前言
底部切换效果已经很常见了,本文介绍其中的一种实现方法:FrameLayout+Fragment
本案例已上传至Github,你可以查看完整源码,也可以下载demo apk体验一下
实现效果如下:
Tab切换
Step1:创建Fragment
创建四个页卡所表示的Fragment以及其布局文件,图中每个页卡都是一个Fragment(碎片)
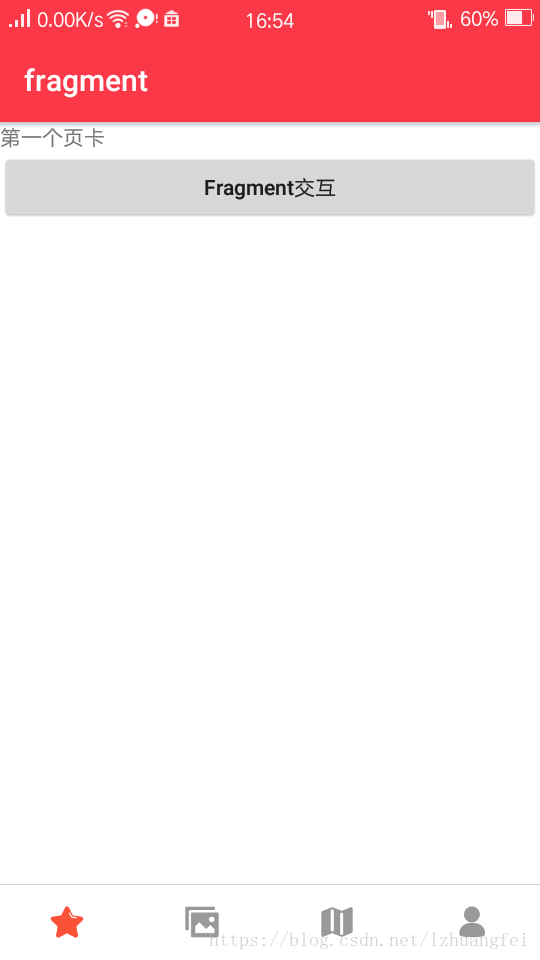
先创建第一个页卡的Fragment以及布局文件
fragment_tab1.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.zhuangfei.fragment.TabFragment1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一个页卡" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/tab1_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:text="Fragment交互"/>
</LinearLayout>TabFragment1.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
*第一个页卡
* A simple {@link Fragment} subclass.
*/
public class TabFragment1 extends Fragment {
View view;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_tab1, container, false);
Button button=view.findViewById(R.id.tab1_btn);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(getContext(),"findViewById()时不要忘了前边的view."
,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
return view;
}
}以下copy3份,并简单的修改一下显示的文字
fragment_tab2.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.zhuangfei.fragment.TabFragment1">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="第二个页卡" />
</LinearLayout>TabFragment2.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
*第二个页卡
* A simple {@link Fragment} subclass.
*/
public class TabFragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_tab2, container, false);
}
}fragment_tab3.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.zhuangfei.fragment.TabFragment1">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="第三个页卡" />
</LinearLayout>TabFragment3.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
*第三个页卡
* A simple {@link Fragment} subclass.
*/
public class TabFragment3 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_tab3, container, false);
}
}fragment_tab4.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.zhuangfei.fragment.TabFragment1">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="第四个页卡" />
</LinearLayout>TabFragment4.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
*第四个页卡
* A simple {@link Fragment} subclass.
*/
public class TabFragment4 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_tab4, container, false);
}
}创建主页面
四个Fragment应该怎么显示在主页面上呢,这里用到了帧布局,主页面的底部是底部导航的布局,中间是一个帧布局
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<!--帧布局,承载四个TAB的Fragment-->
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/id_framelayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@color/app_white" />
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1px"
android:background="@color/app_line"/>
<include layout="@layout/view_bottom" />
</LinearLayout>
view_bottom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/bottomLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="@color/app_white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<!-- 主界面底部4个TAB -->
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/id_tab1_layout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/id_tab1_imageview"
android:layout_width="25dp"
android:layout_height="25dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_tab1" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/id_tab2_layout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/id_tab2_imageview"
android:layout_width="25dp"
android:layout_height="25dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_tab2" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/id_tab3_layout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/id_tab3_imageview"
android:layout_width="25dp"
android:layout_height="25dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_tab3" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/id_tab4_layout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/id_tab4_imageview"
android:layout_width="25dp"
android:layout_height="25dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_tab4" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>MainActivity.java
package com.zhuangfei.fragment;
import android.media.Image;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
/**
* 主页面,显示多个Fragment
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
// 创建Fragment对象
private TabFragment1 tabFragment1;
private TabFragment2 tabFragment2;
private TabFragment3 tabFragment3;
private TabFragment4 tabFragment4;
private ImageView tabImageView1;
private ImageView tabImageView2;
private ImageView tabImageView3;
private ImageView tabImageView4;
private LinearLayout tabLayout1;
private LinearLayout tabLayout2;
private LinearLayout tabLayout3;
private LinearLayout tabLayout4;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
select(0);
}
private void initView() {
tabImageView1=findViewById(R.id.id_tab1_imageview);
tabImageView2=findViewById(R.id.id_tab2_imageview);
tabImageView3=findViewById(R.id.id_tab3_imageview);
tabImageView4=findViewById(R.id.id_tab4_imageview);
tabLayout1=findViewById(R.id.id_tab1_layout);
tabLayout2=findViewById(R.id.id_tab2_layout);
tabLayout3=findViewById(R.id.id_tab3_layout);
tabLayout4=findViewById(R.id.id_tab4_layout);
tabLayout1.setOnClickListener(this);
tabLayout2.setOnClickListener(this);
tabLayout3.setOnClickListener(this);
tabLayout4.setOnClickListener(this);
}
/**
* 初始化Tab的状态
*/
public void initTab() {
int color = getResources().getColor(R.color.app_gray);
// 更改图片颜色为暗色
tabImageView1.setColorFilter(color);
tabImageView2.setColorFilter(color);
tabImageView3.setColorFilter(color);
tabImageView4.setColorFilter(color);
}
/**
* 选中第i个Tab时的处理
*
* @param i
*/
public void select(int i) {
// 得到Fragment管理器以及事务
FragmentManager manager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = manager.beginTransaction();
initTab();
int color = getResources().getColor(R.color.app_orange);
switch (i) {
case 0:
tabImageView1.setColorFilter(color);
if (tabFragment1 == null) {
tabFragment1 = new TabFragment1();
}
transaction.replace(R.id.id_framelayout, tabFragment1);
break;
case 1:
tabImageView2.setColorFilter(color);
if (tabFragment2 == null) {
tabFragment2 = new TabFragment2();
}
transaction.replace(R.id.id_framelayout, tabFragment2);
break;
case 2:
tabImageView3.setColorFilter(color);
if (tabFragment3 == null) {
tabFragment3 = new TabFragment3();
}
transaction.replace(R.id.id_framelayout, tabFragment3);
break;
case 3:
tabImageView4.setColorFilter(color);
if (tabFragment4 == null) {
tabFragment4 = new TabFragment4();
}
transaction.replace(R.id.id_framelayout, tabFragment4);
break;
default:
break;
}
transaction.commit();
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.id_tab1_layout:
select(0);
break;
case R.id.id_tab2_layout:
select(1);
break;
case R.id.id_tab3_layout:
select(2);
break;
case R.id.id_tab4_layout:
select(3);
break;
}
}
}
本文用的是replace()方法来替换显示的Fargment,这种方法的优缺点:
优点:使用简单
缺点:会导致Fargment在每次切换时都实例化一个对象,性能有影响,并且Fargment有嵌套时会出现内部数据消失的问题
还可以使用add()、show()、hide()实现Fragment切换,该方法的优缺点:
优点:提升性能
缺点:可能会出现重影问题
当然,上面提到的两个问题都是有解决方法的,后续的文章中将使用add()、show()、hide()实现Fragment切换,敬请期待…