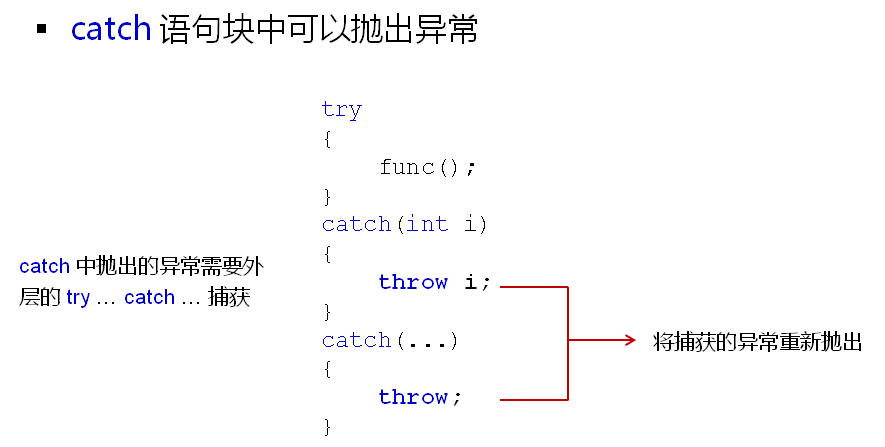
为什么要在catch中重新抛出异常?

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void Demo()
{
try
{
try
{
throw 'c';
}
catch(int i)
{
cout << "Inner: catch(int i)" << endl;
throw i;
}
catch(...)
{
cout << "Inner: catch(...)" << endl;
throw;
}
}
catch(...)
{
cout << "Outer: catch(...)" << endl;
}
}
/*
假设: 当前的函数是第三方库中的函数,因此,我们无法修改源代码
函数名: void func(int i)
抛出异常的类型: int
-1 ==》 参数异常
-2 ==》 运行异常
-3 ==》 超时异常
*/
void func(int i)
{
if( i < 0 )
{
throw -1;
}
if( i > 100 )
{
throw -2;
}
if( i == 11 )
{
throw -3;
}
cout << "Run func..." << endl;
}
void MyFunc(int i)
{
try
{
func(i);
}
catch(int i)
{
switch(i)
{
case -1:
throw "Invalid Parameter";
break;
case -2:
throw "Runtime Exception";
break;
case -3:
throw "Timeout Exception";
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// Demo();
try
{
MyFunc(11);
}
catch(const char* cs)
{
cout << "Exception Info: " << cs << endl;
}
return 0;
}


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
};
class Exception : public Base
{
int m_id;
string m_desc;
public:
Exception(int id, string desc)
{
m_id = id;
m_desc = desc;
}
int id() const
{
return m_id;
}
string description() const
{
return m_desc;
}
};
/*
假设: 当前的函数式第三方库中的函数,因此,我们无法修改源代码
函数名: void func(int i)
抛出异常的类型: int
-1 ==》 参数异常
-2 ==》 运行异常
-3 ==》 超时异常
*/
void func(int i)
{
if( i < 0 )
{
throw -1;
}
if( i > 100 )
{
throw -2;
}
if( i == 11 )
{
throw -3;
}
cout << "Run func..." << endl;
}
void MyFunc(int i)
{
try
{
func(i);
}
catch(int i)
{
switch(i)
{
case -1:
throw Exception(-1, "Invalid Parameter");
break;
case -2:
throw Exception(-2, "Runtime Exception");
break;
case -3:
throw Exception(-3, "Timeout Exception");
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
try
{
MyFunc(11);
}
catch(const Exception& e)
{
cout << "Exception Info: " << endl;
cout << " ID: " << e.id() << endl;
cout << " Description: " << e.description() << endl;
}
catch(const Base& e)
{
cout << "catch(const Base& e)" << endl;
}
return 0;
}