我们先看看我们在没有spring之前,程序间是怎么解耦的。
创建一个maven工程,整体的目录结构

1.创建dao层
IAccountDao.java
package com.itzn.dao; public interface IAccountDao { void save(); }
AccountDaoImpl.java
package com.itzn.dao; public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { public void save() { System.out.println("保存账户"); } }
2.创建service层
IAccountService.java
package com.itzn.service; public interface IAccountService { void save(); }
AccountServiceImpl .java
package com.itzn.service; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itzn.factory.BeanFactory; public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { //默认不解耦方式 //private IAccountDao iAccountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); private IAccountDao iAccountDao =(IAccountDao)BeanFactory.getBean("accountDao"); public void save() { iAccountDao.save(); } }
3.创建配置文件bean.properties
accountService=com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl
accountDao=com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl
4.创建Bean工厂层
BeanFactory.java
package com.itzn.factory; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; public class BeanFactory { /** * 容器 */ private static Map<String, Object> beans; private static Properties props; static { try { //实例化对象 props = new Properties(); //获取properties文件流对象 InputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties"); props.load(in); beans = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration keys = props.keys(); while (keys.hasMoreElements()) { String key = keys.nextElement().toString(); String beanPath = props.getProperty(key); Object value = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance(); beans.put(key, value); } } catch (Exception e) { throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("dfdf"); } } /** * 单例获取对象 * * @param beanName * @return */ public static Object getBean(String beanName) { return beans.get(beanName); } /** * 多实例 * @param beanName * @return */ // public static Object getBean(String beanName) { // Object bean = null; // try { // String beanPath = props.getProperty(beanName); // bean = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance(); // } catch (Exception e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // return bean; // } }
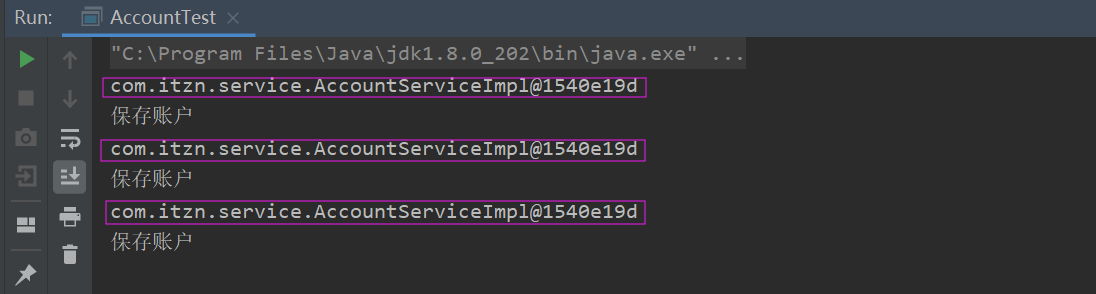
5.测试
AccountTest .java
package com.itzn.ui; import com.itzn.factory.BeanFactory; import com.itzn.service.IAccountService; public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { IAccountService iAccountService= (IAccountService) BeanFactory.getBean("accountService"); System.out.println(iAccountService); iAccountService.save(); } } }
测试结果
spring基于XML的IOC环境搭建入门
下面来看看使用Spring
1.新建maven工程,到spring引用,这里我们用5.0.2.RELEASE版本
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.itzn</groupId> <artifactId>day01_easy_02spring</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2.dao层
IAccountDao.java
package com.itzn.dao; public interface IAccountDao { void save(); }
AccountDaoImpl.java
package com.itzn.dao; public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { public void save() { System.out.println("保存账户"); } }
3.service层
IAccountService.java
package com.itzn.service; public interface IAccountService { void save(); }
AccountServiceImpl.java
package com.itzn.service; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { private IAccountDao iAccountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); public void save() { iAccountDao.save(); } }
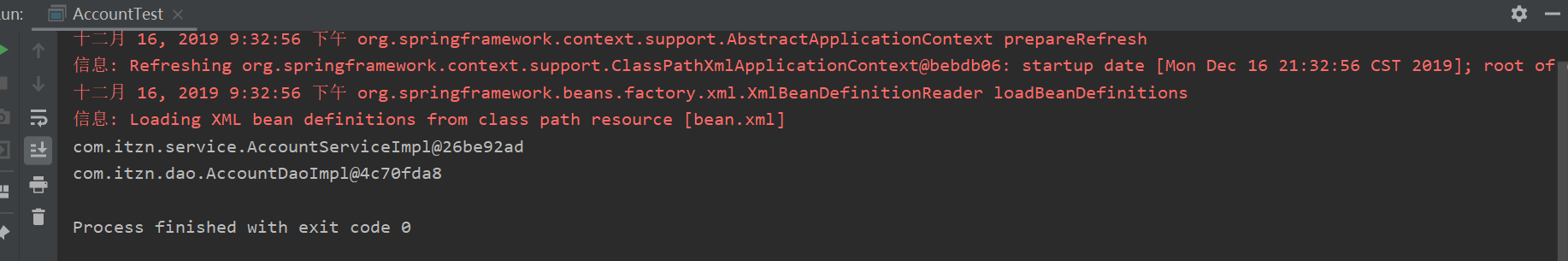
4.测试
AccountTest.java
package com.itzn.ui; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl; import com.itzn.service.IAccountService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //IAccountService iAccountService = new AccountServiceImpl(); ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); IAccountService iAccountService = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService"); IAccountDao iAccountDao=ac.getBean("accountDao", AccountDaoImpl.class); System.out.println(iAccountService); System.out.println(iAccountDao); } }
测试结果
这里说说BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 的区别
BeanFactory 才是 Spring 容器中的顶层接口。
ApplicationContext 是它的子接口。
BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 的区别:
创建对象的时间点不一样。
ApplicationContext:只要一读取配置文件,默认情况下就会创建对象。
BeanFactory:什么使用什么时候创建对象。
ApplicationContext 接口的实现类
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:它是从类的根路径下加载配置文件 推荐使用这种
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:它是从磁盘路径上加载配置文件,配置文件可以在磁盘的任意位置。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:当我们使用注解配置容器对象时,需要使用此类来创建 spring 容器。它用来读取注解。