写在前面
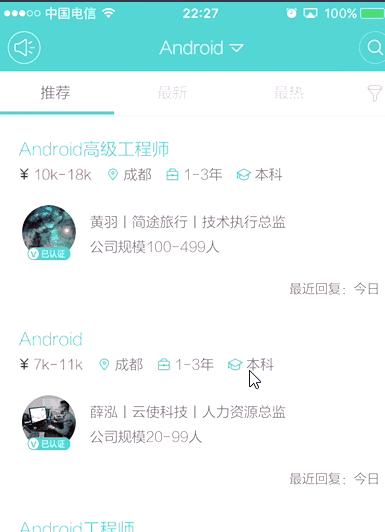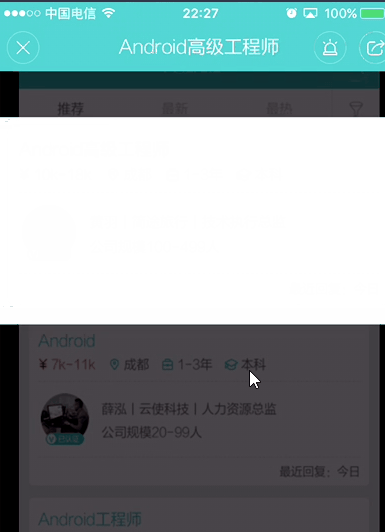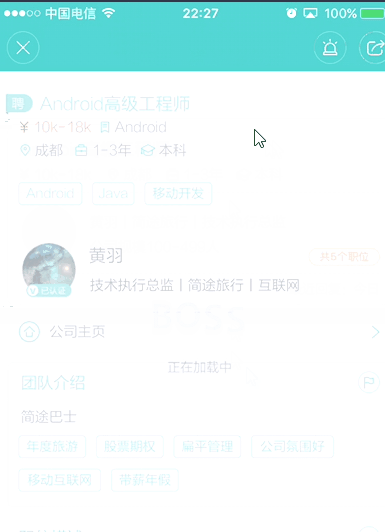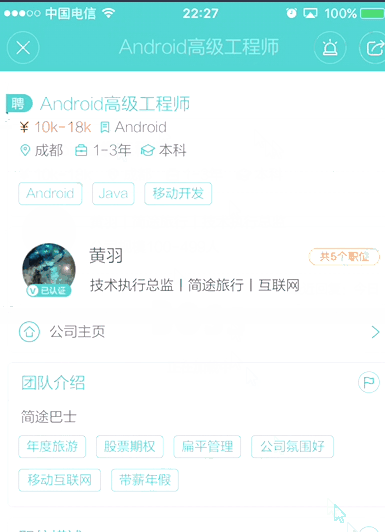
这段时间由于找工作的原因,下载了boss直聘,在ios最新版(4.1)上点击首页列表进行页面跳转的那个效果感觉很炫,但是android最新版本(4.2)上却没有对应的效果,不知道以前版本有没有,感觉很好奇,所以就有了本文…
IOS版本boss直聘的效果
分析
通过多次观察页面跳转动画,发现其实现过程也很简单:
1、获取列表中item的位置。
2、把根布局缩放0.9倍,同时跳出悬浮框,添加一个View(暂且称它为tempView),设置tempView的高度和宽度为列表的item的高度和宽度。
3、对tempView进行缩放,缩放倍数为tempView距离屏幕顶部,距离屏幕底部中的最大值处于tempView高度: Math.max(tempView.locationX, Math.abs(tempView.locationX - ScreenHeight)) / tempView.height。
4、在安卓上,即使设置
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_ANIMATION在部分机型上也无法禁止动画,如果按照正常的步骤,关闭悬浮框再进行页面跳转,就达不到boss直聘上的跳转效果,所以就需要当tempView展开到最大时,马上进行页面跳转。
5、启动加载等待动画,延时1秒后,启动alpha动画,将tempView透明度设置为0,关闭悬浮框。
悬浮框代码
public class BossTransferView extends LinearLayout {
private static final String TAG = "ExpansionTemp";
private View mHandleView;
private WindowManager mWm;
private ImageView mImg;
private View mTemp;
private ImageView mPb;
private int[] mLocation = new int[2];
private View mRootView;
public BossTransferView(Context context, View rootView, View handleView, WindowManager wm) {
super(context, null);
mHandleView = handleView;
mRootView = rootView;
mWm = wm;
init();
}
public BossTransferView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs, 0);
}
public BossTransferView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
private void init() {
LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.layout_boss_transfer, this);
mImg = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img);
mTemp = findViewById(R.id.line);
// mPb = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progress);
mPb = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.progress);
mHandleView.getLocationInWindow(mLocation);
int sbh = Util.getStatusBarHeight(getContext());
mImg.setTranslationY(mLocation[1] - sbh);
mTemp.setTranslationY(mLocation[1] + mImg.getMeasuredHeight() / 2 + sbh);
mPb.setVisibility(GONE);
Bitmap bm = getViewImg(mHandleView);
if (bm != null) {
mImg.setImageBitmap(getViewImg(mHandleView));
}
AnimationDrawable ad = new AnimationDrawable();
ad.addFrame(getDrawable(R.mipmap.icon_refresh_left), 200);
ad.addFrame(getDrawable(R.mipmap.icon_refresh_center), 200);
ad.addFrame(getDrawable(R.mipmap.icon_refresh_right), 200);
mPb.setImageDrawable(ad);
ad.setOneShot(false);
ad.start();
}
private Drawable getDrawable(@DrawableRes int drawable){
return getContext().getResources().getDrawable(drawable);
}
public void show() {
handleRootView();
setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor("#7f000000"));
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mTemp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
expansion();
}
}, 500);
}
private void handleRootView() {
ObjectAnimator setScaleY = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mRootView, "scaleY", 1f, 0.95f);
ObjectAnimator setScaleX = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mRootView, "scaleX", 1f, 0.95f);
AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet();
set.play(setScaleX).with(setScaleY);
set.setDuration(500);
set.start();
}
public Bitmap getViewImg(View view) {
view.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true);
view.buildDrawingCache();
int width = Util.getScreenParams(getContext())[0];
Bitmap bmp = view.getDrawingCache();
if (bmp == null) {
return null;
}
Bitmap bp;
bp = Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp, 0, 0, width, bmp.getHeight());
view.destroyDrawingCache();
return bp;
}
/**
* 扩展到整个屏幕
*/
private void expansion() {
int wh = Util.getScreenParams(getContext())[1];
int sbh = Util.getStatusBarHeight(getContext());
int h = Math.max(mLocation[1], Math.abs(mLocation[1] - wh));
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mTemp, "scaleY", 1f, h + sbh);
animator.setDuration(500);
animator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
mImg.setVisibility(View.GONE);
Intent intent = new Intent(getContext(), BossDetailActivity.class);
getContext().startActivity(intent);
mRootView.setScaleY(1f);
mRootView.setScaleX(1f);
mPb.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
setBackgroundColor(Color.TRANSPARENT);
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
fade();
}
}, 1000);
}
});
animator.start();
}
/**
* 淡出
*/
private void fade() {
mPb.setVisibility(GONE);
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mTemp, "alpha", 1f, 0f);
animator.setDuration(800);
animator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
mTemp.setVisibility(GONE);
// mTemp.setScaleY(1f);
mPb.setVisibility(GONE);
mWm.removeView(BossTransferView.this);
}
});
animator.start();
}
}由于涉及到两个Activity间的跳转,所以悬浮框就需要一直处于最显示层的最顶层,并且该悬浮框需要全局通用。
在andorid里面可以使用WindowManager配合自定义View来实现悬浮框功能,上面便是悬浮框的自定义View。
上面的核心参数是:mLocation,该数组是item在屏幕上的位置,通过
view.getLocationInWindow(mLocation);方法,便可以轻松得到一个View在屏幕上的位置,不同于boss直聘上tempView的空白展开的是,我这里使用了item的图像缓存代替了boss直聘上tempView的位置,而填充整个页面任务是由tempView处于中间位置的一个1dp高度的view进行展开,进而覆盖整个屏幕。
当展开到最大屏幕时,进行页面跳转,并将加载动画显示出来,将动画加载一秒,进行淡出操作,最终,将自定义的悬浮框View从WindowManager移除
跳转类
由于一个工程项目中不可能只有一个列表,因此需要创建一个跳转帮助类,来实现跳转
public class TurnHelp {
/**
* 带动画跳转详情页面
*/
public static void turn(Context context, View rootView, View itemView) {
WindowManager wm = (WindowManager) context.getApplicationContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
WindowManager.LayoutParams wmParams;
BossTransferView temp = new BossTransferView(context, rootView, itemView, wm);
wmParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
wmParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT; // 系统提示类型,重要
wmParams.format = 1;
wmParams.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE; // 不能抢占聚焦点
wmParams.flags = wmParams.flags | WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH;
wmParams.flags = wmParams.flags | WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS; // 排版不受限制
wmParams.flags = wmParams.flags | WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL; // 排版不受限制
wmParams.alpha = 1.0f;
wmParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP; //调整悬浮窗口至左上角
//以屏幕左上角为原点,设置x、y初始值
wmParams.x = 0;
wmParams.y = 0;
//设置悬浮窗口长宽数据
wmParams.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
wmParams.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
//显示myFloatView图像
wm.addView(temp, wmParams);
temp.show();
}
}上面没啥好说的,就是WindowManager添加View的基本操作
启动代码
mList.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
TurnHelp.turn(MainActivity.this, findViewById(android.R.id.content), view);
}
});