模式识别:Python实现BP神经网络
前言:BP神经网络是理解神经网络原理的基础,代码实现有助于我们快速入门,深入理解。在此把本人在校期间模式识别的BP神经网络的作业题发出来和大家一起讨论,也望各位大佬指出不足之处,共同学习。
1.作业要求
-
请编写两个通用的三层前向神经网络反向传播算法程序,一个采用批量方式更新权重, 另一个采用单样本方式更新权重。其中,隐含层结点的激励函数采用双曲正切函数,输出 层的激励函数采用 sigmoid 函数。目标函数采用平方误差准则函数。
-
将数据带入所设计的BP神经网络
2.Python代码实现
"""
三层反向传播神经网络
批处理更新权重
不同的梯度更新步长对训练的影响
默认参数
rate= 0.001 0.004 0.006
node = 6
step = 5000
"""
import numpy as np
from numpy import dot, exp, ones, zeros, random, zeros_like, ones_like, multiply
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 给定数据 共三类,每类取7个作为训练数据,3个作为测试数据
class1 = np.array([[1.58, 2.32, -5.8], [0.67, 1.58, -4.78], [1.04, 1.01, -3.63],
[-1.49, 2.18, -3.39], [-0.41, 1.21, -4.73], [1.39, 3.16, 2.87],
[1.20, 1.40, -1.89], [-0.92, 1.44, -3.22], [0.45, 1.33, -4.38],
[-0.76, 0.84, -1.96]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, 3)
label1 = np.zeros_like(class1)
label1[:, 0] = ones([len(label1)], dtype=float)
class1 = np.hstack((class1, label1))
ext = np.ones(len(class1))
ext = ext.reshape(10, -1)
class1 = np.hstack((ext, class1))
class2 = np.array([[0.21, 0.03, -2.21], [0.37, 0.28, -1.8], [0.18, 1.22, 0.16],
[-0.24, 0.93, -1.01], [-1.18, 0.39, -0.39], [0.74, 0.96, -1.16],
[-0.38, 1.94, -0.48], [0.02, 0.72, -0.17], [0.44, 1.31, -0.14],
[0.46, 1.49, 0.68]]).reshape(-1, 3)
label2 = zeros_like(class2)
label2[:, 1] = ones([len(label2)], dtype=float)
class2 = np.hstack((ext, class2, label2))
class3 = np.array([[-1.54, 1.17, 0.64], [5.41, 3.45, -1.33], [1.55, 0.99, 2.69],
[1.86, 3.19, 1.51], [1.68, 1.79, -0.87], [3.51, -0.22, -1.39],
[1.40, -0.44, -0.92], [0.44, 0.83, 1.97], [0.25, 0.68, -0.99],
[0.66, -0.45, 0.08]]).reshape(-1, 3)
label3 = zeros_like(class3)
label3[:, 2] = ones([len(label3)], dtype=float)
class3 = np.hstack((ext, class3, label3))
#all_class = np.vstack((class1, class2, class3))
train_data = np.vstack((class1[:7], class2[:7], class3[:7]))
test_data = np.vstack((class1[7:], class2[7:], class3[7:]))
# 激励函数及相应导数
def tan_h(x):
return math.tanh(x)
def diff_tang_h(x):
return 1.0 / (1 + pow(x, 2))
# sigmoid
def sigmoid(x):
return 1.0 / (1 + exp(-x))
# sigmoid 求导
def diff_sigmoid(x):
out = sigmoid(x)
return out * (1 - out)
# 线性函数
def linear(x):
return x
# 线性函数求导
def diff_linear(x):
return ones_like(x) # 对线性函数求导 结果全是1
# 定义神经网络
class NN:
# 输入层、隐藏层、输出层的节点(数)
def __init__(self, n_i, n_h, n_o):
# 获取各层节点数量
self.n_i = n_i # 还需 增加一个偏差节点
self.n_h = n_h
self.n_o = n_o
# 激活神经网络的所有节点(向量) 存储加权求和之后 对应 net
self.data_i = ones(self.n_i) # n+1 x 1
self.data_net_h = ones(self.n_h) # node_num x 1
self.data_net_o = ones(self.n_o) # c x 1
# 对应书上 y z
self.data_y = ones(self.n_h) # .reshape(-1,1) # node_num x 1
self.data_z = ones(self.n_o) # c x 1
self.f0_net_k = ones(self.n_o)
self.delta_k = ones(self.n_o)
# 初始化权重矩阵
self.wi = random.random((self.n_h, self.n_i)) # 输入到隐含层权重 nxd
self.wo = random.random((self.n_h, self.n_o)) # 隐含层到输出 nxc
# 待更新缓存
self.delta_wi_temp = self.wi
self.delta_wo_temp = self.wo
def calculate_output(self, input): # 传进来单个样本 dx1
# input layer
self.data_i = input
# in - hidden
self.data_net_h = dot(self.wi, self.data_i) # nxd x dx1 -- nx1
self.data_y = np.array(list(map(tan_h, self.data_net_h)))
# self.data_y = self.data_y.reshape(-1, 1) # 初始化技巧! 1xn
# hidden - output
self.data_net_o = dot(self.data_y, self.wo) # 1xn nxc
self.data_z = list(map(sigmoid, self.data_net_o))
return self.data_z # 输出
def BP(self, target, updata_flag, rate_1, rate_2):
# -1 Layer Delta 计算更新量
# get误差
error_t_k = target - self.data_z
for i in range(self.n_o): # 对net k求导 1xc
self.f0_net_k[i] = diff_sigmoid(self.data_net_o[i])
self.delta_k = np.multiply(self.f0_net_k, error_t_k)
data_y_temp = self.data_y.reshape(-1, 1)
delta_wo = dot(data_y_temp, self.delta_k.reshape(1, 3))
# -2 Layer Delta
epsilon = zeros(self.n_h).reshape(-1, 1) # n_hx1
for i in range(self.n_h):
epsilon[i] = multiply(self.delta_k, self.wo[i:i + 1][0]).sum() # epsilon=(delta_k x wo[]) .sum n x 1
# print(epsilon)
delta_wi = rate_2 * dot(epsilon, self.data_i.reshape(1, -1))
self.delta_wo_temp = self.delta_wo_temp + delta_wo
self.delta_wi_temp = self.delta_wi_temp + delta_wi
if updata_flag == 1:
# Updata
# -1
self.wo = self.wo + rate_2 * delta_wo
# -2
self.wi = self.wi + rate_1 * delta_wi
error = 0.5 * dot((target - self.data_z), (target - self.data_z).reshape(-1, 1))
return error
def train(self, patterns, input_data, rate_1, rate_2): # 输入全部样本
stop_flag = 0
error_set = []
acc_set = []
step = 0
sample_len = len(patterns)
sample_num = 0
rate_temp = 0
# while stop_flag == 0:
for m in range(5000):
step += 1
updata_flag = 1
for p in patterns: # 样本集
sample_num += 1
inputs = p[1:4].reshape(-1, 1) # 前三个是数据
targets = p[4:] # 后三个是目标 -标签
if sample_num == sample_len:
updata_flag = 1
self.calculate_output(inputs) # 更新网络前向输出
error = self.BP(targets, updata_flag, rate_1, rate_2)
rate = self.test(input_data)
rate_temp = rate_temp + rate
if step % 100 == 0:
error_set.append(error)
print("error", error,"acc:",rate)
if step % 10 == 0:
rate_temp = rate_temp / 10
acc_set.append(rate_temp)
rate_temp = 0
return error_set, acc_set
def test(self, input_data):
# 测试!!
ok = 1
for p in input_data: # 测试样本集
inputs = p[1:4].reshape(-1, 1) # 前三个是数据
targets = p[4:] # 后三个是目标
output = self.calculate_output(inputs) # 更新网络前向输出
out_class = np.where(output == np.max(output))
if targets[out_class] == 1:
ok = ok + 1
rate = ok / len(input_data)
return rate
def plot_plot(self, error_set0, error_set1, error_set2):
set_len = len(error_set1)
plt.plot(range(set_len), error_set0, range(set_len), error_set1, '-', range(set_len), error_set2, '--')
plt.legend(['rate1 = 0.001','rate2 = 0.004', 'rate3 = 0.006'], loc='best')
plt.title("ErrorCurve")
plt.show()
def Run(test_data=test_data):
pat = train_data
test_data = test_data
rate_1 = 0.001
rate_2 = 0.004
rate_3 = 0.006
# 创建一个神经网络:输入层 隐藏层 输出层
n0 = NN(3, 3, 3)
error_set0, acc0 = n0.train(pat, test_data, rate_2, rate_2)
n1 = NN(3, 6, 3)
error_set1, acc1 = n1.train(pat, test_data, rate_2, rate_2)
n2 = NN(3, 8, 3)
error_set2, acc2 = n1.train(pat, test_data, rate_2, rate_2)
n2.plot_plot(acc0, acc1, acc2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Run()
# Liu Yaohua 2019.11.21 in UCAS
3.结果分析
(1)通过给定不同的rate,得到误差曲线如下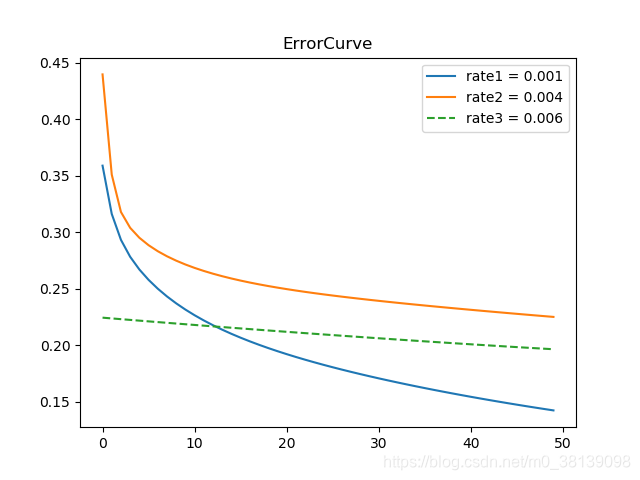
4.参考文献
《模式分类》 第二版
