http://blog.csdn.net/tujiaw/article/details/52124102
Qt中使用QListWidget, QTableWidget,QTreeWidget(只考虑最大3层)自定义子widget来展示数据的时候,通常子widget的个数达到了上千加载展示就会很慢,而且很耗内存。原因是new出来的widget太多了。下面的解决方案希望能帮助你。
原理:
其实一个列表展示给用户看的高度是很有限的不会超过一个屏幕的高度,而这个高度只需要很少的子widget就可以填充满,所以,当你有1万个数据要展示时,并不需要每个数据都new一个widget(自定义的)来展示,你只需要new显示出来的那几个widget,当滚动条滚动的时候将超出屏幕的widget隐藏起来,将要新展示的数据重用隐藏的widget来展示而不需要new新的widget,只有当widget个数不足以覆盖列表显示的区域时才new新的(最多也就覆盖一个屏幕需要的个数)
组件组成
- 一个父widget,容纳子widget和滚动条
- 子widget使用move方法填充满展示区域
- 滚动条加载更多内容
基本方法
- 在showEvent里面刷新要展示的数据到widget
- resizeEvent的时候会改变展示区域的大小需要重新刷新数据到widget使其新的区域能完全被widget展示出来
- wheelEvent需要改变滚动条当前值
- 连接QScrollBar::valueChanged事件,当事件发生时要将新的数据展示到widget上
怎样重用子widget
QList<ItemWidget*> m_widgets;- 1
m_widgets来缓存所有创建出来的子widget,当需要新widget的时候看缓存里是否有隐藏的,如果有就拿出来进行新数据的展示,如果没有就根据数据的类型来创建新的widget
ItemWidget *TreeWidget::getWidget(const ItemInfo &info)
{
// 存在这种类型的widget,并且没有被使用(不可见)直接返回
ItemWidget *widget = nullptr;
for (int i=0; i<m_widgets.size(); i++) {
if (m_widgets[i]->data().type == info.type && !m_widgets[i]->isVisible()) {
widget = m_widgets[i];
break;
}
}
if (widget == nullptr) {
if (info.type == Top) {
widget = new TopWidget(this);
} else if (info.type == Parent) {
widget = new ParentWidget(this);
} else if (info.type == Child) {
widget = new ChildWidget(this);
} else {
Q_ASSERT(0);
}
connect(widget, &ItemWidget::sigMousePress, [this, widget]() {
if (widget->data().type != Child) {
ItemInfo newInfo = widget->data();
newInfo.isExpand = !newInfo.isExpand;
updateItemInfo(newInfo);
refreshWidgets();
} else {
gotoSelected(widget->data().id);
}
emit sigItemMousePress(widget->data());
});
connect(widget, &ItemWidget::sigMouseDoubleClick, [this, widget]() {
emit sigItemMouseDoubleClick(widget->data());
});
m_widgets.append(widget);
}
widget->setData(info);
// 如果是当前选中的widget
if (widget->data().type == Child) {
widget->setSelected(widget->data().id == m_curChildId);
}
widget->resize(this->width(), widget->height());
widget->show();
return widget;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
重点是刷新数据到widget上
首先,将所有可见widget隐藏起来,遍历所有数据,y轴从0开始每次增加遍历数据展示时需要的高度,当y值大于滚动条值并且小于组件高度时就需要将子widget展示出来
组件高度就是滚动条page step值
滚动条mininum为0,maxinum为y - pageStep
公式:document length = maxinum() - minimum() + pageStep()
void TreeWidget::refreshWidgets()
{
for (int i=0; i<m_widgets.size(); i++) {
m_widgets[i]->resize(this->width(), m_widgets[i]->height());
m_widgets[i]->hide();
}
auto moveItem = [this](const ItemInfo &item, int &y, int &startPos, bool &isContinue) {
if (y >= m_scrollbar->value() && isContinue) {
getWidget(item)->move(0, startPos);
startPos += item.height;
isContinue = startPos < this->height();
}
y += item.height;
};
int y = 0, startPos = 0;
bool isContinue = true;
for (int i=0; i<m_list.count(); i++) {
const ItemInfo &topItem = m_list[i];
moveItem(topItem, y, startPos, isContinue);
if (topItem.childList.count() > 0 && topItem.isExpand) {
for (int j=0; j<topItem.childList.count(); j++) {
const ItemInfo &parentItem = topItem.childList[j];
moveItem(parentItem, y, startPos, isContinue);
if (parentItem.childList.count() > 0 && parentItem.isExpand) {
for (int k=0; k<parentItem.childList.count(); k++) {
const ItemInfo &childItem = parentItem.childList[k];
moveItem(childItem, y, startPos, isContinue);
}
}
}
}
}
qDebug() << "y:" << y << ", startPos:" << startPos << ", height:" << this->height();
m_scrollbar->move(this->width() - m_scrollbar->width(), 0);
m_scrollbar->resize(m_scrollbar->width(), this->height());
m_scrollbar->setPageStep(this->height());
if (y > startPos) {
m_scrollbar->setMaximum(y - m_scrollbar->pageStep());
m_scrollbar->show();
m_scrollbar->raise();
} else {
m_scrollbar->setMaximum(0);
m_scrollbar->setValue(0);
m_scrollbar->hide();
}
qDebug() << "min:" << m_scrollbar->minimum() << ", max:" << m_scrollbar->maximum() << ", value:" << m_scrollbar->value();
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
结尾
- 性能优化
- 响应事件扩充
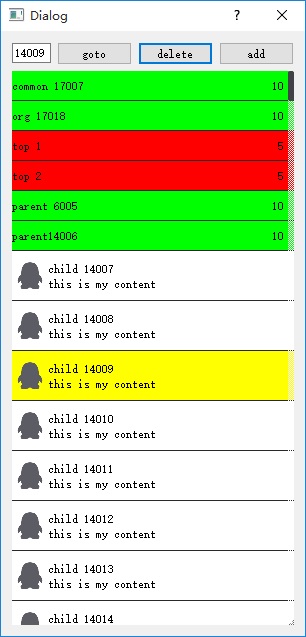
- 代码中展示的元素有17000多个效率还是很高的
- 代码中有三层也有两层,当然一层的话相信更简单
- 红色item是最顶层
- 绿色item是中间层
- 白色item是最底层