Spring IoC是一个独立的模块,它并不是直接在Web容器中发挥作用的。如果要在Web环境中使用IoC容器,需要Spring为IoC设计一个启动过程,把IoC容器导人,并在Web容器中建立起来。具体说来,这个启动过程是和Web容器的启动过程集成在一起的。在这个过程中,一方面处理Web容器的启动,另一方面通过设计特定的Web容器拦截器,将IoC容器载入到Web环境中来.并将其初始化。在这个过程建立完成以后, IoC容器才能正常工作,而SpringMVC是建立在IoC容器的基础上的,这样才能建立起MVC框架的运行机制,从而响应从Web容器传递的HTTP请求。
下面以Tomcat容器为例子进行分析。在Tomcat中,web.xml是应用的部署描述文件。在web.xm.中常常看到与Spring相关的部署描述如下:
<!-- 加载spring容器 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext-*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- springmvc的前端控制器 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>tt-manager</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- contextConfigLocation不是必须的, 如果不配置contextConfigLocation, springmvc的配置文件默认在:WEB-INF/servlet的name+"-servlet.xml" -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>tt-manager</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
这里看到的部署描述是Spring MVC与Tomcat的接口部分。在这个部署描述文件中。首先定义了一个Servlet对象,它是Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet。这个DispatcherServlet是MVC中很重要的一个类,起着分发请求的作用。同时,在部署描述中,为这个DispatcherServlet定义了应的URL映射,这些URL映射为这个Servlet指定了需要处理的HTTP请求。
context-param参数的配里用来指定Spring IoC容器读取Bean定义的XML文件的路径,在这里。这个配且文件被定义为classpath:spring/applicationContext-*.xml下的文件中,可以看到Spring应用的Bean配置。最后,作为Spring MVC的启动类,Contex tLoaderListener被定义为一个监听器,这个监听器是与Web服务器的生命周期相关联的。由ContextLoaderListener监听器负责完成IoC容器在Web环魂中的启动工作.
IoC容器启动的基本过程
IOC容器的启动过程就是建立上下文的过程,该上下文是与SerVietContext相伴而生的,同时也是IoC容器在Web应用环境中的具体表现之一。由ConteztLoaderListener启动的上下文为根上下文。在根上下文的基础上.还有一个与Web MVC相关的上下文用来保存控制器(DispatcherServlet)需要的MVC对象,作为根上下文的子上下文,构成一个层次化的上下文体系。
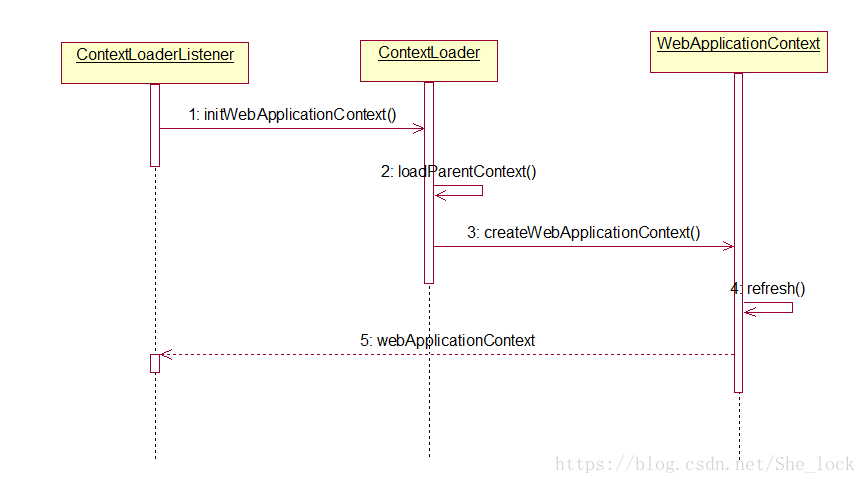
在Web容器中启动Spring应用程序时.首先建立根上下文.然后建立这个上下文体系的,这个上下文体系的建立是由ContextLoder来完成的。具体如下图:
在web.xml中,已经配了ContextLoaderListener,这个ConteztLoaderListener提Spring提供的类,是为在Web容器中建立IoC容器服务的。它实现了ServletContextListener接口。这个接口是在Servlet API中定义的,提供了与Servlet生命周期结合的回调,比如contextlnitialized方法和contextDestroyed方法。
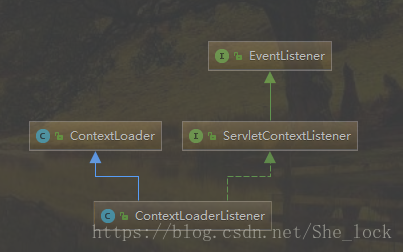
而在Web容器中,建立WebApplicationContext的过程,是在contextlnitialized的接口实现中完成的。具体的载入IoC容器的过程是由ContextLoaderListener交由ContextLoader来完成的,而ContextLoader本身就是ContextLoaderListener的基类.它们之间的类关系如下图:
总之,ContextLoaderListener是SpringMVC的入口,通过父类ContextLoader来实现IoC容器的初始化,通过实现ServletContextListener接口,通过监听来创建或销毁WebApplicationContext(IoC容器)。
Web容器中的上下文设计
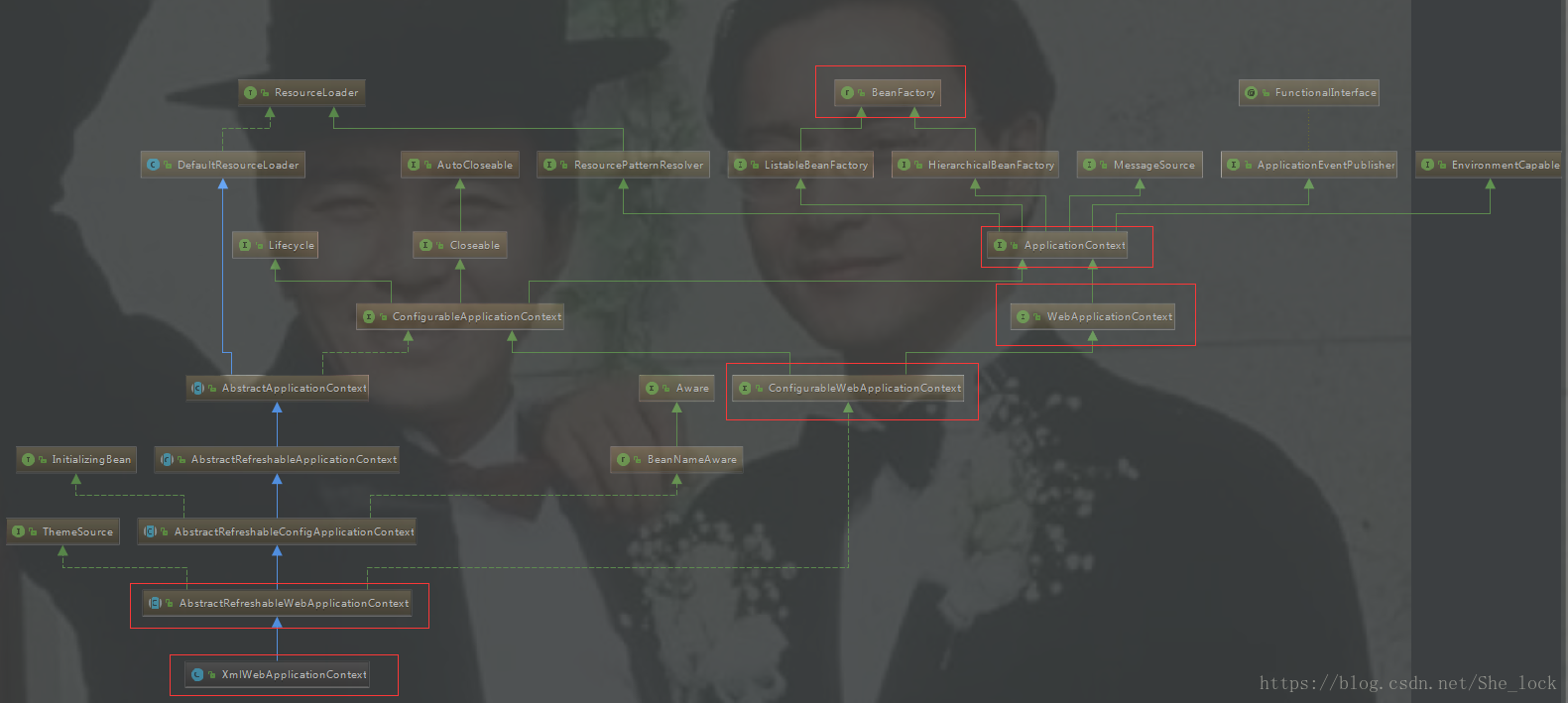
为了方便在Web环境中使用IoC容器,Spring为Web应用提供了上下文的扩展接口WebApplicationContext来满足启动过程的需要。
在这个类继承关系中,可以从熟悉的XmlWebApplicationContext入手来了解它的接口实现.在接口设计中,最后是通过ApplicationContex接口与BeanFactory接口对接的,而对于具体的功能实现,很多都是封装在其基类AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext中完成的。
WebApplicationContext和XmlWebApplicationContext中定义了很多常量,如下:
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
//用于在ServletContext中存取 根上下文
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
@Nullable
ServletContext getServletContext(); //可以取得Web容器的ServletContext
}public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {
//默认的Bean信息路径
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml";
//默认的配置文件位里在/WEB-INF/目录下
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX = "/WEB-INF/";
//默认的配置文件后缀名.xml文件
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX = ".xml";
public XmlWebApplicationContext() {
}
//refresh()时启动
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
this.initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader) {
}
//这个初始化过程是由refreshBeanFactory方法来完成的.这里只是负责载入BeanDefinition
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
String[] configLocations = this.getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
String[] var3 = configLocations;
int var4 = configLocations.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String configLocation = var3[var5];
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
//这里是取得Resource位置的地方.使用了设定的默认配置位置!默认的配置位置是/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
protected String[] getDefaultConfigLocations() {
return this.getNamespace() != null ? new String[]{"/WEB-INF/" + this.getNamespace() + ".xml"} : new String[]{"/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml"};
}
}从代码中可以看到,在XmlWebApplicationContext中,基本的上下文功能都已经通过类的继承获得,这里需要处理的是,如何获取Bean定义信息,在这里,就转化为如何在Web容器环境如这里指定的/WEB -INF/applicationContext.xml中获得Bean定义信息。这就解释了为什么我们开发的时候,web.xml文件一般放在/WEB -INF/下。
ContextLoader的设计与实现
对于Spring承载的Web应用而言,可以指定在Web应用程序启动时载人IoC容器(或者称为WebAppl icationCon text)。这个功能是由ContextLoaderListener这样的类来完成的,它是在Web容器中配置的监听器。这个ContextLoaderListener通过使用ContextLoader来完成实际的WebApplicationContext,也就是IoC容器的初始化工作。这个ContextLoader就像Spring应用程序在Web容器中的启动器。这个启动过程是在Web容器中发生的,所以需要根据Web容器部署的要求来定义ContextLoader。
下面分析具体的根上下文的载入过程。在ContextLoaderListener中,实现的是ServletContextListener接口,这个接口里的函数会结合Web容器的生命周期被调用。因为ServletContextListener是ServletContext的监听者,如果ServletContext发生变化.会触发出相应的事件,而监听器一直在对这些事件进行监听,如果接收到了监听的事件,就会做出预先设计好的响应动作。
由于ServletContext的变化而触发的监听器的响应具体包括:在服务器启动时,ServletContext被创建。服务器关闭时,ServletContext将被销毁等。对应这些事件及Web容器状态的变化,在监听器中定义了对应的事件响应的回调方法。比如在服务器启动时,ServletContextListener的contextlnitialized()方法被调用,服务器将要关闭时,ServletContextListener的contextDestroyed()方法被调用。
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
//在服务器启动时,ServletContext被创建
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); //具体的初始化工作交给ContextLoader来完成
}
//服务器关闭时,ServletContext将被销毁
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}看看ContextLoader中的创建方法:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//判断是否已经有上下文存在,key就是之前WebApplicationContext定义的
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
} else {
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
if (this.context == null) {
//创建根上下文
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
//这里载入根上下文的双亲上下文
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//将根上下文存储到servletContext中,key是之前WebApplicationContext中定义的
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
} else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" + WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
} catch (RuntimeException var8) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", var8);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var8);
throw var8;
} catch (Error var9) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", var9);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var9);
throw var9;
}
}
}
//创建根上下文的方法
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
//这里判断使用什么样的类在Web容界中作为IoC容界
Class<?> contextClass = this.determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
} else {
//直接实例化要产生的IOC容器
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
}在初始化这个上下文以后,该上下文会被存储到SevletContext中,这样就建立了一个全局的关于整个应用的上下文。同时,在启动Spring MVC时.我们还会看到这个上下文被以后的DispatcherServlet在进行自己持有的上下文的初始化时,设置为DispatcherServlet自带的上下文的双亲上下文。