1.引入jar包
MySQL驱动包 和 io包:
2.数据库类型
ps:MySQL支持多种类型,大致可以分为三类:数值、日期/时间和字符串(字符)类型。
2.1数值类型

2.2日期和时间类型

2.3字符串类型
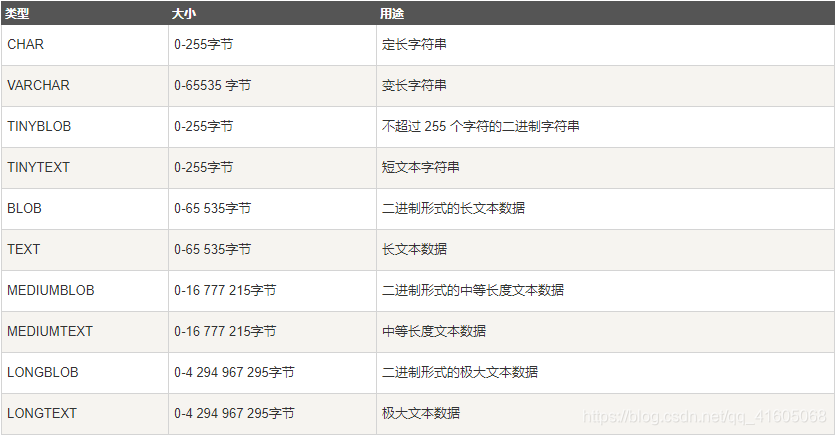
3.上传/下载 图片/音频 数据库
(上传文件到数据库有两种方式:
1.将此文件以二进制的方式存入数据库中[列类型为:longblob];
2.将此文件上传到磁盘文件目录下,数据库中保存此文件的路径[列类型为:varchar]。)
3.1建表(二进制流方式)
3.2.1上传(二进制流方式)
public int upload(String sql) { //上传
try { //String sql ="insert into demo_p(pname,pp) values(?,?)" 主键自增
psta = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //Connention conn 连接对象
psta.setString(1, "头像");
String path = "C:\\Users\\123\\Pictures\\6.png"; //待上传图片存放路径
File file = new File(path);
try {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); //输入流
try {
byte[] byteArray = IOUtils.toByteArray(fileInputStream); //字节流
SerialBlob blob = new SerialBlob(byteArray); //实例化blob
psta.setBlob(2, blob);
int i = psta.executeUpdate();
fileInputStream.close(); //关闭资源
if(i == 1) return 1; //成功
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("转化为字节错误!");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("生成fileinputstream错误!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("上传文件失败!");
}finally{
if (rSet != null){try {
rSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (psta != null){try {
psta.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (conn != null){try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
}
return 0;
}结果:
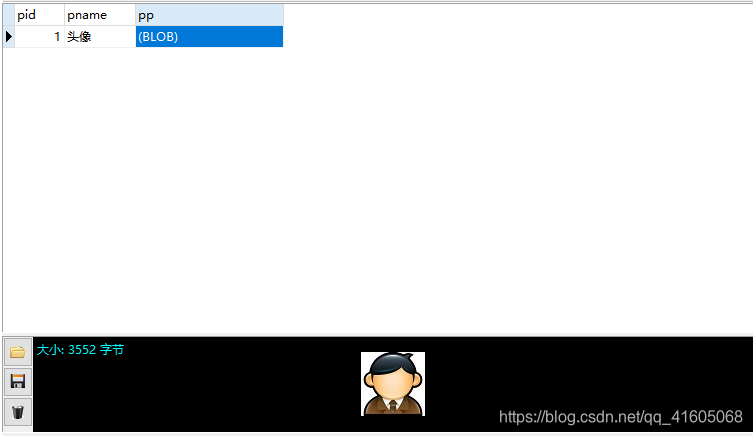
3.2.2下载(二进制流的形式)
public int down(String sql) { //下载
try { //sql = "select pid,pname,pp from demo_p where pid = ?"
psta = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译
psta.setInt(1, 1); //?
rSet = psta.executeQuery(); //执行sql
Blob blob = null;
InputStream is = null;
if (rSet.next()) { //找到
blob = rSet.getBlob(3); //读出二进制
is = blob.getBinaryStream(); //生成InputStream流
}
String path = "D:\\XA_DM_java\\java\\scsx\\upload\\xz.png"; //下载位置
File file = new File(path);
try {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);//输出流
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)blob.length()];
try {
while(is.read(bytes) != -1){
fileOutputStream.write(bytes); //写
}
fileOutputStream.flush(); //刷
fileOutputStream.close(); //关闭资源
is.close();
return 1; //成功
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("写入出错!!!");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("下载输出流出错!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("下载预编译出错!");
}finally{
if (rSet != null){try {
rSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (psta != null){try {
psta.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (conn != null){try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
}
return 0;
}结果:
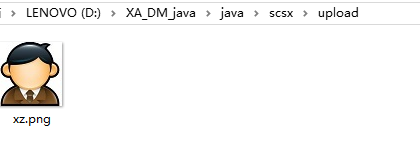
3.3上传/下载 图片/音频 数据库(保存路径)
3.3.1建表
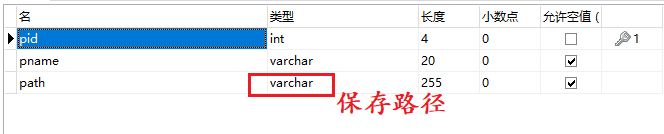
3.3.2上传(保存路径)
public int uploadPath(String sql) { //上传
try { //sql = "insert into demo_path(pname,path) values(?,?)" 主键自增
psta = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译
String fileName = "头像1"; //上传后的图片名
psta.setString(1, fileName);
String pathIn ="C:\\Users\\123\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\6.png";//待上传图片
File filePathIn = new File(pathIn);
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePathIn); //输入流
try {
String savePath="C:\\Users\\123\\Desktop\\tchuhu";//上传后图片存放目录
File savePathFile = new File(savePath);
if (!savePathFile.exists()) {//若保存路径不存在则 新建
savePathFile.mkdir();//新建
}
String pathOut = "C:\\Users\\123\\Desktop\\tchuhu\\"+fileName+".png";
//上传图片的保存路径
File filePathOut = new File(pathOut);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePathOut); //输出流
byte[] byteOut = new byte[(int)filePathIn.length()];
while((fis.read(byteOut)) != -1){ //写
fos.write(byteOut);
}
fos.flush();
fos.close(); //关闭资源
fis.close();
psta.setString(2, pathOut);
int i = psta.executeUpdate();
if(i == 1) return 1; //成功
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("读成二进制流出错!!!");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("输入流出错!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("预编译出错!!!");
}finally{
if (rSet != null){try {
rSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (psta != null){try {
psta.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (conn != null){try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
}
return 0;
}结果:
3.3.3下载(保存路径)
public int downPath(String sql) { //下载
try { //sql = "select pid,pname,path from demo_path where pid = ?" 主键自增
psta = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
psta.setInt(1, 1);
rSet = psta.executeQuery();
if(rSet.next()){
String fileName = rSet.getString(2);
String path = rSet.getString(3); //得到路径
//源文件
File file = new File(path);
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); //输入流
//保存到
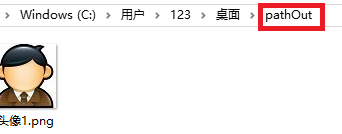
String pathOutFile = "C:\\Users\\123\\Desktop\\pathOut";//存放目录
File fileOut = new File(pathOutFile);
if (!fileOut.exists()) fileOut.mkdir(); //若不存在则新建
String pathOut = pathOutFile+"\\"+fileName+".png";//存放路径
File file2 = new File(pathOut);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2); //输出流
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)file.length()];
try {
while( (fis.read(bytes) != -1)){ //写
fos.write(bytes);
}
fos.flush(); //刷
fos.close(); //关闭
fis.close();
return 1; //成功
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if (rSet != null){try {
rSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (psta != null){try {
psta.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if (conn != null){try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
}
return 0;
} 结果:
4.总结
1. 何时使用输入流,何时使用输出流?比如↓
前提:源文件(A), Java平台(JVM),目标文件(B) 【注意:A、B、JVM 仅为代号】
需求:将A写入到B中
分析: 不管是A还是B(属于万变),不变的是我们的桥梁基站JVM,对于JVM来说,就需要将A的内容变成序列化流来表示,那么什么流?可以这样想,是将A通过流进入JVM,所以对于JVM来说是入,即为FileInputStream输入流。同理,要将流写至B,对于JVM来说是需要出,所以为FileOutputStream输出流。这时就明显的区分了何时用输入流何时用输出流。
2.流分类
字节流:FileInputStream FileOutputStream
字符流:FileReader FileWriter
对象流:ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStream
转换流:InputStreamReader(字节转字符) OutputStreamWriter(字符转字节)
带缓存的流:BufferedOutputStream BufferedInputStream BufferedReader BufferedWriter
(如有错,请留言指正...)