前言
编程过程种会碰到各种bug,出现bug时会调用异常分析和处理方法显示在控制台或日志
异常
如果某个方法不能按照正常的途径完成任务,就可以通过另一种路径退出方法。在这种情况下会抛出一个封装了错误信息的对象。此时,这个方法会立刻退出同时不返回任何值。另外,调用这个方法的其他代码也无法继续执行,异常处理机制会将代码执行交给异常处理器。
(copy的图,出处看标记)
Throwable 是 Java 语言中所有错误或异常的超类,它有两个子类:Error和Exception
可以去看Throwable的源码(jdk->rt.jar->java->lang):
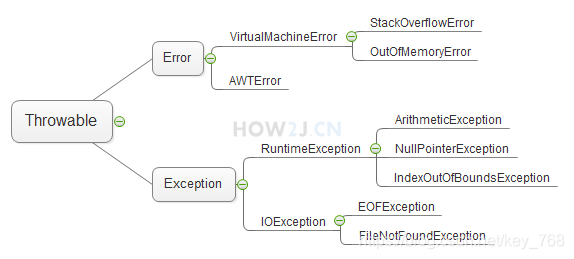
异常可大致分为3类:
- 可查异常
- 运行时异常
- 错误
Throwable接口有两个子类:Error和Exception,它们又各有子类
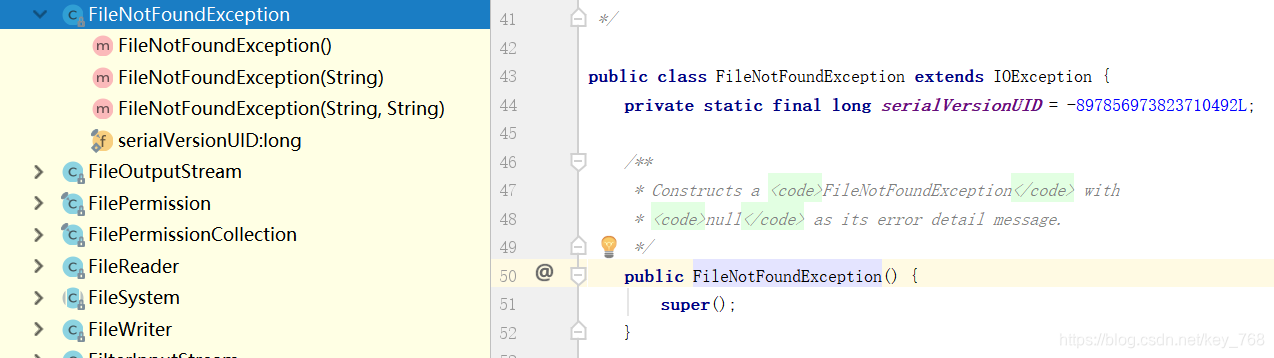
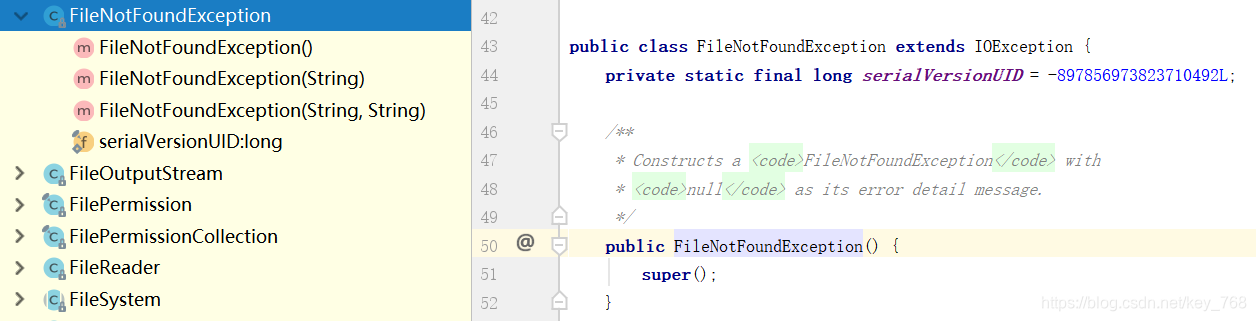 发现FileNotFoundExcepton、Exception都是通过super继承Throwable的方法,本身并没有其他的方法
发现FileNotFoundExcepton、Exception都是通过super继承Throwable的方法,本身并没有其他的方法
可查异常
可查异常即必须进行处理的异常
要么try catch住,要么往外抛,谁调用,谁处理,比如 FileNotFoundException
如果不处理,编译器就不让你通过
除了RuntimeException与其派生类(子类),以及错误(Error),其他的差不多都是检查异常
例:写一个打开文件的类
package com.company;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class JavaThrowable extends Throwable {
public static void main(String[] args){
File f= new File("d:/hhh.txt");
try{
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/hhh.txt");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("d:/hhh.txt不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
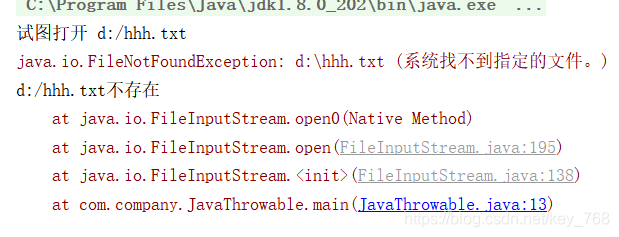
根据控制台输出,可以看出运行过程
FileInputStream文件输入流无法打开文件,FileNotFoundException报错异常,然后调用catch解决方法
强制程序去捕捉异常
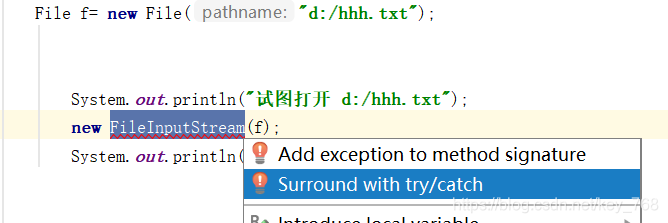
可查一般是外部错误,这种异常都发生在编译阶段,Java 编译器会强制程序去捕获此类异常,即会出现要求你把这段可能出现异常的程序进行 try catch,该类异常一 般包括几个方面:
- 试图在文件尾部读取数据
- 试图打开一个错误格式的 URL
- 试图根据给定的字符串查找 class 对象,而这个字符串表示的类并不存在
运行时异常:RunTimeException及子类
RuntimeException 是:
那些可能在 Java 虚拟机正常运行期间抛出的异常的超类。
如果出现 RuntimeException,那么一定是程序员的错误
运行时异常RuntimeException指: 不是必须进行try catch的异常
常见运行时异常:
除数不能为0异常:ArithmeticException
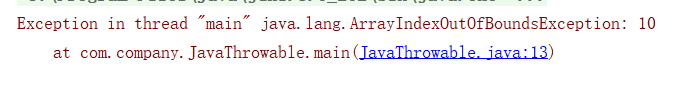
下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
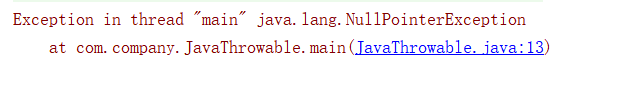
空指针异常:NullPointerException
int i=5/0;
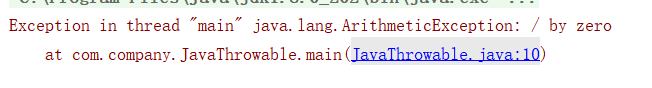
int[] arr=new int[5];
int m=arr[10];
String str = null;
str.length();
程序中可以选择捕获处理,也可以不处理,这些异常一般是由程序逻辑错误引起的,程序应该从逻辑角度尽可能避免这类异常的发生
错误Error
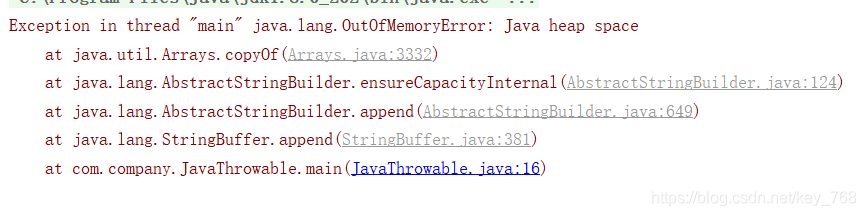
错误Error,指的是系统级别的异常,通常是内存用光了
在默认设置下,一般java程序启动的时候,最大可以使用16m的内存
不停的给StringBuffer追加字符,很快就把内存使用光了。抛出OutOfMemoryError
与运行时异常一样,错误也是不要求强制捕捉的
StringBuffer sb =new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
sb.append('a');
}
处理异常
处理异常要么抛出要么捕捉
异常处理常见手段: try catch finally throws throw
try catch
- 将可能抛出FileNotFoundException 文件不存在异常的代码放在try里
- 如果文件存在,就会顺序往下执行,并且不执行catch块中的代码
- 如果文件不存在,try 里的代码会立即终止,程序流程会运行到对应的catch块中
- e.printStackTrace(); 会打印出方法的调用痕迹
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/hhh.txt");
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/hhh.txt");
try {
new FileInputStream(f);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
当然FileNotFoundException的父类Exception也可以放catch块
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/hhh.txt");
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/hhh.txt");
try {
new FileInputStream(f);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
因为FileNotFoundException就是完全继承父类的方法,当然可以用父类代替FileNotFoundException
也可以多段catch
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:/hhh.txt");
try {
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/hhh.txt");
new FileInputStream(f);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = sdf.parse("2016-06-03");
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("打开失败");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("时间格式错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
finally:无论是否出现异常,finally中的代码都会被执行
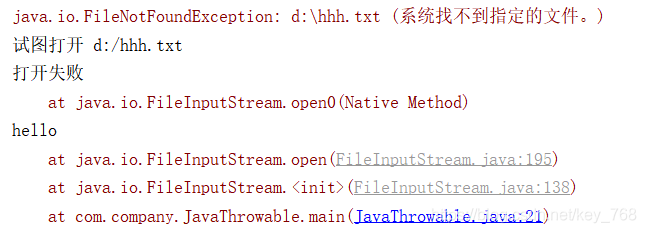
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:/hhh.txt");
try {
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/hhh.txt");
new FileInputStream(f);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = sdf.parse("2016-06-03");
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("打开失败");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("时间格式错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
抛出异常有3种形式:throw、 throws,还有一种系统自动抛异常
throws用在函数上,后面跟着异常类

throw 用在函数内,后面跟的是异常对象

throw和throw的区别:
-
位置上:throws用在函数上,throw 用在函数内
-
throws 用来声明异常,让调用者只知道该功能可能出现的问题,可以给出预先的处理方式;
throw 抛出具体的问题对象,执行到 throw,功能就已经结束了,跳转到调用者,并将具体的问题对象抛给调用者。也就是说 throw 语句独立存在时,下面不要定义其他语句,因为执行不到

-
throws 表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常;throw 则是抛出了异常,执行 throw 则一定抛出了某种异常对象
两者都是消极处理异常的方式,只是抛出或者可能抛出异常,但是不会由函数去处理异常,真正的处理异常由函数的上层调用处理。
