之前写过了spring的IOC实现方式,现在则写DI依赖注入的实现方式
贴类图
由于在实现完DI进行测试的时候,会用到junit包,所以在pom.xml导入依赖
<!--SpringDI-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13-beta-3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
接下来开始写,先创建几个需要的注解
package com.spring.DI.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAutowired {
}
package com.spring.DI.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponent {
public String scope() default "";
}
package com.spring.DI.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyValue {
public String value();
}
再创建实体类(为节省空间,get和set方法就省略了)
package com.spring.DI.pojo;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyComponent;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyValue;
@MyComponent(scope = "prototype")
public class User {
@MyValue(value = "1")
private Integer id;
@MyValue(value = "冬瓜")
private String name;
@MyValue(value = "123456")
private String password;
public User() {
System.out.println("无参构造方法执行");
}
public void login() {
System.out.println("用户登录:id = " + id + ", name" + name + ", password= " + password);
}
}
接下来创建UserService类,在Service类中使用依赖注入User;
package com.spring.DI.service;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyAutowired;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyComponent;
import com.spring.DI.pojo.User;
@MyComponent
public class UserService {
@MyAutowired
User user1;
@MyAutowired
User user2;
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("用户1:"+user1);
user1.login();
System.out.println("用户2:"+user2);
user2.login();
}
}
创建注解工厂类
package com.spring.DI.applicationContext;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyAutowired;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyComponent;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyValue;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext {
private Map<String, Class<?>> beanDefinationFactory = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Class<?>>();
private Map<String, Object> singletonBeanFactory = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(String... packageNames) {
for (String packageName : packageNames) {
System.out.println("开始扫描包:" + packageName);
scanPkg(packageName);
}
dependencyInjection();
}
}
在工厂类的构造方法中,可以接收多个包路径,并且遍历循环扫描每一个包路径,扫描包的scanPkg方法如下:
private void scanPkg(final String pkg) {
String pkgDir = pkg.replaceAll("\\.", "/");
URL url = getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(pkgDir);
File file = new File(url.getFile());
File[] fs = file.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
String fName = file.getName();
if (file.isDirectory()) {
scanPkg(pkg + "." + fName);
} else {
if (fName.endsWith(".class")) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
});
for (File f : fs) {
String fName = f.getName();
fName = fName.substring(0, fName.lastIndexOf("."));
String beanId = String.valueOf(fName.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + fName.substring(1);
String pkgCls = pkg + "." + fName;
try {
Class<?> c = Class.forName(pkgCls);
if (c.isAnnotationPresent(MyComponent.class)) {
beanDefinationFactory.put(beanId, c);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
开始注入
private void dependencyInjection() {
Collection<Class<?>> classes = beanDefinationFactory.values();
for (Class<?> cls : classes) {
String clsName = cls.getName();
clsName = clsName.substring(clsName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
String beanId = String.valueOf(clsName.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + clsName.substring(1);
Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)) {
try {
String fieldName = field.getName();
System.out.println("属性名:" + fieldName);
Object fieldBean = null;
if (beanDefinationFactory.get(fieldName) != null) {
fieldBean = getBean(fieldName, field.getType());
} else {
String type = field.getType().getName();
type = type.substring(type.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
String fieldBeanId = String.valueOf(type.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + type.substring(1);
System.out.println("属性类型ID:" + fieldBeanId);
fieldBean = getBean(fieldBeanId, field.getType());
}
System.out.println("要为属性注入的值:" + fieldBean);
if (fieldBean != null) {
Object clsBean = getBean(beanId, cls);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(clsBean, fieldBean);
System.out.println("注入成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("注入失败");
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
在注入期间,调用了getBean方法:
public Object getBean(String beanId) {
Class<?> cls = beanDefinationFactory.get(beanId);
MyComponent annotation = cls.getAnnotation(MyComponent.class);
String scope = annotation.scope();
try {
if ("singleton".equals(scope) || "".equals(scope)) {
if (singletonBeanFactory.get(beanId) == null) {
Object instance = cls.newInstance();
setFieldValues(cls, instance);
singletonBeanFactory.put(beanId, instance);
}
return singletonBeanFactory.get(beanId);
}
if ("prototype".equals(scope)) {
Object instance = cls.newInstance();
setFieldValues(cls, instance);
return instance;
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public <T> T getBean(String beanId, Class<?> c) {
return (T) getBean(beanId);
}
在getBean方法中,需要为对象成员属性赋值,调用setFieldValues方法
private void setFieldValues(Class<?> cls, Object obj) {
Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(MyValue.class)) {
String fieldName = field.getName();
String value = field.getAnnotation(MyValue.class).value();
String type = field.getType().getName();
fieldName = String.valueOf(fieldName.charAt(0)).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
String setterName = "set" + fieldName;
try {
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod(setterName, field.getType());
if ("java.lang.Integer".equals(type) || "int".equals(type)) {
int intValue = Integer.valueOf(value);
method.invoke(obj, intValue);
}else if ("java.lang.String".equals(type)){
method.invoke(obj,value);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
最后释放资源
public void close(){
beanDefinationFactory.clear();
beanDefinationFactory=null;
singletonBeanFactory.clear();
singletonBeanFactory=null;
}
至此DI实现完毕,开始测试
package com.spring.DI.springTest;
import com.spring.DI.annotation.MyComponent;
import com.spring.DI.applicationContext.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.spring.DI.service.UserService;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
@MyComponent
public class TestSpringDi {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx;
UserService userService;
@Before
public void init() {
ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
("com.spring.DI.pojo",
"com.spring.DI.service", "com.spring.DI.springTest");
userService = ctx.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
}
@Test
public void userLogin() {
userService.userLogin();
}
@After
public void close() {
ctx.close();
}
}
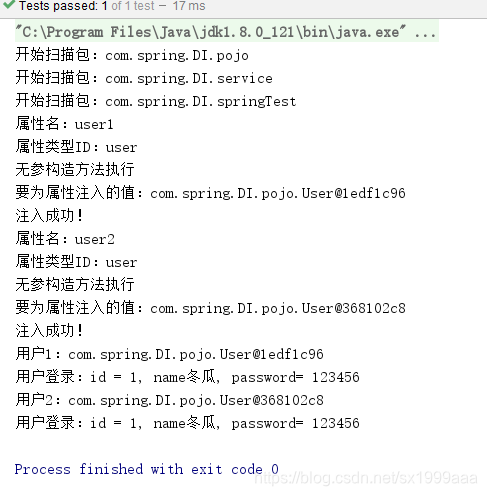
运行结果