一、问题
在平时的业务模块开发过程中,难免会需要做一些全局的任务、缓存、线程等等的初始化工作,那么如何解决这个问题呢?方法有多种,但具体又要怎么选择呢?
二、资源初始化
1、既然要做资源的初始化,那么就需要了解一下springboot启动过程(这里大体说下启动过程,详细:https://www.cnblogs.com/dennyzhangdd/p/8028950.html)
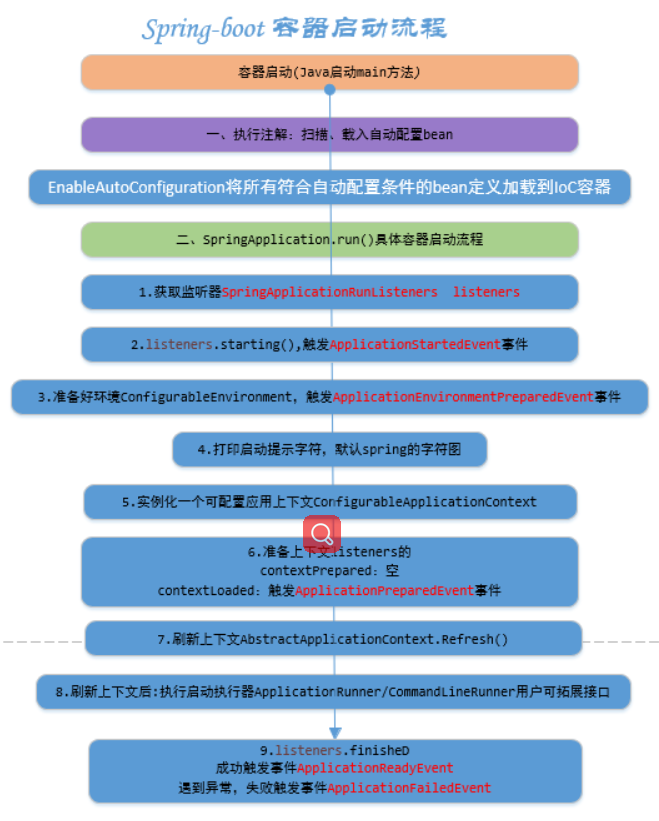
按照前面的分析,Spring-boot容器启动流程总体可划分为2部分:
- 执行注解:扫描指定范围下的bean、载入自动配置类对应的bean加载到IOC容器。
- man方法中具体SpringAppliocation.run(),全流程贯穿SpringApplicationEvent(经典的spring事件驱动模型),有6个子类:
- ApplicationFailedEvent.class
- ApplicationPreparedEvent.class
- ApplicationReadyEvent.class
- ApplicationStartedEvent.class
- ApplicationStartingEvent.class
- SpringApplicationEvent.class
2、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
由上可知,我们只要实现这两个中的任何一个接口便可以完成我们的资源初始化任务,可以看到它们的加载是在容器完全启动之前。它两的区别是:前者的run方法参数是String...args,直接传入字符串,后者的参数是ApplicationArguments,对参数进行了封装。功能上是一样的。同时也可以使用 @Order注解来实现资源加载的先后顺序,值越小,优先级越高。实例如下:
@Component
@Order(1)
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("...init resources by implements CommandLineRunner"); } } @Component @Order(2) public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) throws Exception { System.out.println("...init resources by implements ApplicationRunner"); } }3、@PostConstruct
在具体Bean的实例化过程中执行,@PostConstruct注解的方法,会在构造方法之后执行,顺序为Constructor > @Autowired > @PostConstruct > 静态方法,所以这个注解就避免了一些需要在构造方法里使用依赖组件的尴尬(与之对应的还有@PreDestroy,在对象消亡之前执行,原理差不多)。使用特点如下:
- 只有一个非静态方法能使用此注解
- 被注解的方法不得有任何参数
- 被注解的方法返回值必须为void
- 被注解方法不得抛出已检查异常
-
此方法只会被执行一次
@Component public Class AAA { @Autowired private BBB b; public AAA() { System.out.println("此时b还未被注入: b = " + b); } @PostConstruct private void init() { System.out.println("此时b已经被注入: b = " + b); } }
4、InitializingBean
InitializingBean 是 Spring 提供的一个接口,只包含一个方法 afterPropertiesSet()。凡是实现了该接口的类,当其对应的 Bean 交由 Spring 管理后,当其必要的属性全部设置完成后,Spring 会调用该 Bean 的 afterPropertiesSet()。在Bean在实例化的过程中执执行顺序为:Constructor > @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method
public class InitSequenceBean implements InitializingBean { public InitSequenceBean() { System.out.println("InitSequenceBean: constructor"); } @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { System.out.println("InitSequenceBean: postConstruct"); } public void initMethod() { System.out.println("InitSequenceBean: init-method"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("InitSequenceBean: afterPropertiesSet"); } }5、ApplicationListener
ApplicationListener 就是spring的监听器,能够用来监听事件,典型的观察者模式。如果容器中有一个ApplicationListener Bean,每当ApplicationContext发布ApplicationEvent时,ApplicationListener Bean将自动被触发。这种事件机制都必须需要程序显示的触发。其中spring有一些内置的事件,当完成某种操作时会发出某些事件动作。比如监听ContextRefreshedEvent事件,当所有的bean都初始化完成并被成功装载后会触发该事件,实现ApplicationListener接口可以收到监听动作,然后可以写自己的逻辑。同样事件可以自定义、监听也可以自定义,完全根据自己的业务逻辑来处理。所以也能做到资源的初始化加载!
@Component
public class DataSourceInitListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {//ContextRefreshedEvent为启动事件 private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataSourceInitListener.class); @Autowired private SystemConfigService systemConfigService; @Autowired private ItemService itemService; @Autowired private SystemResultService systemResultService; @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { if(event.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {//判断是否执行过,执行过则不再执行 LOGGER.info("初始化systemConfig数据"); systemConfigService.initConfig(); LOGGER.info("初始化返回消息数据"); systemResultService.initResult(); LOGGER.info("系统初始化结束..........."); } } }