两个线程导致的错误
-
两个线程进行index++操作,两个线程会相互干扰,导致结果不一定准确,现在想找出出错的位置和出错次数
public class MultiThreadError1 implements Runnable { static MultiThreadError1 instance = new MultiThreadError1(); int index = 0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance); Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println(instance.index); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { index++; } } }
改造过程
1、标记
-
改造思路:先用一个标记数组来 marked[index] 将index存起来,如果一个线程已经操作了index++,另一个就不要再进行了,结合原子整型来获得真实执行次数
public class MultiThreadError1 implements Runnable { static MultiThreadError1 instance = new MultiThreadError1(); int index = 0; final boolean marked[] = new boolean[100000]; static AtomicInteger realIndex = new AtomicInteger(); static AtomicInteger errorCount = new AtomicInteger(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance); Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println("表面"+instance.index); System.out.println("实际"+realIndex.get()); System.out.println("错误"+errorCount.get()); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { index++; realIndex.incrementAndGet(); if (marked[index]){ System.out.println("error: " + index); errorCount.incrementAndGet(); } //置为true表示已经进行了操作 marked[index] = true; } } }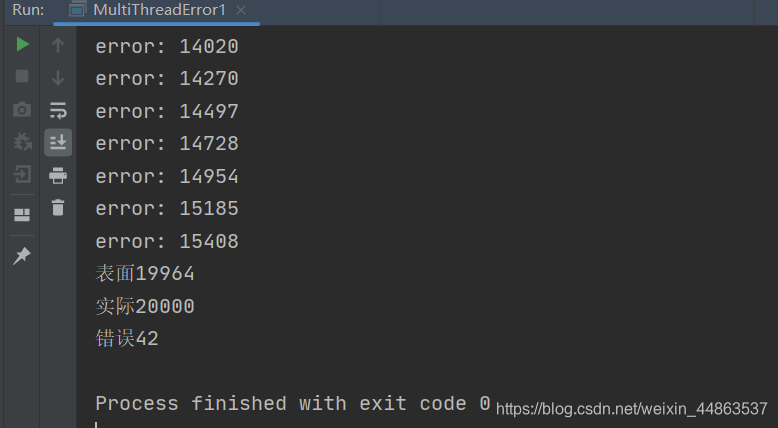
-
错误原因:在
if (marked[index])位置发生错误,例如程序开始运行,线程1执行run,执行完index++后,index变为1,这时marked[1]为false,于是要将marked[1]置为true,但还未来得及执行时;切换到了线程2,依然执行index++,index变为1,但线程1本来要将index为1标记,这时线程2检测不到,依然往下执行,于是发生错误
2、同步
-
发生了这个错误之后,便想用synchronized来解决,使不同线程间同步访问
public class MultiThreadError1 implements Runnable { static MultiThreadError1 instance = new MultiThreadError1(); int index = 0; final boolean marked[] = new boolean[100000]; static AtomicInteger realIndex = new AtomicInteger(); static AtomicInteger errorCount = new AtomicInteger(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance); Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println("表面"+instance.index); System.out.println("实际"+realIndex.get()); System.out.println("错误"+errorCount.get()); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { index++; realIndex.incrementAndGet(); synchronized (instance) { if (marked[index]) { System.out.println("error: " + index); errorCount.incrementAndGet(); } //置为true表示已经进行了操作 marked[index] = true; } } } }结果依然不对

-
这回冲突发生在
index++位置了,线程1执行完index++,也将marked[1]置为true;轮到线程2执行,执行完index++,还没来得及进入同步代码块检查;又切回到线程1,执行index++,index为2;切到线程2,刚才还没来得及检查的1已经变成2了,发生错误。简单来说就是有的线程执行得太快了
3、限制
-
这时要用一道道闸门来限制以下线程的速度,使用
CyclicBarrier,加了闸门的地方要两个线程都到达了这个位置才能继续向下执行,在index++前面加上是防止有的线程执行太快,而在后面加上是防止一个线程还没来得及marked的时候,切到另一个线程执行index++,然后又切换回时,发生错误public class MultiThreadError1 implements Runnable { static MultiThreadError1 instance = new MultiThreadError1(); int index = 0; final boolean marked[] = new boolean[100000]; static AtomicInteger realIndex = new AtomicInteger(); static AtomicInteger errorCount = new AtomicInteger(); static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier1 = new CyclicBarrier(2); static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier2 = new CyclicBarrier(2); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance); Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println("表面"+instance.index); System.out.println("实际"+realIndex.get()); System.out.println("错误"+errorCount.get()); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { try { cyclicBarrier2.reset(); cyclicBarrier1.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } index++; try { cyclicBarrier1.reset(); cyclicBarrier2.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } realIndex.incrementAndGet(); synchronized (instance) { if (marked[index]) { System.out.println("error: " + index); errorCount.incrementAndGet(); } //置为true表示已经进行了操作 marked[index] = true; } } } }两道栅栏加完但还是错误

debug发现只有偶数位被置为true,因为在index++之后加了闸门,所以两个线程,每个执行一次index++,index从0开始,所以只有偶数位被置为true

-
事实上这并不是发生了线程冲突导致的,而是由于synchronized的可见性,线程能知晓相互之间的状态,线程1和线程2进入同步代码块后,都能看见偶数位被置为true,认为发生错误,其实并没有发生冲突,只是跳过了奇数位的标记,因此需要完善以下冲突判断条件
marked[index] && marked[index - 1]synchronized (instance) { if (marked[index] && marked[index - 1]) { System.out.println("error: " + index); errorCount.incrementAndGet(); } //置为true表示已经进行了操作 marked[index] = true; }
完整代码
public class MultiThreadError1 implements Runnable {
static MultiThreadError1 instance = new MultiThreadError1();
int index = 0;
final boolean marked[] = new boolean[100000];
static AtomicInteger realIndex = new AtomicInteger();
static AtomicInteger errorCount = new AtomicInteger();
static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier1 = new CyclicBarrier(2);
static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier2 = new CyclicBarrier(2);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("表面"+instance.index);
System.out.println("实际"+realIndex.get());
System.out.println("错误"+errorCount.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
marked[0]=true;
try {
cyclicBarrier2.reset();
cyclicBarrier1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
index++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :cyclicBarrier前: "+index);
try {
cyclicBarrier1.reset();
cyclicBarrier2.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :cyclicBarrier后: "+index);
realIndex.incrementAndGet();
synchronized (instance) {
if (marked[index] && marked[index - 1]) {
System.out.println("error: " + index);
errorCount.incrementAndGet();
}
//置为true表示已经进行了操作
marked[index] = true;
}
}
}
}