类内操作符重载
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class complex { //复数类 public: //外部接口 complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0) { real = r; imag = i; } //构造函数_ const complex operator+(const complex &c) const ; const complex operator - (const complex &c) const; void display(); //输出复数 private: //私有数据成员 double real; //复数实部 double imag; //复数虚部 }; const complex complex:: operator+(const complex &c) const { return complex(real + c.real, imag + c.imag); } const complex complex:: operator-(const complex &c) const { return complex(real - c.real, imag - c.imag); } void complex::display() { cout << "(" << real << "," << imag << " i)" << endl; } void main() { complex c1(5, 4), c2(2,10), c3; //三个复数类的对象 cout << "c1="; c1.display(); cout << "c2="; c2.display(); c3 = c1 + c2; //使用重载运算符完成复数加法 cout << "c3=c1+c2="; c3.display(); c3 = c1 - c2; //使用重载运算符完成复数减法 cout << "c3=c1-c2="; c3.display(); }
类外通过友元函数重载操作符
class complex { public:complex(double a=0,double b=0);
friend complex operator *(complex a,complex b); private: double real; double imag; } complex operator *(complex a,complex b) { complex temp; temp.real=a.real*b.real-a.imag*b.imag; temp.imag=a.real*b.imag+a.imag*b.real;
return temp;//return complex(a.real*b.real-a.imag*b.imag,a.real*b.imag+a.imag*b.real);
} int main(){ complex A(2.3,4.6),B(2.6,4.3),C; C=A*B;}

声明 friend type operator @(参数表);
定义 type operator@(参数表){};
每当一个函数被调用的时候,系统都会将其参数和变量保存在内存的一个区域,此区域是一个栈(stack)的结构,其中的元素按后进先出(last-in first-out)的方式存取;当一个函数调用另一个函数时调用者的栈空间被完好无缺地保留,系统会分配新的空间来处理新的函数调用。当一个函数完成它的工作,返回其调用者时,它关联的栈空间将被释放。
局部对象的内存地址已经被释放了,如果这时又有新创建的函数栈,那么就会覆盖原有的局部对象,然后就会出错。
也就是说,函数调用完之后,会销毁临时对象,返回引用或者指针会导致未定义的行为,无法指向局部对象的指针,返回局部对象的指针的唯一办法就是创建动态对象,关键字new,能在内存里创建新的空间(不同于函数的栈空间),处于堆中,除了用关键字delete来销毁。
————————————————
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qianliudw2/article/details/7858380
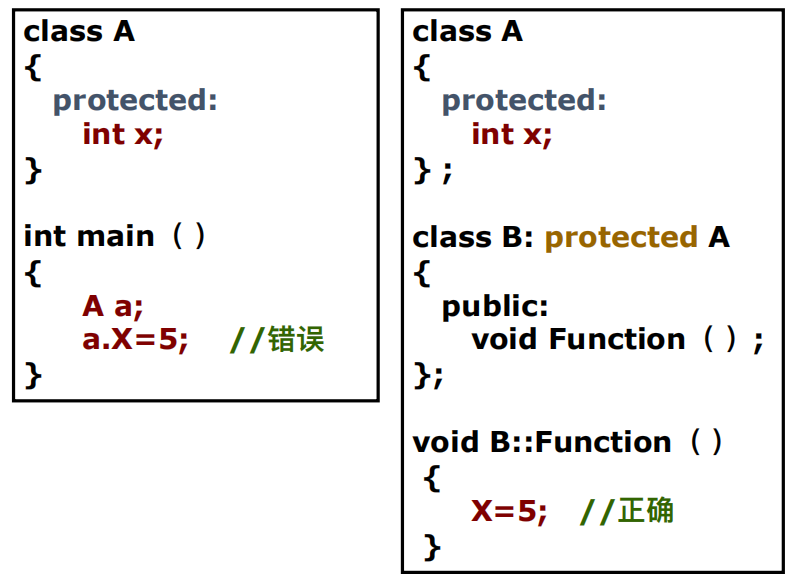
私有成员 继承类内类外均不可访问
保护成员 继承类内可以访问类外不可访问
保护成员 不能被类外访问 但是可以被派生类的成员函数引用 相当于公有成员
3.多态派生类中同名函数必须与基类虚函数完全一致(即函数名、参数个数与类型、返回类型都相同)。
采用基类对象指针或引用来调用虚函数。
公共函数,派生类必须以公用方式继承。
class CCircularShape { public: static const double PI; CCircularShape() {……} CCircularShape(double r) { radius = r; } void setHeight(double h) { height = h; } void setRadius(double r) { radius = r; } //虚函数(CCircularShape) virtual char *Type() const { return NULL; } virtual double Volume() const { return 0;} virtual double SurfaceArea() const { return 0; } protected: double radius; double height; }; class CCylinder : public CCircle { public: char *Type() const{return "圆柱";} double SurfaceArea() const double Volume() const};
class CSphere : public CCircularShape
{ public: char *Type() const { return "球"; }
double SurfaceArea() const
double Volume() const };