一 实验准备
下载实验代码源文件
$ git clone
https://os.inf.tu-dresden.de/repo/git/mkc.git
$ make后产生如下源文件
二 实验分析
打开user/src/start.S
汇编源码文件内容如下:
.text //编译器关键词 指定后续编译出来内容放在代码段(可执行)
.global __start //编译器关键词 告诉编译器后续跟的为全局变量名
__start: //编译链接后的程序起始地址
mov $stack_top, %esp
call main_func //1. 将函数返回地址入桟 2. 让指针%eip指向函数开始处
ud2 // 让CPU产生invaild opcode exception的软件指令,内核一旦发现该指令,立即停止运行
打开user/src/user.cc
C++源码文件:
#define NORETURN __attribute__((noreturn)) //表示此函数无返回值
#define EXTERN_C extern "C" //限定extern类型, 修饰的变量或函数按C语言方式编译与链接EXTERN_C NORETURN
void main_func ()
{
while (1) ;
}
打开user/src/linker.ld
链接(C程序与汇编)脚本文件: 描述输入文件中的节如何被映射到输出文件中,并控制输出文件的内存分布
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-i386") //输出目标文件格式
OUTPUT_ARCH("i386") //运行平台
ENTRY(__start) //设置程序入口点
PHDRS //此命令仅在生成elf文件时有效,elf目标格式用program headers 程序头来描述如何被载入内存
{
data PT_LOAD FLAGS(6);//PT_LOAD为属性,表示程序运行时应被加载入内存
text PT_LOAD FLAGS(5); //描述定义了两个段
}
SECTIONS // 描述输出文件的内存布局,告诉ld如何把输入文件的sections映射到输出文件的sections
{. = 0x1000 + SIZEOF_HEADERS; //定义当前地址
.data :
{
BYTE(42); // 分配一个字节,存放值42
. = ALIGN(0x1000); //以一页4KB为单位对齐桟指针
stack_top = .;
*(.data);
*(.bss); //将输入文件中的所有.data.bss section都链接到输出文件的.data section 部分
} : data //将输出文件的.data section分配到PHDRS命令定义的data的section中
.text :
{
. = ALIGN(0x1000);
*(.text); //将输入文件中的所有.text section都链接到输出文件的.text section 部分
} : text //将输出文件的.text section分配到PHDRS命令定义的text的section中
}
Goto user/build and make user binary(ELF 目标文件)
打开user.nova.debug.map 可以看到对应地址
00002000 T __start
0000200c T main_func
00002000 D stack_top
再将此ELF binary file 作为启动模块通过boot loader加载到kernel之后
$ ls boot
$ cat boot/menu.lst
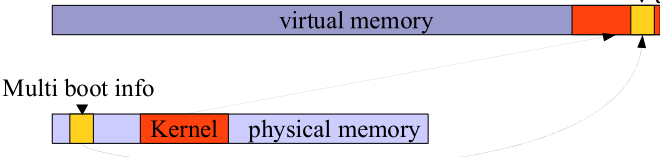
Multiboot Information 格式与内容
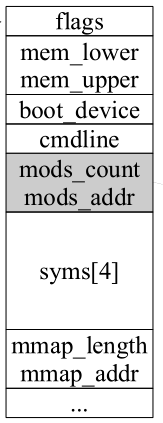
当flags[3]置位时,变量mods_count和mods_addr值有效。
mod_addr是一个length为mods_count阵列模块结构的物理地址。
物理地址需要映射到内核重映射区域的虚拟地址,通过函数void * Ptab::remap(phys_addr)
每次映射会覆盖掉之前的映射,因此每次调用remap函数时,旧的指针会无效。 remap area
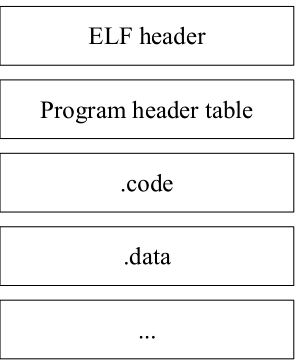
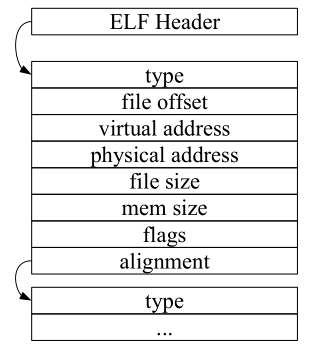
Executable and Linkable Format(ELF)
ELF Header 包含查询到 Program header table 的偏移量(ph_offset)
Program header table描叙程序运行时使用的段(告诉系统如何建立一个进程的内存映像)
ELF Header Format:
magic,data,type(2):magic魔数(四个字节)用于确认文件是否是ELF格式的目标文件,data指定elf文件编码方式,type=2表示为可执行文件。
entry: user EIP (指令指针寄存器)系统的第一个传输控制的虚拟地址,在此启动进程
ph_offset:find PH table
ph_count:PH table number
PH Table Format:
type:PT_LOAD(load the segment)
flags:writable?
offset:该节相当于elf文件起始位置的偏移
virtual address:该节的映射地址
file/mem size:在文件和内存中的segment size
alignment:地址对齐的约束
三 实验代码编写与分析
打开 kern/src/ec.cc
{
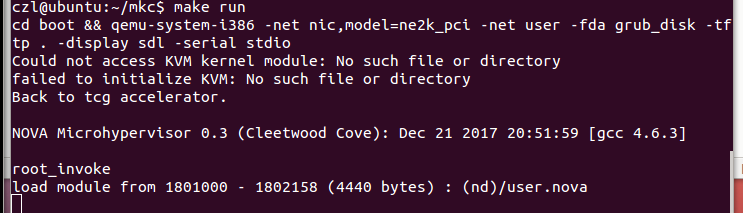
printf ("root_invoke\n");
// TODO
// - current->regs.eax holds pointer to Multiboot info (see multiboot.h)
// - get mbi remapped, find single Multiboot_module
// - get module descriptor mapped, print physical addr and size, check
// - if its size is correct (should be equal to filesize of user.nova)
// - get module remapped (its an elf binary, see elf.h for details)
// - sanity check and decode elf binary
// - finally start user module via ret_user_iret()
Multiboot * mbi = static_cast<Multiboot *>(Ptab::remap (current->regs.eax));//强制类型转换 ,内核中只能访问虚拟地址空间,要访问硬件寄存器则需要将其物理地址先映射到虚拟地址空间
if (!(mbi->flags & 8) || (mbi->mods_count != 1))//check flafs[3](判断mod_count与mod_addr是否有效),mods_count(是否有模块)
panic ("exactly ONE multi boot module is required.\n");
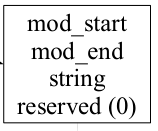
// load module desciptor
Multiboot_module mod = *static_cast<Multiboot_module *>(Ptab::remap (mbi->mods_addr));
printf ("load module from %x - %x (%u bytes) : ", mod.mod_start, mod.mod_end, mod.mod_end - mod.mod_start);
char * cmd = static_cast<char *>(Ptab::remap (mod.cmdline));
printf ("%s\n",cmd);
// remap elf header
Eh * e = static_cast<Eh *>(Ptab::remap (mod.mod_start));
if (e->ei_magic != 0x464c457f || e->ei_data != 1 || e->type != 2)//check elf 文件
panic ("No ELF\n");
unsigned count = e->ph_count;
current->regs.eip = e->entry;
// remap program headers
Ph * p = static_cast<Ph *>(Ptab::remap (mod.mod_start + e->ph_offset));
for (; count--; p++) {
if (p->type == Ph::PT_LOAD) {
unsigned attr = p->flags & Ph::PF_W ? 7 : 5;
if (p->f_size != p->m_size || p->v_addr % PAGE_SIZE != p->f_offs % PAGE_SIZE)//check 两个基本的equal要求
panic ("Bad ELF\n");
mword phys = align_dn (p->f_offs + mod.mod_start, PAGE_SIZE);
mword virt = align_dn (p->v_addr, PAGE_SIZE);
mword size = align_up (p->f_size, PAGE_SIZE);
while (size)
Ptab::insert_mapping (virt, phys, attr);
virt += PAGE_SIZE;
phys += PAGE_SIZE;
size -= PAGE_SIZE;
}
}
}
ret_user_iret();//返回用户态
FAIL;//判断循环流是否可以结束
}
打开 kern/src/ptab.cc
// add 4k mappings only
void Ptab::insert_mapping (mword virt, mword phys, mword attr)
{
mword* pdir = static_cast<mword*>(Kalloc::phys2virt(Cpu::cr3()));// kern/include/cpu.h 得到全局寄存器cr3值(page directory的起始物理地址)转换成虚拟地址
mword* ptab; // page table
if ((pdir[virt >> 22] & 1) == 0) { //virt is linear address,1 means entry vaild
// add ptab if necessaryptab = static_cast<mword*>(Kalloc::allocator.alloc_page(1, Kalloc::FILL_0));//得到一个新的页表的起始虚拟地址
mword p = Kalloc::virt2phys (ptab);
pdir[virt >> 22] = p + 0x23 + (attr & 4);//将新的页表的物理地址放入相应页目录
} else {
ptab = static_cast<mword*>(Kalloc::phys2virt (pdir[virt >> 22] & ~PAGE_MASK)); }//得到y页目录对应的页表的起始虚拟地址
assert ((phys & PAGE_MASK) == 0);//为假则输出信息
ptab[(virt >> PAGE_BITS) & 0x3ff] = (phys & ~PAGE_MASK) | (attr & PAGE_MASK);//(virt >> PAGE_BITS) & 0x3ff取虚拟地址的中间10位得到页表序号,相应页表中存入前20 位为物理页面起始地址,后12位为属性
}
{
mword* pdir = static_cast<mword*>(Kalloc::phys2virt(Cpu::cr3()));
// flush TLB : old 4M mapping
pdir[REMAP_SADDR >> 22] = 0; //REMAP_SADDR映射到的虚拟线性地址(kern/include/memory.h)
Cpu::flush(REMAP_SADDR); //clean the TLB of the memory address(REMAP_SADDR) kern/include/cpu.h
// insert new mapping
pdir[REMAP_SADDR >> 22] = (addr & 0xfff00000) + 0xe3;
return reinterpret_cast<void *>(REMAP_SADDR + (addr & 0xfffff));
}
打开 kern/src/kalloc.cc
{
if (begin + size * PAGE_SIZE > end)
panic ("kernel : no mem\n");
void * p = reinterpret_cast<void*>(begin);//强制无关类型间的转化,产生的值保持相同的比特位
begin += size * PAGE_SIZE;
if (fill)
memset (p, fill == FILL_0 ? 0 : ~0, size * PAGE_SIZE);//分配size张页大小的内存(kern/include/string.h)
return p;
}
void * Kalloc::phys2virt (mword phys)
{
mword virt = phys + reinterpret_cast<mword>(&OFFSET);// &:GET ADDRESS
return reinterpret_cast<void*>(virt);
}
mword Kalloc::virt2phys (void * virt)
{
mword phys = reinterpret_cast<mword>(virt) - reinterpret_cast<mword>(&OFFSET);
return phys;
}
四 实验结果
在ec.cc文件中添加编写程序所需头文件,multiboot.h,elf.h
$make
$make run
得出如下实验结果:(实验是搭建在qemu虚拟平台上)