首先使用maven创建一个工程,随便一个java工程即可

在环境中加入依赖
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
建立Controller类
package controller; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String helo(){ return "hello world"; } public static void main(String[] args){ SpringApplication.run(HelloController.class, args); } }
可以直接运行main方法,这样就可以直接在浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/hello,就可以看到响应内容hello world;spring约定大于配置,springboot会提供默认配置,我们可以使用配置项来替代默认配置springboot只有一个配置文件.properties或.yml,这个好死后与我们在recourses文件加一个application.yml文件
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /api
这个时候访问接口就会变成:http://localhost:8081/api/hello
接下来看一下springboot的启动文件
启动文件中的注解:@SpringBootApplication,如果不加这个,项目是无法启动的,我们看一下源码
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication { }
我们看住支撑这个项目启动的主要有是三个注解
@SpringBootConfiguration 表示Spring 播哦他的配置注解
@EnableAutoConfiguration 表示自动配置
@ComponentScan 表示Spring Boot扫描Bean的规则,扫描那些包
也就是说,我们更换为下属代码,也是可以正常运行的
//@SpringBootApplication @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
接下来看一下注解@Value,他的作用就是我们在application中定义的属性,这个注解就可以帮助我们提取出来,实现解耦,看一下这个代码,这样在访问/hello接口时,就可以收到这个应用运行的端口号
@RestController @SpringBootApplication public class HelloController { @Value("${server.port}") String port; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return port; } }
接下来看一下@SpringBootConfiguration一般的用法,我们首先新建一个拦截器
/** * 拦截器 */ public class ApiInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("来到拦截器"); return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception { } }
我们在搞springMVc时,是将这个类写入SpringMvc的 配置文件,拿在SpringBoot中,我们将其加入其配置
/** * 将拦截器注册到springboot中 */ @SpringBootConfiguration public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { @Override protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { super.addInterceptors(registry); // 注册我们写的拦截器 registry.addInterceptor(new ApiInterceptor()); } }
这样在代码运行的时候,就可以看到拦截器其作用了
接下来,看一下异常处理,我们使用spring的aop思想,切入点就是有RequestMapping的方法
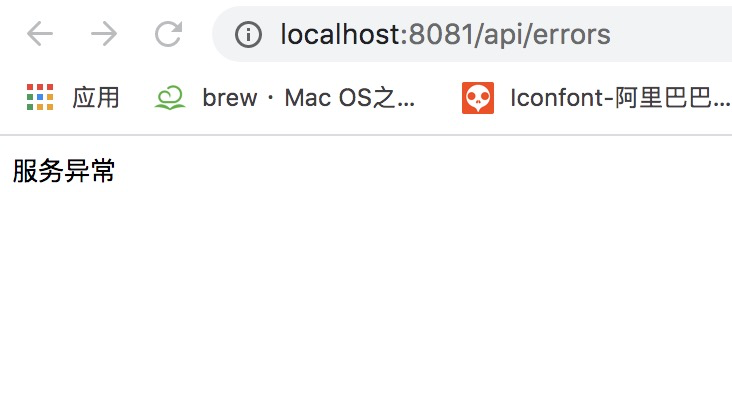
package com.example.demo.exception; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder; import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @Aspect @Component public class WebExceptionAspect { // 凡事注解了@RequestMapping的方法都会拦截 @Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping)") private void webPoint(){} @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "webPoint()", throwing = "e") public void handleThrowing(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); // 调用写内容到浏览器 writeContent("服务异常"); } // 将内容输出到浏览器中 private void writeContent(String content){ HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse(); response.reset(); response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"); response.setHeader("icop-content-type", "exception"); PrintWriter writer = null; try{ writer = response.getWriter(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } writer.print(content); writer.flush(); writer.close(); } }
在控制层模拟出错
@RequestMapping("/errors")
public String errors(){
// 手动模拟异常
System.out.println(1/0);
return "error";
}
我们可以看到访问这个接口,收到的信息时服务异常