字符串
概述及特点
Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 “abc” )都作为此类的实例实现。 即程序当中的所有双引号内的字符串,都是String字符串的对象。
特点
- 字符串是常量;它们的值在创建之后不能更改。字符串缓冲区支持可变的字符串。因为 String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享。
- 因为字符串不可改变,字符串可以共享使用
- 字符串效果上相当于char[] 字符数组。
创建字符串
JDK_API 中提供的构造方法如图:
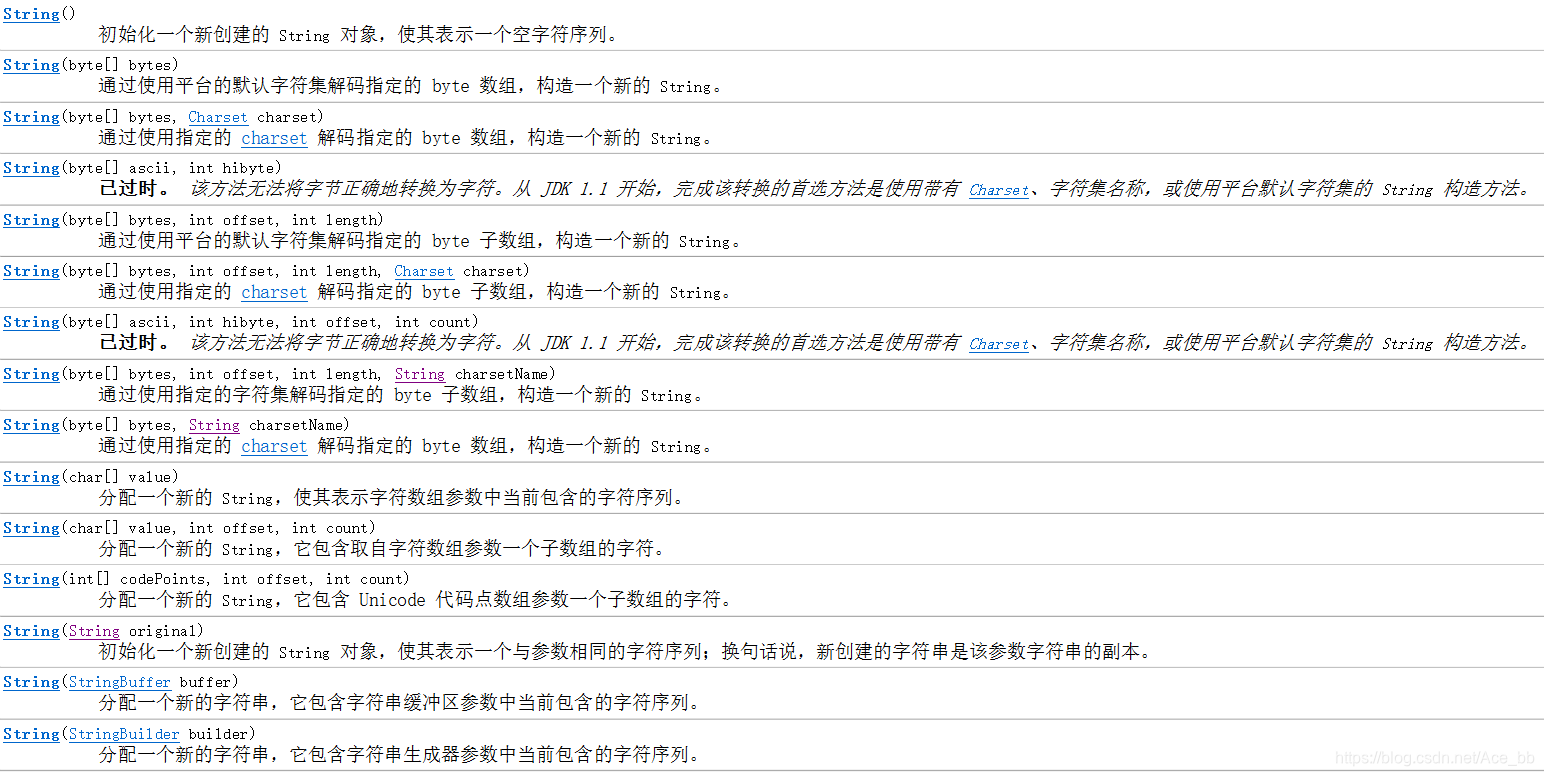
主要使用三种构造方法:
public String(): 创建-个空白字符串, 不含有任何内容。
public String(char[] array): 根据字符数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串。
public String(byte[] array): 根据字节数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串。
- -种直接创建:
代码示例:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用空参构造
String str1 = new String();
System.out.println("第一个字符串"+str1);
//根据字符串数组创建字符串
char[] charArray = {'A', 'B', 'C'};
String str2 = new String(charArray);
System.out.println("第二个字符串" + str2);
//根据字节数组创建字符串
byte[] byteArray = {97,98,99};
String str3 = new String(byteArray);
System.out.println("第三个字符串" + str3);
// 直接创建
String str4 = "Hello";
System.out.println(str4);
}
}
输出结果如图:

字符串内存分析
- 在Java语言中双引号直接写的字符串在常量池当中,new的不在池当中。
- 对于引用类型来说,==进行的是地址值的比较
先写以下三个字符串,进行比较:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
char[] charArray = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str3 = new String(charArray);
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
System.out.println(str2 == str3);
}
}
输出结果如下:
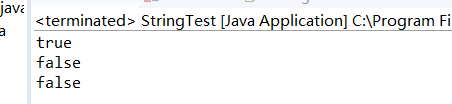
可见 str1 与 str2 是两个相同的字符串,地址也相同。
以下是内存分析图:
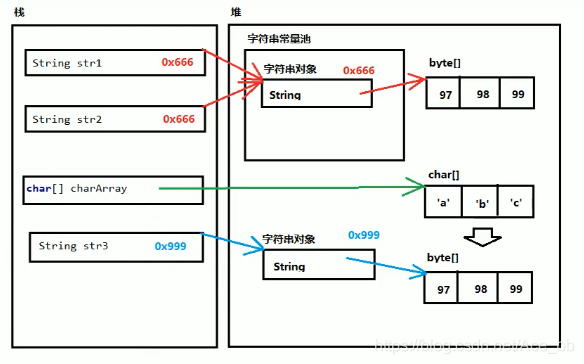
可见直接写的字符串是存在字符串类型池当中,当有不同变量直接定义为同一个字符串时,会指向同一个字符串地址。 而用**new创建的字符串都写在堆当中,**会指向不同的地址。
字符串的常用方法
在API中介绍的部分方法有:
| 类型 | 方法名 | 用法|
| 类型 | 方法名 | 用法 |
|---|---|---|
| char | charAt(int index) | 返回指定索引处的 char 值。 |
| int | codePointAt(int index) | 返回指定索引处的字符 |
| int | codePointBefore(int index) | 返回指定索引之前的字符 |
| int | codePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 返回此 String 的指定文本范围中的 Unicode 代码点数。 |
| int | compareTo(String anotherString) | 按字典顺序比较两个字符串。 |
| int | compareToIgnoreCase(String str) | 按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写。 |
| String | concat(String str) | 将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。 |
| boolean | contains(CharSequence s) | 当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true。 |
| boolean | contentEquals(CharSequence cs) | 将此字符串与指定的 CharSequence 比较。 |
| boolean | contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) | 将此字符串与指定的 StringBuffer 比较。 |
| static String | copyValueOf(char[] data) | 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 String。 |
| static String | copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count) | 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 String。 |
| boolean | endsWith(String suffix) | 测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。 |
| boolean | equals(Object anObject) | 将此字符串与指定的对象比较。 |
| boolean | equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) | 将此 String 与另一个 String 比较,不考虑大小写。 |
| static String | format(Locale l, String format, Object… args) | 使用指定的语言环境、格式字符串和参数返回一个格式化字符串。 |
| static String | format(String format, Object… args) | 使用指定的格式字符串和参数返回一个格式化字符串。 |
| byte[] | getBytes() | 使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。 |
| byte[] | getBytes(Charset charset) | 使用给定的 charset 将此 String 编码到 byte 序列,并将结果存储到新的 byte 数组。 |
| byte[] | getBytes(String charsetName) | 使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。 |
| void | getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) | 将字符从此字符串复制到目标字符数组。 |
| int hashCode() | 返回此字符串的哈希码。 | |
| int | indexOf(int ch) | 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。 |
| int | indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符处的索引,从指定的索引开始搜索。 |
| int | indexOf(String str) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。 |
| int | indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始。 |
| String | intern() | 返回字符串对象的规范化表示形式。 |
| boolean | isEmpty() | 当且仅当 length() 为 0 时返回 true。 |
| int | lastIndexOf(int ch) | 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引。 |
| int | lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索。 |
| int | lastIndexOf(String str) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引。 |
| int | lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索。 |
| int | length() | 返回此字符串的长度。 |
| boolean | matches(String regex) | 告知此字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。 |
| int | offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset) | 返回此 String 中从给定的 index 处偏移 codePointOffset 个代码点的索引。 |
| boolean | regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) | 测试两个字符串区域是否相等。 |
| boolean | regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) | 测试两个字符串区域是否相等。 |
| String | replace(char oldChar, char newChar) | 返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。 |
| String | replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) | 使用指定的字面值替换序列替换此字符串所有匹配字面值目标序列的子字符串。 |
| String | replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | 使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。 |
| String | replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串。 |
| String[] | split(String regex) | 根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。 |
方法示例
equal() 方法
==是进行对象的地址值比较,如果确实需要字符串的内容比较,可以使用两个方法:
public_ boolean equals(object obj): 参数可以是任何对象,只有参数是一个字符串并 且内容相同的才会给true;否则返回false
注意事项:
1.任何对象都能用object进行接收。
2. equals方法具有对称性,也就是a. equals(b)和b. equals(a)效果一样。
3.如果比较双方一个常量一个变量,推荐把常量字符串写在前面。
推荐: “abc”. equals(str)
不推荐: str. equals(“abc”)
** public boolean equalsIgnoreCase ( String str )** 忽略大小写,进行内容比较。
示例代码:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = "Hello";
char[] charArray = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
String str3 = new String( charArray);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // true
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3)); // true
System.out.println(str3.equals("Hello")); // true
System.out.println("Hello".equals(str1)); // true
String str4 = "hello";
System.out.println(str1.equals(str4)); // false
System.out.println("===============");
String str5 = null;
System.out.println("abc".equals(str5)); //推荐: false
//System.out.println(str5.equals("abc")); //不推荐:报错,空指针异常NullPointerException
System.out.println("===============");
String strA = "Java";
String strB = "java";
System.out.println(strA.equals(strB)); // false, 严格区分大小写
System.out.println(strA.equalsIgnoreCase(strB)); // true, 忽略大小写
}
}
输出结果:

与获取相关的方法
public int length(): 获取字符串当中含有的字符个数,得到字符串长度。
public String concat(String str): 将当前字符串和参数字符串拼接成新的字符串返回
public char charAt(int index): 获取指定索引位置的单个字符。(索引从0开始。 )
public int indexOf(String str): 查找参数字符串在本字符串当中首次出现的索引位置,如果没有返回-1值。
示例代码:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取字符串的长度
int length = "asdasfeutrvauevbueyvb" .length() ;
System.out.println("字符串的长度是:" + length);
//拼接字符串
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = "World";
String str3 = str1.concat(str2);
System.out.println(str1); // Hello, 原封不动
System.out.println(str2); // World, 原封不动
System.out.println(str3); // HelloWorld, 新的字符串
System.out.println("=============");
//获取指定索引位置的单个字符
char ch = "Hello". charAt(1);
System.out.println("在1号索引位置的字符是:"+ ch);
System.out.println("============");
//查找参数字符串在本来字符串当中出现的第一次索引位置
//如果根本没有,返回-1值
String original = "HelloWorldHelloWorld";
int index = original.indexOf("llo");
System.out.println("第一次索引值是:" + index); // 2
}
}

字符串的截取方法
public String substring(int index): 截取从参数位置一直到字符串末尾, 返回新字符串。
public String substring(int begin, int end): 截取从begin开始,一直到end结束, 中间的字符串。
备注: [begin,end), 包含左边,不包含右边。
示例代码:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "HelloWorld" ;
String str2 = str1. substring(5);
System.out.println(str1); // HelloWorld,原封不动
System.out.println(str2); // World,新字符串
System.out. println("================");
String str3 = str1. substring(4, 7);
System.out.println(str3); // oWo
System.out.println("================");
}
}

与转换相关的方法
String当中与转换相关的常用方法有:
public char[] toCharArray(): 将当前字符串拆分成为字符数组作为返回值。
public byte[] getBytes(): 获得当前字符串底层的字节数组。
public String. replace(CharSequence oldString, CharSequence newString):
将所有出现的老字符串替换成为新的字符串,返回替换之后的结果新字符串。
备注:CharSequence表示可以接收字符串类型
示例代码:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] chars ="Hello".toCharArray();
System.out.println(chars[0]); // H
System.out.println( chars.length); // 5
System.out.println("==============");
//转换成为字节数组
byte[] bytes = "abc".getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes .length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
System.out.println("==============");
//字符串的内容替换
String str1 = "How do you do?";
String str2 = str1.replace("o", "*");
System.out .println(str1); // How do you do?
System.out.println(str2); // H*w d* y*u d*?
System.out.println("==============");
}
}
输出结果:

replace方法可以用于敏感词过滤
字符串分割方法split
public String[ ] split(String regex) :
按照参数的规则,将字符串切分成为若干部分.
示例代码:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "aaa,bbb,ccc";
String[] array1 = str1.split("," ) ;
for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(array1[i]);
}
System.out.println("===============");
String str2 = "aaa bbb ccc";
String[] array2 = str2.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(array2[i]);
}
System.out.println("===============");
}
}
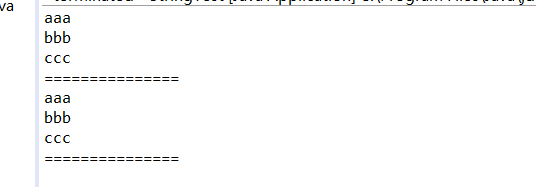
————————————————————
