 版权声明:署名,允许他人基于本文进行创作,且必须基于与原先许可协议相同的许可协议分发本文 (Creative Commons)
版权声明:署名,允许他人基于本文进行创作,且必须基于与原先许可协议相同的许可协议分发本文 (Creative Commons)
文章目录
简易代码 · 扫描文件夹
编译环境 + 结果截图
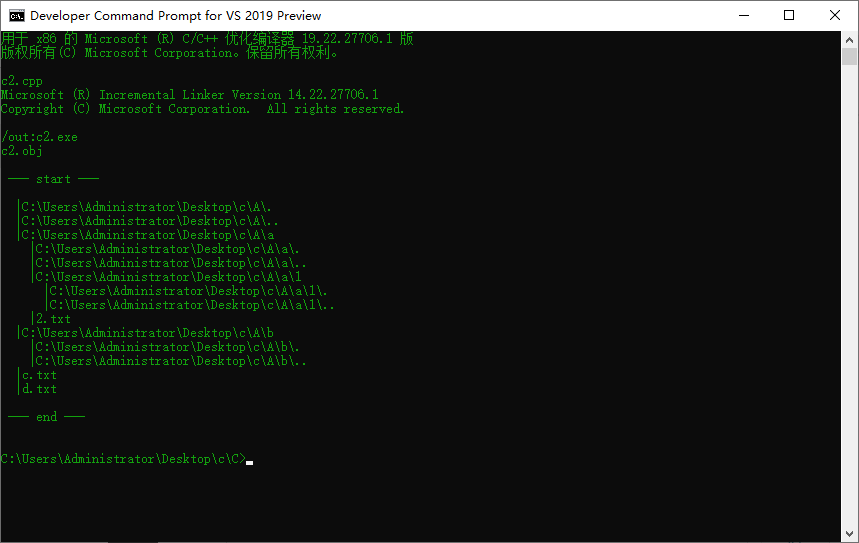
#pragma warning(disable : 4530)
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <io.h>
using namespace std;
#define ArrLnt 200
void fnFind(char *fileName)
{
char fileNameNew[ArrLnt];
intptr_t findHandle;
_finddata_t findData;
strcpy(fileNameNew, fileName);
strcat(fileNameNew, "\\*.*");
findHandle = _findfirst(fileNameNew, &findData);
if (findHandle == -1)
return;
static char indent[ArrLnt];
strcat(indent, " ");
do
{
cout << indent << "|";
if (findData.attrib == _A_SUBDIR)
{
strcpy(fileNameNew, fileName);
strcat(fileNameNew, "\\");
strcat(fileNameNew, findData.name);
cout << fileNameNew << endl;
if (strcmp(findData.name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(findData.name, "..") == 0)
continue;
fnFind(fileNameNew);
indent[strlen(indent) - 2] = '\0';
}
else
{
cout << findData.name << endl;
}
} while (_findnext(findHandle, &findData) == 0);
_findclose(findHandle);
}
int main()
{
char fileName[ArrLnt] = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\c\\A";
cout << "\n --- start --- \n"
<< endl;
fnFind(fileName);
cout << "\n --- end --- \n"
<< endl;
return 0;
}
错误:无法从“std::string”转换为“char *”
C++ 将 std::string 转换为 char*,必须通过string对象的c_str()方法,获取C-style的字符串。
如果希望效率高,还是使用[](可能会超出边界)来访问,如果希望稳定性好,最好使用at()来访问。
_finddata_t、_findfirst、_findnext和_findclose
#include <io.h>
_finddata_t 文件信息结构体
struct _finddata_t
{
unsigned attrib; // attribute
time_t time_create; // # define time_t long
time_t time_access; //
time_t time_write; //
_fsize_t size; // # define _fsize_t unsigned long
char name[260]; //
};
file attribute 文件属性
cout
<< _A_NORMAL << endl // 正常 0
<< _A_RDONLY << endl // 只读 1
<< _A_HIDDEN << endl //隐藏 2
<< _A_SYSTEM << endl //系统 4
<< _A_SUBDIR << endl //子文件夹 16
<< _A_ARCH << endl //存档 32 archived file
<< endl;
这些都是在头文件中定义的宏,是一个无符号整型。
_findfirst
long _findfirst(const char *_FileName, struct _finddata_t *_FindData);
- 第一个参数为文件名,可以用
*.*来查找所有文件,也可以用*.cpp来查找.cpp文件。 - 第二个参数是
_finddata_t结构体指针。若查找成功,返回文件句柄,若失败,返回-1。
char *fileName = "C:";
intptr_t findHandle;
_finddata_t findData;
_findfirst(fileName, findData);
_findnext
intptr_t _findfirst64i32(const char *_FileName, _finddata64i32_t *_FindData)
第一个参数为文件句柄,第二个参数为_finddata_t结构体指针。若查找成功,返回0,失败返回-1。
intptr_t findHandle;
_finddata_t findData;
_findnext(findHandle, &findData);
typedef long long intptr_t;
_findclose
int __cdecl _findclose(intptr_t _FindHandle);只有一个参数,文件句柄。若关闭成功返回0,失败返回-1。
intptr_t findHandle;
_findclose(findHandle);
#pragma warning(disable : 4530)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cstring> // for strcat()
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <io.h>
using namespace std;
#define PathLength 200
vector<char *> getFilesList(char *dir)
{
vector<char *> allPath;
char dirNew[PathLength];
strcpy(dirNew, dir);
strcat(dirNew, "\\*.*"); // 在目录后面加上"\\*.*"进行第一次搜索
cout << dirNew << endl;
system("pause");
intptr_t handle;
_finddata_t findData;
if ((handle = _findfirst(dirNew, &findData)) == -1)
{ // 检查是否成功
cout << "can not found the file ... " << endl;
return allPath;
}
do
{
if (findData.attrib & _A_SUBDIR) // 是否含有子目录
{
// 若该子目录为"."或"..",则进行下一次循环,否则输出子目录名,并进入下一次搜索
if (strcmp(findData.name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(findData.name, "..") == 0)
continue;
cout << findData.name << "\t<dir>\n";
// 在目录后面加上"\\"和搜索到的目录名进行下一次搜索
strcpy(dirNew, dir);
strcat(dirNew, "\\");
strcat(dirNew, findData.name);
vector<char *> tempPath = getFilesList(dirNew);
allPath.insert(allPath.end(), tempPath.begin(), tempPath.end());
}
else //不是子目录,即是文件,则输出文件名和文件的大小
{
char *filePath = new char[PathLength];
strcpy(filePath, dir);
strcat(filePath, "\\");
strcat(filePath, findData.name);
allPath.push_back(filePath);
cout << filePath << "\t" << findData.size << " bytes.\n";
}
} while (_findnext(handle, &findData) == 0);
_findclose(handle); // 关闭搜索句柄
return allPath;
}
int main()
{
char dir[PathLength] = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\c";
// cout << "\nEnter a directory: ";
// cin >> dir;
cout << "\nOutput all file paths :" << endl;
getFilesList(dir);
// for (auto path : getFilesList(dir))
// cout << path << endl;
return 0;
}
Directory 目录
- C++ 中vector的使用方法 - 那年聪聪 - CSDN博客
- C++读取文件夹中所有文件的路径,包含子文件夹 - pan_jinquan的博客 - CSDN博客
- windows下c++读取一个目录下的所有文件 - FeiFreedom的博客 - CSDN博客
- C\C++ 获取当前路径 - cscmaker的专栏 - CSDN博客
unistd.h
unistd.h在windows下面是没有的 - 为了孩子他娘 - CSDN博客
- 在 Linux 下编写的程序是默认包含这个头文件的,不需要特别的去包含这个文件。
- 在 windows 下面没有这个东西,所以在 windows下面需要写一下这个头文件
自建一个 unistd.h ,文件内容为
#ifndef _UNISTD_H
#define _UNISTD_H
#include <io.h>
#include <process.h>
#endif /* _UNISTD_H */
其作用等同于 windows 下的 windows.h 。
chdir、getcwd
#include <stdio.h>
#include <direct.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (chdir(argv[1]) == -1)
{ // 将当前工作目录切换到 argv[1](从命令行传进来的路径)
perror("chdir");
return -1;
}
printf("\n Current Working Directory : %s!\n", getcwd(NULL, 0));
return 0;
}
getcwd
Get Current Working Directory
#include <stdio.h>
#include <direct.h>
int main()
{
printf("\nCurrent Working Directory : %s\n", getcwd(NULL, 0));
return 0;
}
fopen
FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode);
fopen - C++ Reference
mode
C string containing a file access mode.
| mode | |
|---|---|
| r | read: Open file for input operations. The file must exist. |
| w | write: Create an empty file for output operations. If a file with the same name already exists, its contents are discarded and the file is treated as a new empty file. |
| a | append: Open file for output at the end of a file. Output operations always write data at the end of the file, expanding it. Repositioning operations (fseek, fsetpos, rewind) are ignored. The file is created if it does not exist. |
| r+ | read/update: Open a file for update (both for input and output). The file must exist. |
| w+ | write/update: Create an empty file and open it for update (both for input and output). If a file with the same name already exists its contents are discarded and the file is treated as a new empty file. |
| a+ | append/update: Open a file for update (both for input and output) with all output operations writing data at the end of the file. Repositioning operations (fseek, fsetpos, rewind) affects the next input operations, but output operations move the position back to the end of file. The file is created if it does not exist. |
fscanf
fprintf
fclose
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
FILE *fp=fopen("in.txt","r");
char cr;
fscanf(fp,"%c",&cr);
fclose(fp);
fp=fopen("out.txt","w");
fprintf(fp,"%c",cr);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
freopen
FILE * freopen ( const char * filename, const char * mode, FILE * stream );
- FILE * stream 通常使用标准流文件(stdin/stdout/stderr)
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); //输入重定向,输入数据将从in.txt文件中读取
freopen("out.txt","w",stdout); //输出重定向,输出数据将保存在out.txt文件中
freopen("CON","r",stdin); //从控制台读入
freopen("CON","w",stdout);//从控制台输出
fclose(stdin);//关闭文件
fclose(stdout);//关闭文件
把预定义的标准流文件定向到由 filename 指定的文件中。
标准流文件具体是指 stdin、stdout和stderr。其中
- stdin是标准输入流,默认为键盘
- stdout是标准输出流,默认为屏幕
- stderr是标准错误流,默认为屏幕。
通过调用freopen,就可以修改标准流文件的默认值,实现重定向。
若要恢复句柄,可以重新打开标准控制台设备文件,只是这个设备文件的名字是与操作系统相关的。
DOS/Windows
freopen("CON", "r", stdin);
Linux
freopen("/dev/console", "r", stdin);
system
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
system("color 02");
system("calc");
system("title shotdown");
// system("pause");
printf("ha\n");
Sleep(1000);
system("cls");
system("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\c\\c.txt");
return 0;
}
/、…、. 根目录、父目录、当前目录
/ 根目录
…、…/ 上一层目录(父目录)
.、./ 当前目录
文件路径中 /、\ 斜杠、反斜杠区别
-
一般在 Windows 中使用
\、\\和/没有本质区别。 -
在 Linux 和 Unix 中使用
/。
\一般是表示本地目录的,C:\windows/主要表示远程电脑或者网络地址,https://www.baidu.com
U盘
C 用文件指针操作文件。
C++ 基于**文件流(即非标准的输入输出)**操作文件。
程序预期功能:自我复制,短暂等待后启动(能否植入注册表),读取文件类型,删除或加密文件