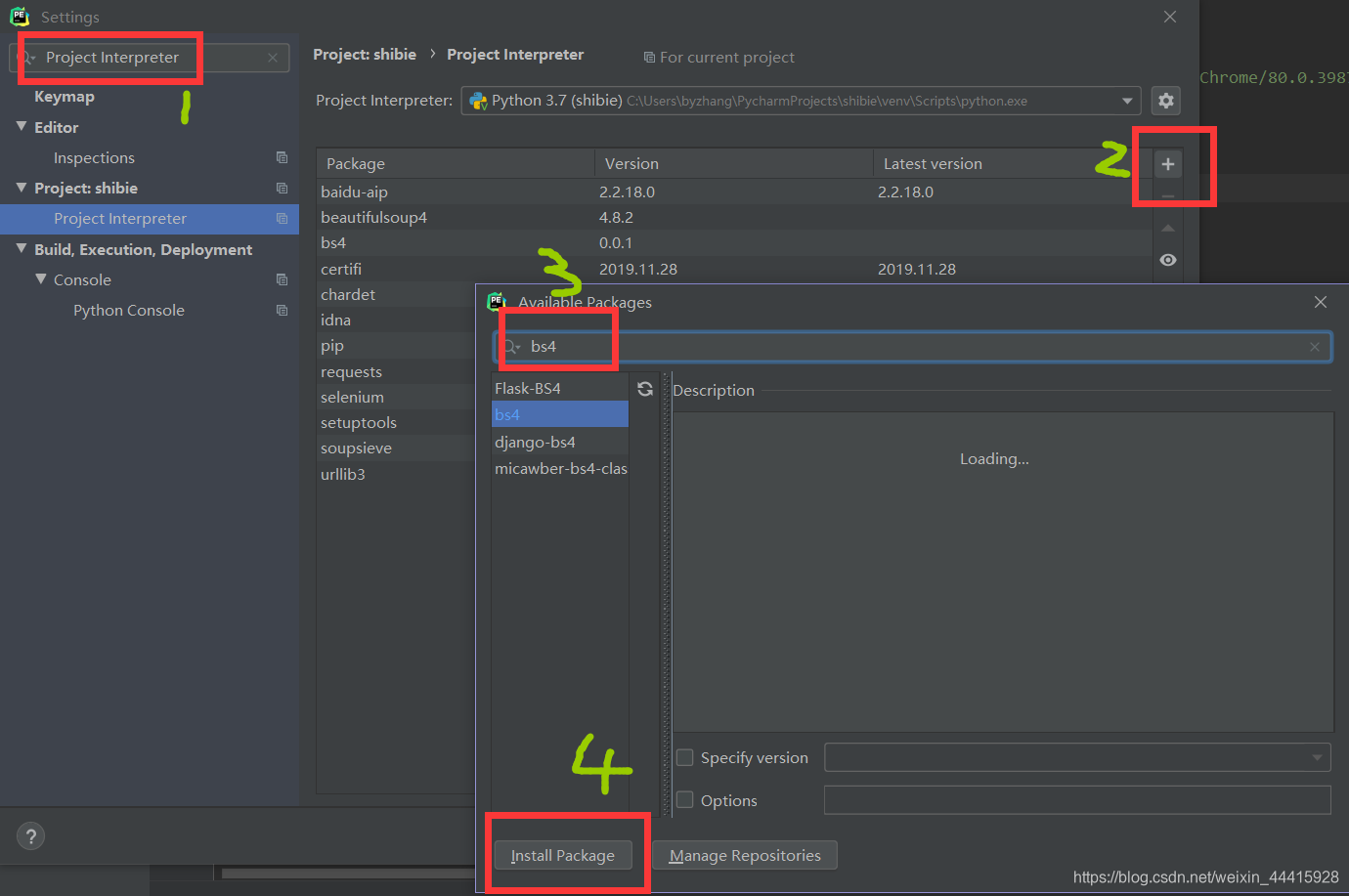
BeautifulSoup4库是一个用来解析网页的库,多用于对网页数据的分析,整合,下面介绍一下他的安装依旧很简单pip install bs4就可以,若使用pycharm的话,可以点击settings然后搜索Project Interpreter,然后点击加号搜索bs4,点击install即可
以下是一些BeautifulSoup4的常用解析库
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html.parser”) | Python的内置标准库,执行速度适中,文档容错能力强 | Python2.7.3和Python3.2.2之前的版本中文容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “lxml”) | 速度快,文档容错能力差 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XMl解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “xml”) | 速度快,唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html5lib”) | 拥有最好的容错性,以浏览器的方式解析文档,生成HTML5格式的文档 | 速度慢,不依赖外部扩展 |
下面介绍BeautifulSoup常用的方法
以下面的这一段代码做例子(只是用来演示BeautifulSoup的用法)
<html>
<head>
<title>this is a title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="first" id="one">this is an a label</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="second" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="third" id="three">an a label also</a>
</body>
</html>
1.标签选择器
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
text = '''<html>
<head><title>this is a title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="first" id="one">this is an a label</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="second" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="third" id="three">an a label also</a>
'''
# 这里我定义了一个大的字符串就是上边的那个测试代码,注意我把</body></html>这俩闭合标签删掉了
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, "lxml")
print(soup.prettify())
(结果)太长了我就不粘了,你会发现,打印的就是整理好的HTML代码,他把每个标签都补上并且格式化了
################################################################
'''标签选择器'''
#### 选择元素
print(soup.title) # 该方法会把title标签和内容打印出来
(结果)<title>this is a title</title>
print(type(soup.title)) # 打印标签的类型看看
(结果)<class 'bs4.element.Tag'> # 表示就是一个bs4的元素标签
print(soup.head) # 打印head标签和内容
(结果)<head><title>this is a title</title>
</head> # 因为源字符串我们是有回车的 所以这里有一个回车
print(soup.p)
(结果)<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
# 可以发现他只打印了第一个p标签,这点要注意
#### 获取属性
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, 'lxml')
print(soup.p.attrs("name"))
(结果)first
print(soup.p["name"])
(结果)first
'''两种方式都可以打印出name属性的值,这里的p依旧是只获取第一个p标签的值'''
#### 获取标签的内容
print(soup.p.string)
(结果)this is a p label
'''string可以获取该标签里的内容'''
#### 嵌套选择
print(soup.head.title.string)
(结果)this is a title
'''就是通过层层迭代的形式吧title内容选出来'''
#### 子节点和子孙节点
print(soup.head.string)
(结果)None # 结果竟然是None
print(soup.head.contents)
(结果)[<title>this is a title</title>, '\n']
'''没错,string只可以打印标签内部的字符串内容,对于嵌套的标签就无能为力
我们可以用contents来打印子标签
'''
print(soup.body.children)
(结果)<list_iterator object at 0x000001DE702CB508>
'''没错,他返回了一个迭代器对象,我们可以通过一下方法遍历出来'''
for i, child in enumerate(soup.body.children):
print(i, child)
(结果)
0
1 <p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
2
3 <p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
4
5 <p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
6
7 <a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
8
9 <a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
10
11 <a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a>
'''他会把每一个子内容都打印出来,连回车都不放过'''
print(soup.body.descendants)
(结果)
0
1 <p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
2 this is a p label
3
4 <p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
5 <b>this is a p label, too</b>
6 this is a p label, too
7
8 <p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
9 also, a p label
10
11 <a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
12 this is an a label
13
14 <a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
15 this is an a label, too
16
17 <a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a>
18 an a label also
'''我们可以看到descendants方法是吧所有的子孙节点打印了出来
第二个p标签是有一个嵌套的,children没有打印出来,而descandants则全都打印了出来
children只打印孩子节点,这点要区分开
'''
#### 获取父节点和祖先节点
print(soup.a.parent)
(结果)
<body>
<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
<a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
<a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a></body>
'''可以注意到他把第一个a标签的父节点body打印了出来,
我们知道text里边的body是不完整的,这里还把body补全了'''
print(soup.b.parents)
(结果)<generator object PageElement.parents at 0x0000013DB0A7E7C8>
# 可以发现这又是一个枚举类型,我们用for遍历他
for i, parent in enumerate(soup.b.praents):
print(i, parent)
(结果) #####这个是结果######################################
0 <p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
1 <body>
<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
<a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
<a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a></body>
2 <html>
<head><title>this is a title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
<a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
<a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a></body></html>
3 <html>
<head><title>this is a title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
<a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
<a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a></body></html>
'''可以看到吧所有的祖先标签都打印出来了
最后一个枚举是吧整个文档输出了一遍,其实和倒数第二个一样
'''
#### 兄弟节点
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, 'lxml')
for i,brother in enumerate(soup.p.next_siblings):
print(i, brother)
(结果) # 他会打印第一个p标签下边的所有并列的标签
0
1 <p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
2
3 <p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
4
5 <a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>
6
7 <a class="second" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="two">this is an a label, too</a>
8
9 <a class="third" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="three">an a label also</a>
for i, brother in enumerate(body.a.previous_siblings):
print(i, brother)
(结果)
0
1 <p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>
2
3 <p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>
4
5 <p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
6
'''打印第一个a标签上边的并列的所有标签'''
2.标准选择器
#### find_all()
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all("p"))
(结果)
[<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>,
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>,
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>]
'''他返回了一个列表,里边是所有的p标签,解决了soup.p的鸡肋'''
print(soup.find_all('p')[0]) # 获取第一个p标签
#### attrs
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'class': 'first'}))
(结果)[<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>,
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>]
'''可以看到他打印了所有Class为first的标签,其他标签用法都一样
对于id和class它本身自带了id和Class的查找方法,如下所示
'''
print(soup.find_all(class_="first")
(结果)[<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>,
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>]
'''可以看到和上边的查询结果是一样的,这里要注意class要写作class_
主要原因是class本身在python中是类的意思,他是一个专有名词,对于HTML里边的class,就要用class_代替
id 的用法就可以直接写作find_all(id="first")
'''
#### find()
print(soup.find('p'))
(结果)<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>
'''可以看到他只会返回一个,第一个元素,好吧相对于find_all()稍微有点鸡肋'''
3.CSS选择器
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, 'lxml')
print(soup.select(".first"))
(结果)[<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>,
<a class="first" href="http://www.baidu.com" id="one">this is an a label</a>]
'''可以看到他可以把class为first的全部选择出来,前边加.就是class, 加#就是id'''
print(soup.select("p"))
(结果)[<p class="first" name="first">this is a p label</p>,
<p class="second" name="second"><b>this is a p label, too</b></p>,
<p class="third" name="third">also, a p label</p>]
'''可以看到他也可以选择标签和jquery很像很像
也可以嵌套选择,如下
'''
print(soup.select("body p b"))
(结果)[<b>this is a p label, too</b>]
#### 获取属性
temp = soup.select("p")
for i in temp:
print(i['id'])
print(i.attrs['id'])
(结果)
['first']
['first']
['second']
['second']
['third']
['third']
'''可以看到两种方式都可以把属性的值打印出来'''
#### 获取内容(最后一个)
temp = soup.select("p")
for i in temp:
print(i.get_text())
(结果)
this is a p label
this is a p label, too
also, a p label
完结撒花…以上就是BeautifulSoup的常用用法,多写写,多练练就OK
