前端发请求,调用后端接口,来获取特定格式的数据,老板问了,你会前后端交互模式吗?vue的那种。异步接口调用,常常使用到的语法,promise的概念是什么呢?调用接口的方式,第一种为,fetch进行接口调用,第二种为,axios进行接口的调用。
es7的语法结构?async/await方式调用接口,基于不同接口的调用方式来实现案例。
让我们了解一下前后端的交互模式,学习一下promise的语法,来回答面试官的问题,基于promise来实现异步调用,就算你会promise?那你了解fetch用法和async/await用法吗?处理异步调用接口的方式。
网上一图,回调地狱:看到晕,使代码难以理解和维护。

前后端的交互是什么
前后端的交互就是前端的浏览器去调用后端的接口,拿到后端的数据,在做前端的处理,进行渲染。客户端与服务器的通信模式,前后端交互,调用接口的方法,第一种,原生的ajax,第二种,基于jquery的ajax,第三种,基于fetch,第四种,基于axios。
前端是通过请求地址向后端发送请求的,标准的url格式是什么样的呢?
格式如下:
schema://host:port/path?query#fragment
第一个schema为协议,比如http,https,ftp等,第二个,host为域名或者ip地址,第三个port为端口,http默认为80端口,是可以省略的,第四个path为路径,比如/index,第五个query为查询参数,比如name=dada&age=12,第六个fragment为锚点,哈希Hash,是用于定位页面的某个位置。
符合规则的url有哪些是正确的呢?
http://www.dada.cn
http://www.dada.cn/index/dada
http://www.dada.cn/index/dada?name=dada
http://www.dada.cn/index/dada?name=dada#theme
新型的url地址,restful形式的。HTTP的请求方式,第一种,使用GET为查询,第二种,使用POST为添加,第三种,使用PUT为修改,第四种,使用DELETE为删除。

符合规则的url地址:
http://www.dada.com/index GET
http://www.dada.com/index POST
http://www.dada.com/index/1 PUT
http://www.dada.com/index/2 DELETE
promise对象
promise用于表示一个异步操作的最终完成(或失败),以及结果值。
Promise对象有以下两个特点
对象的状态不受外界影响
一旦状态改变,就不会再变,任何时候都可以得到这个结果
const promise1 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
resolve('foo');
}, 300);
});
promise1.then(function(value) {
console.log(value);
// expected output: "foo"
});
console.log(promise1);
// expected output: [object Promise]
语法:
new Promise( function(resolve, reject) {...} /* executor */ );

因为 Promise.prototype.then 和 Promise.prototype.catch 方法返回promise 对象, 所以它们可以被链式调用。



promise用法
promise是什么呢?它是用于异步计算,将异步操作队列化,按照期望的顺序执行,返回符合预期的结果,可以在对象之间传递和操作promise。

创建promise
const da = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve(someValue); // fulfilled
// reject("failure reason"); // rejected
});
function da(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.onload = () => resolve(xhr.responseText);
xhr.onerror = () => reject(xhr.statusText);
xhr.send();
});
};
简单的实例
new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('hello')
}, 2000)
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
异步操作,事件监听
document.getElementById('#start').addEventListener('click',start,false);
function start() {
// 响应事件,进行相应的操作
}
//jquery on 监听
$("#start").on("click", start)
回调
$.ajax(url, {
success(res) {
}
})
// 在页面加载完毕后回调
$(function() {
// 页面结构加载完成
})
在JavaScript中,异步情况,第一种为定时任务,第二种为ajax,第三种事件函数。
new Promise(
function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('成功') // 数据处理完成
// reject('失败') // 数据处理出错
}
).then(
(res) => {console.log(res)}, // 成功
(err) => {console.log(err)} // 失败
)
异步编程与promise
$.ajax({
url: '',
success: function(data) {
console.log(data)
}
});
index.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const bodyParser = require('body-parser')
// 处理静态资源
app.use(express.static('public'))
// 处理参数
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false}));
// 设置允许跨域访问服务
app.all("*", function(req,res,next){
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "PUT,GET,POST,DELETE,OPTIONS");
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers","X-Requested-With");
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers","Content-Type");
next();
});
// 路由
app.get('/data', (req,res) => {
res.send("hello world!")
})
// 启动监听
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("runing...")
})
异步编程,多次异步调用,结果顺序结果不确定

promise是异步编程的一种解决方案,从语法上来讲,promise是一个对象,从它可以获取异步操作的消息。使用promise的好处有哪些呢?
它可以避免多层异步调用嵌套问题(回调地狱),promis对象提供了简洁的api,使得控制异步操作更加容易。回调地狱,多层嵌套请求问题,请求接口调用后台数据,有两种可能性,一种为成功回调,一种为失败回调,成功后写一下成功后的操作代码,失败后也要写一下失败后的操作代码。
在JavaScript中的世界里,所有的代码都是单线程执行的。因为这个缺点,所以会导致在JavaScript中的所有网络操作,浏览器事件,都必须是异步执行的,异步执行可以用回到函数实现。
function callback() {
console.log("dada");
}
console.log("dada setTimeout()");
setTimeout(callback, 1000);
// 1秒后调用callback函数
注意,异步操作会在将来某个时间点触发一个函数调用。
ajax的经典异步操作
request.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(request.readyState === 4) {
if(request.status === 200) {
return success(request.responseText);
}else{
return fail(request.status);
}
}
}
'use strict';
new Promise(function() {} );
// 直接运行测试:
console.log('支持Promise!');
如果同时发送多个ajax的请求,返回来的结果是不确定的,要想返回的结果顺序确定下来,就必须进行嵌套,如果嵌套就会有回调地狱的问题,这样导致的代码可读性就会降低,所以就有promise语法来解决这一回调地狱的问题。
所以promise的出现的好处就是为了解决地狱回调,可以避免嵌套问题,和简洁的代码结构,可读性增强。
console.log(typeof Promise)
示例
let da = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
// 当异步代码执行成功时,会调用 resolve(...)
// 当异步代码失败时, 会调用 reject(...)
//使用setTimeout(...)来模拟异步代码
setTimeout(function(){
resolve("成功!");
}, 250);
});
da.then(function(res){
//res的值是上面调用resolve(...)方法传入的值.
console.log("dada" + res);
});
promise的基本用法
首先实例化promise对象,构造函数中传递函数,该函数中用于处理异步任务,有两个参数,resolve和reject用于处理成功和失败的两种情况,并通过p.then获取处理结果。
then()方法返回一个promise:
const da = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
resolve('da!');
});
da.then(function(value) {
console.log(value);
// expected output: "da!"
});
语法
p.then(onFulfilled[, onRejected]);
p.then(value => {
// fulfillment
}, reason => {
// rejection
});
var dada = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功!');
// or
// reject(new Error("出错了!"));
});
dada.then(value => {
console.log(value); // 成功!
}, reason => {
console.error(reason); // 出错了!
});
catch()方法返回一个promise,并且处理拒绝的情况
p.catch(onRejected);
p.catch(function(reason) {
// 拒绝
});
finally()方法返回一个promise,在promise结束时,无论结果是fulfilled或者是rejected,都会执行指定的回调函数。
p.finally(onFinally);
p.finally(function() {
// 返回状态为(resolved 或 rejected)
});
new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('hello')
}, 2000)
}).then(val => {
console.log(val) // 参数val = 'hello'
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('world')
}, 2000)
})
}).then(val => {
console.log(val) // 参数val = 'world'
})
代码例子:
var p = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 成功回调 resolve()
// 失败回调 reject()
});
p.then(function(ret) {
// resolve得到正常的结果
},function(ret) {
// reject得到错误的结果
});
resolve作用为将promise对象的状态从“未完成”变成为“成功”,即是从Pending变为resolved,在异步操作成功时调用,并将异步操作的结果,作为参数传递出去,而reject的作用是将promise对象的状态从“未完成”变成“失败”,就是从Pending变成rejected,在异步操作失败时调用,并将异步操作报出的错误,作为参数传递出去。
promise有三种状态,第一种为Pending,待定,初始状态,第二种状态为fulfilled,实现,操作成功,第三种状态为rejected,被否决,操作失败。
当promise状态发生改变时,就会触发then()里面的响应函数处理,promise状态一旦改变,就不会再变了。所以promis对象的状态改变有两种情况,第一种,从pending变为fulfilled,第二种为,从pending变为rejected。

基于promise处理ajax请求,处理原生ajax
function queryData(url) {
return new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if(xhr.status == 200) {
resolve(xhr.responseText)
}else {
reject('出错了');
}
}
xhr.open('get',url);
xhr.send(null);
})
}
发送多个ajax请求
queryData()
.then(function(data){
return queryData();
})
.then(function(data){
return queryData();
})
.then(function(data){
return queryData();
});
// return 是新的promise对象
then参数中的函数返回值
第一种,返回promsie实例对象,返回的实例对象会调用下一个then
第二种,返回普通值,返回的普通值会直接传递给下一个then,通过then参数中函数的参数接收该值
promise常用的api
实例方法有三种,第一种,p.then()得到异步任务的正确结果,第二种,p.catch()获取异常信息,第三种,p.finally()成功与否都会执行。
queryData()
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
})
.catch(function(data){
console.log(data);
})
.finally(function(){
console.log('finished');
});
promise常用api-实例方法
function da() {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
// resolve(123);
reject('error');
},100);
})
}
da()
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)
})
.catch(function(data){
console.log(data)
})
.finally(function(){
console.log('dada')
});
da()
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)
},function(data){
console.log(data)
})
.finally(function(){
console.log('dada')
});
对象方法
promise.all()并发处理多个异步任务,所有任务都执行完成才能得到结果
promise.race()并发处理多个异步任务,只要有一个任务完成就能得到结果
Promise.all([p1,p2,p3]).then(result) => {
console.log(result);
})
Promise.race([p1,p2,p3]).then(result) => {
console.log(result);
})
代码:
function queryData(url) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if(xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200) {
// 处理正常的情况
resolve(xhr.responseText);
}else{
// 处理异常情况
reject('服务器出错');
};
xhr.open('get',url);
xhr.send(null);
});
}
var p1 = queryData(url);
var p2 = queryDate(url1);
Promise.all([p1,p2]).then(function(result){
console.log(result)
})
在promise中常用到回调函数延时绑定,返回值,错误冒泡。

const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1)
resolve()
console.log(2)
})
promise.then(() => {
console.log(3)
})
console.log(4)
VM49:2 1
VM49:4 2
VM49:9 4
VM49:7 3
undefined
其中,promise构造函数是执行同步的作用,promise.then是执行异步函数的操作。
let pro = new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('hello world')
}, 2000)
})
setTimeout(() => {
pro.then(value => {
console.log(value)
// hello world
})
}, 2000)
接口调用fetch的用法
fetch的概述,它更加简单的数据获取方式,功能更加强大,更加灵活,基于promise实现的。
语法结构:
fetch(url).then()
.then()
...
.catch()
fetch的基本用法
fetch('/da').then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret={
console.log(ret);
});
text()方法属于fetchapi中的一部分,它返回一个promise实例对象,用于获取后台返回的数据。
fetch请求参数
method(string)
http请求方法,默认为GET,可以使用POST,PUT,DELETE
body(string)
http的请求参数
headers(object)
http的请求头
fetch('/da', {
method; 'get'
}).then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret=>{
console.log(ret);
});
GET请求方式的参数传递
fetch('/da?id=123').then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret=>{
console.log(ret);
});
fetch('/da/123', {
method: 'get'
}).then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret=>{
console.log(ret);
});
delete请求方式的参数传递
fetch('/da/123', {
method: 'delete'
}).then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret=>{
console.log(ret);
});
fetch请求参数的post请求方式的参数传递
fetch('/da', {
method: 'post',
body: 'name=dada',
headers: {
'content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
}
}).then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret=>{
console.log(ret);
});
post请求方式的参数传递
fetch('/da', {
method: 'post',
body: JSON.stringify({
name: 'dada',
age: 12
})
headers;{
'Conent-Type': 'application/json',
}
}).then(data=>{
return data.text();
}).then(ret=>{
console.log(ret);
});
fetch响应结果
响应数据格式
text()
将返回体处理成字符串类型
json()
返回结果和json.parse(presponseText)相同
接口调用axios用法
第三方的库,很强大,是一个局域promise用于浏览器和node.js的HTTP客户端。
它的特性,第一点是支持浏览器和node.js,第二点是支持promise,第三点,能够拦截请求和响应,第四点,可以自动转换json类型。
axios的基本用法
axios.get('/dada')
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data);
});
axios的常用api
get,查询数据,post,添加数据,put,修改数据,delete,删除数据。
get传递参数,第一,通过url传递参数,第二种,通过params传递参数
axios.get('/da?id=123')
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data);
})
restful传参
axios.get('/dada/123')
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data)
})
axios.get('/da', {
params: {
id: 123
}
})
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data)
})
delete传递参数
参数传递方式与get类似
axios.delete('/da?id=1)
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data)
})
axios.delete('/da/2)
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data)
})
axios.delete('/da', {
params: {
id:1
}
})
.then(ret=>{
console.log(ret.data);
})
post传递参数
axios.post('/da', {
name; 'dada',
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
默认传递的是json格式的数据。
post传递参数,通过URLSearchParams传递参数
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
const params = new URLSearchParams();
params.append('param1','value1');
params.append('param2','value2');
axios.post('/api/da', params).then(res => {
console.log(res.data)
})
put传递参数
参数传递方式与post类似
axios.put('/da/1', {
name: 'dada',
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
axios的响应结果
data为响应回来的数据,headers为响应头信息,status为响应状态码,statusText响应状态信息。
axios.post('/da-json').then(res=>{
console.log(res)
})
axios的全局 配置
axios.default.timeout = 3000; // 超时时间
axios.default.baseURL = 'http...' // 默认地址
axios.default.headers['mytoken'] = 'xxxx' //设置请求头
// 配置请求的基准url地址
axios.default.baseURL = 'http://localhost:xxx/';
axios.get('da-json').then(function(res){
console.log(res.data.name);
});
axios拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(function(config){
//在拿过去发出之前进行一些信息设置
return config;
},function(err) {
// 处理响应的错误信息
});
在获取数据之前对数据做一些加工处理。
接口调用async/await用法
async/await是es7引入的语法,更加方便了异步操作。

async function queryData(id) {
const res = await axios.get('/data');
return res;
}
queryData.then(res=>{
console.log(res)
})
async关键字用于函数上,await关键字用于async函数中。
async function name([param[, param[, ... param]]]) { statements }
name:
函数名称
param:
要传递给函数的参数的名称
statements:
函数体语句
返回值:
返回的Promise对象会以async function的返回值进行解析
或者以该函数抛出的异常进行回绝。
多个异步请求的async/await处理
async function queryData(id) {
const da1 = await axios.get('/da1');
const da2 = await axios.get('/da2?name=dada');
return res;
}
queryData.then(res=>{
console.log(res)
})
出现了async/await之前,我们有三种异步书写我们的代码,第一,嵌套回调,第二,以promise为主的链式回调,使用generators。

async function dada(x) {
let a = 1;
return x+a;
}
undefined
dada(10);
Promise {<resolved>: 11}__proto__:
Promisecatch: ƒ catch()constructor:
ƒ Promise()finally: ƒ finally()then:
ƒ then()Symbol(Symbol.toStringTag):
"Promise"__proto__: Object[[PromiseStatus]]:
"resolved"[[PromiseValue]]:
11
await只能在async函数内部使用,用在普通函数里就会报错。async/await实际上是Generator的语法糖。async关键字代表后面的函数中有异步操作,await表示等待一个异步方法执行完成。async 函数返回一个Promise对象,因此 async 函数通过 return 返回的值,会成为 then 方法中回调函数的参数。
await 就是异步等待,它等待的是一个Promise,async函数调用不会造成代码的阻塞,但是await会引起async函数内部代码的阻塞。
带async关键字的函数,是声明异步函数,返回值是promise对象
async function test() {
return 'da'
}
test();
返回值为 Promise {<resolved>: "da"}。

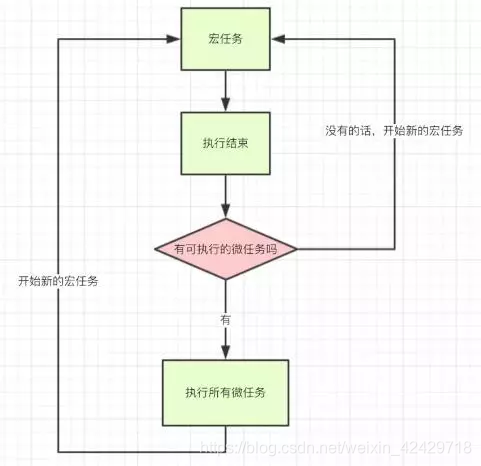
宏任务和微任务都是队列
宏任务有script、setTimeout、setInterval等
微任务有Promise.then,catch,finally,process.nextTick等
参考地址:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1022910821149312/1023024413276544
学如逆水行舟,不进则退
