
}
//ch=fgetc(fp);
pos=ftell(fp);
ch=fgetc(fp);
while(!feof(fp))
//使用 while(!feof(fp))效果更好,EOF在文件读取结束和读取出错时都将返回相同的结果
//判断读取是否出错,使用ferror判断
{
printf("%c,%ld\n",ch,pos);
pos=ftell(fp);
ch=fgetc(fp);
//putchar(ch);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
hello将之前的覆盖
w的打开方式是如果文件已经存在就会覆盖
想添加到末尾就是要用“a"
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void Fun(char *fname,char *st)
{
FILE *myf;
int i;
myf=fopen(fname,"w");
if (myf == NULL)
{
printf("cannot open the file.\n");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;i<strlen(st); i++)
{
fputc(st[i],myf);
}
fclose(myf);
}
int main()
{
Fun("test","new world");
Fun("test","hello");
return 0;
}
